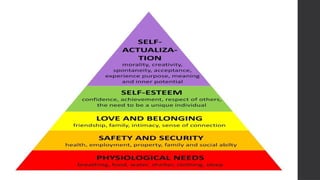
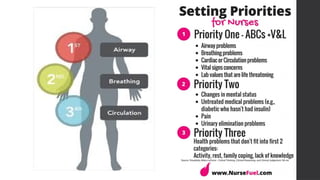
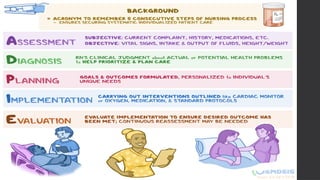
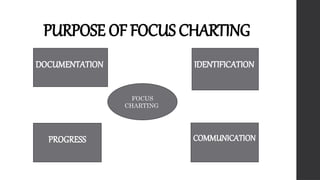
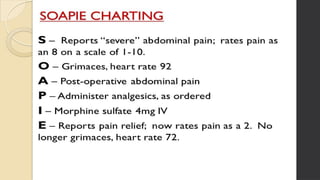
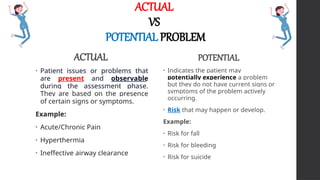
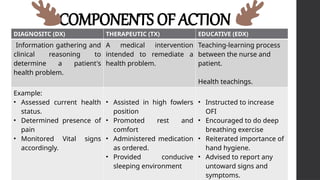
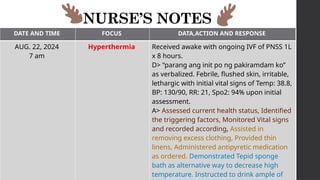
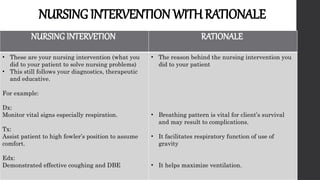
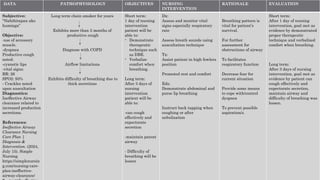
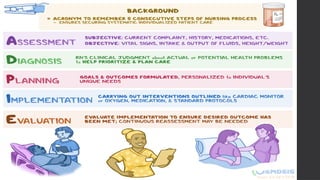
This document outlines Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs as a framework for understanding human motivation, emphasizing the importance of meeting foundational needs such as physiological requirements, safety, and belonging before achieving self-esteem and self-actualization. It describes the nursing process as a systematic method for delivering patient-focused care, highlighting characteristics like patient-centeredness and the need for critical thinking. Additionally, it covers documentation approaches in nursing, such as focus charting and SOAPIE notes, for monitoring patient status and nursing interventions.