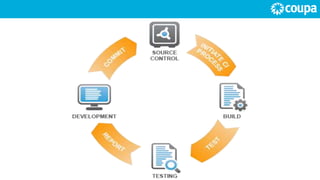
DevOps is a set of practices aimed at reducing the time between committing code changes and deploying to production while ensuring high quality. It involves treating operations teams as first-class citizens in requirements, making developers responsible for incidents, enforcing consistent deployment processes, using continuous delivery and infrastructure as code. The DevOps lifecycle integrates requirements, development, build, testing, deployment and execution with tools for continuous integration, delivery and monitoring. Adopting DevOps and CI/CD can accelerate time to market, build the right products through frequent feedback, improve productivity and release reliability, boost quality and satisfaction.