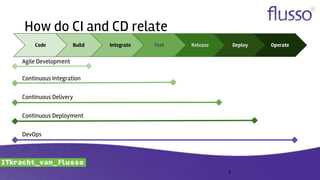
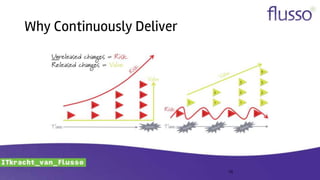
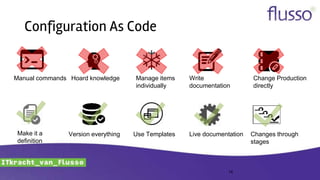
This document discusses continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD). It defines CI as frequently integrating work and verifying it through automated builds and tests. It defines CD as ensuring every change can be released and any version can be deployed with the push of a button. The document outlines why organizations adopt CI/CD, advanced concepts like infrastructure as code, and provides recommendations for implementing CI/CD such as starting small, automating tasks, and forming cross-functional teams.







![Continuous Delivery
"[CD] is an approach in which teams ensure that every
change to the system is releasable, and that we can release
any version at the push of a button. CD aims to make
releases boring, so we can deliver frequently and get fast
feedback on what users care about.“ – Thought Works
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cicdjoost-161006103118/85/Flusso-Continuous-Integration-Continuous-Delivery-8-320.jpg)