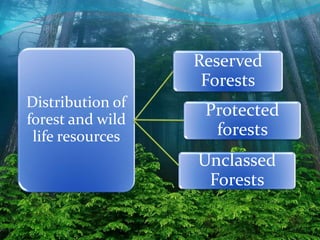
Forests and wildlife form a complex ecological web on which humans depend for survival. India has immense biodiversity with over 81,000 fauna and 47,000 flora species, many of which are endangered due to habitat loss, poaching, and human activities like mining, grazing, and fuelwood collection. The government manages forests through categories like reserved, protected, and unclassed forests, and takes conservation measures like wildlife protection acts and projects to protect threatened species and their habitats.