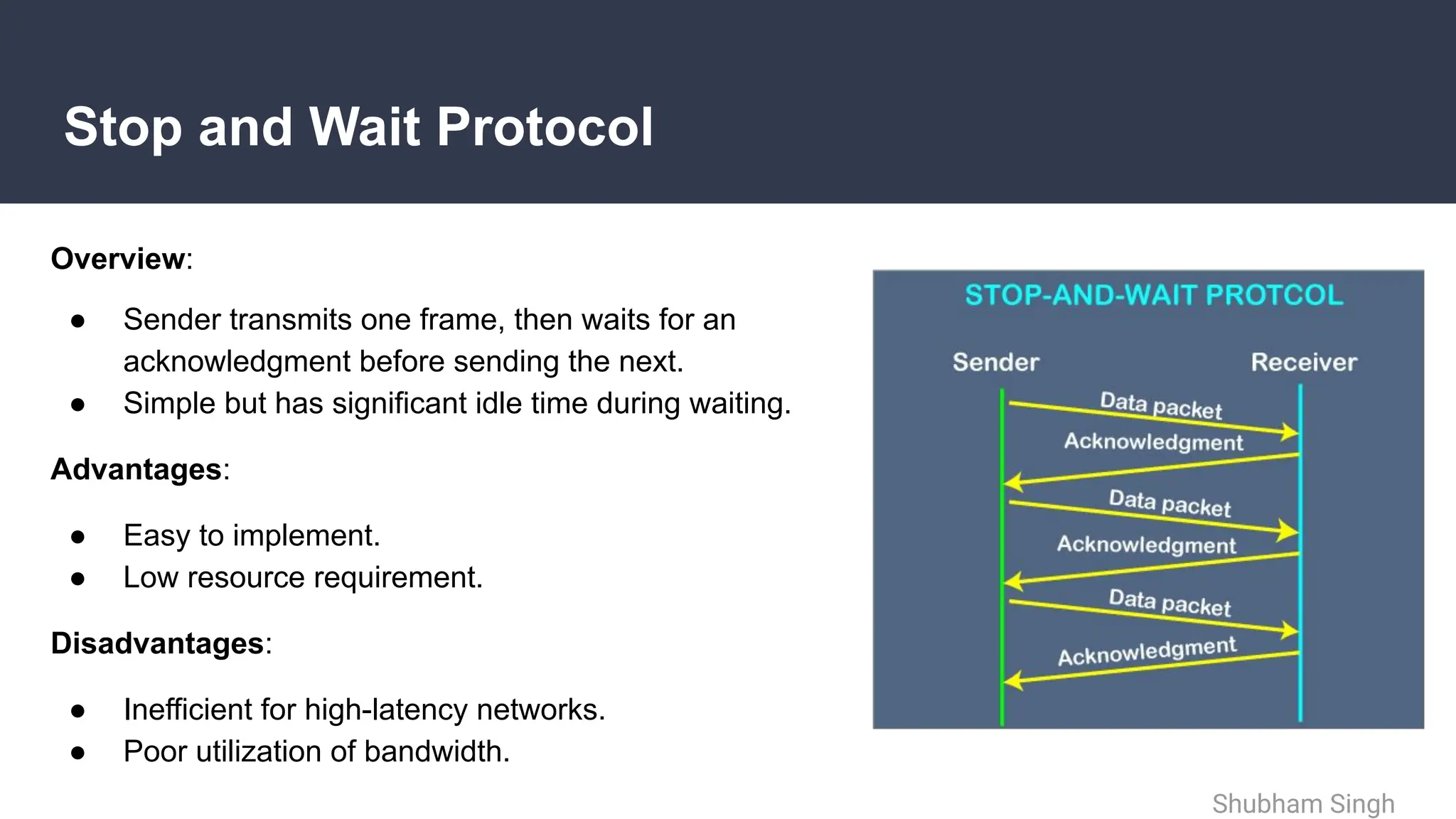
