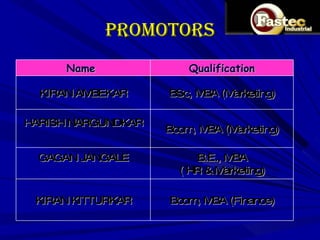
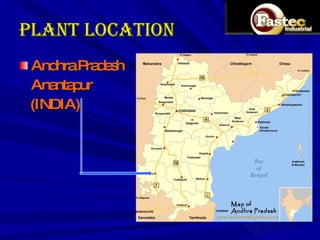
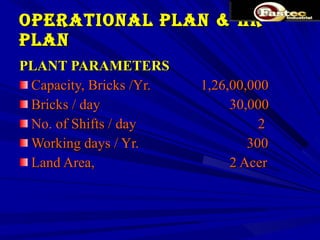
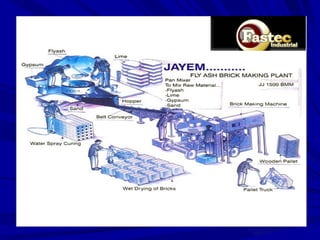
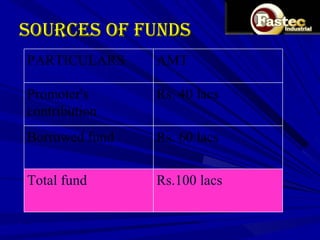
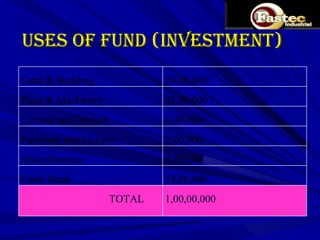
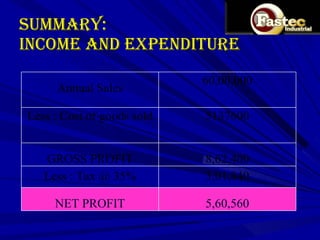
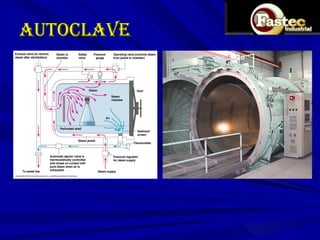
This document presents a business plan for Fastec Industrial, a company that manufactures fly ash bricks. Fly ash is a byproduct of coal combustion in thermal power plants and is currently a major environmental pollutant. The business aims to utilize fly ash to produce bricks, helping reduce pollution while providing a construction material. The plan discusses the production process, market opportunity, promotion strategy, financial projections, and concludes that Fastec can help generate a pollution free environment through this environmentally friendly brick manufacturing business.