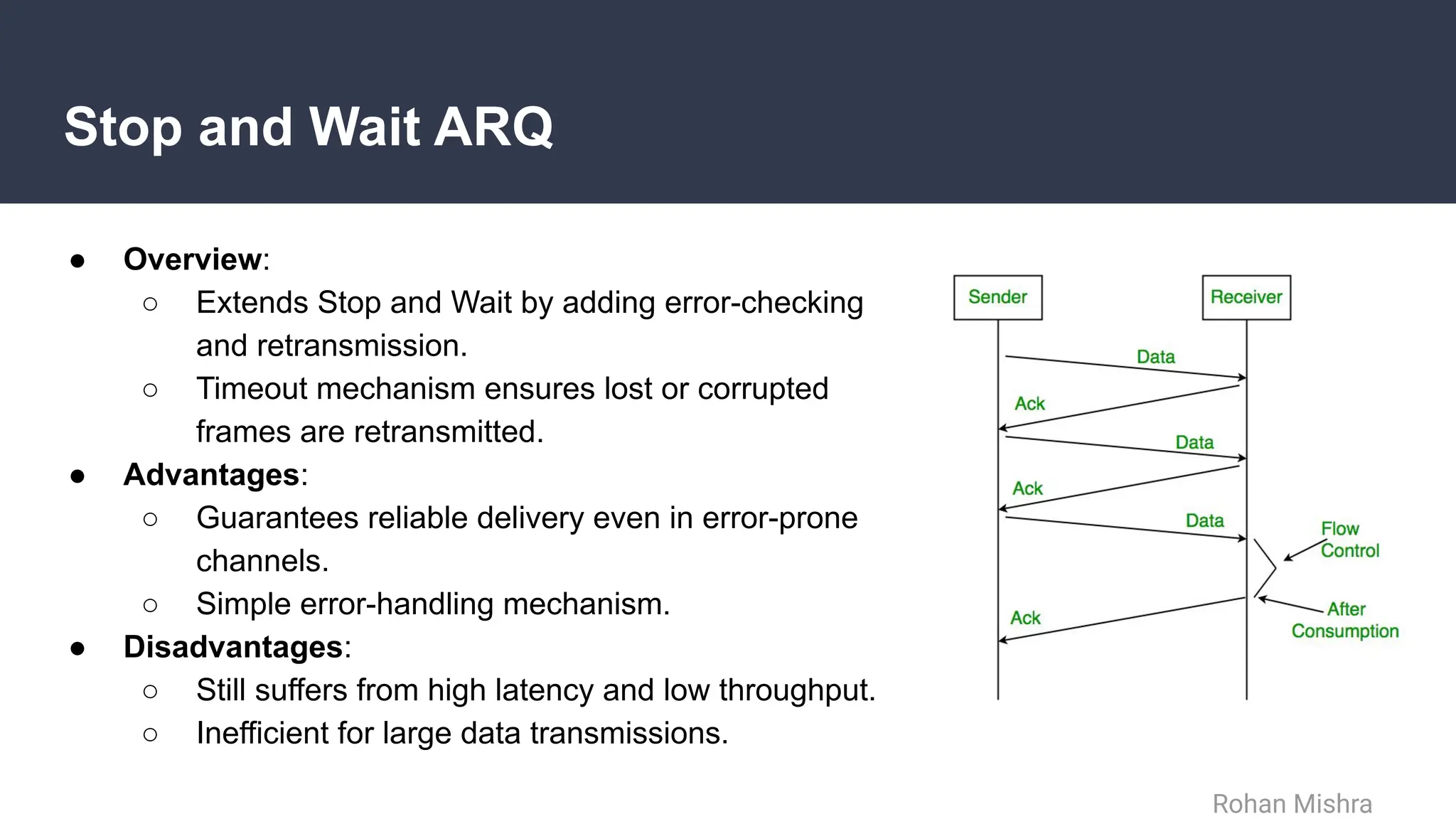
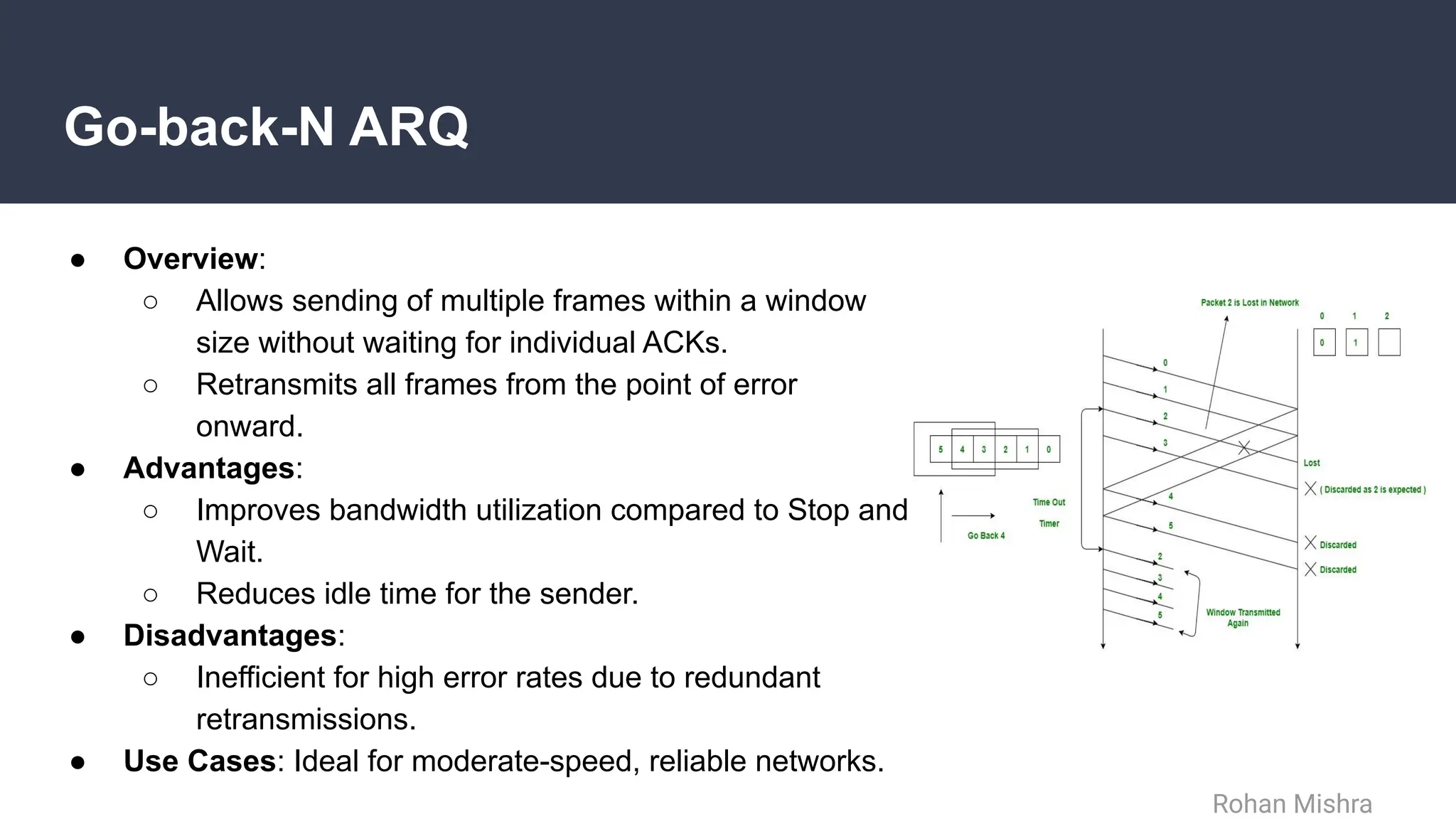
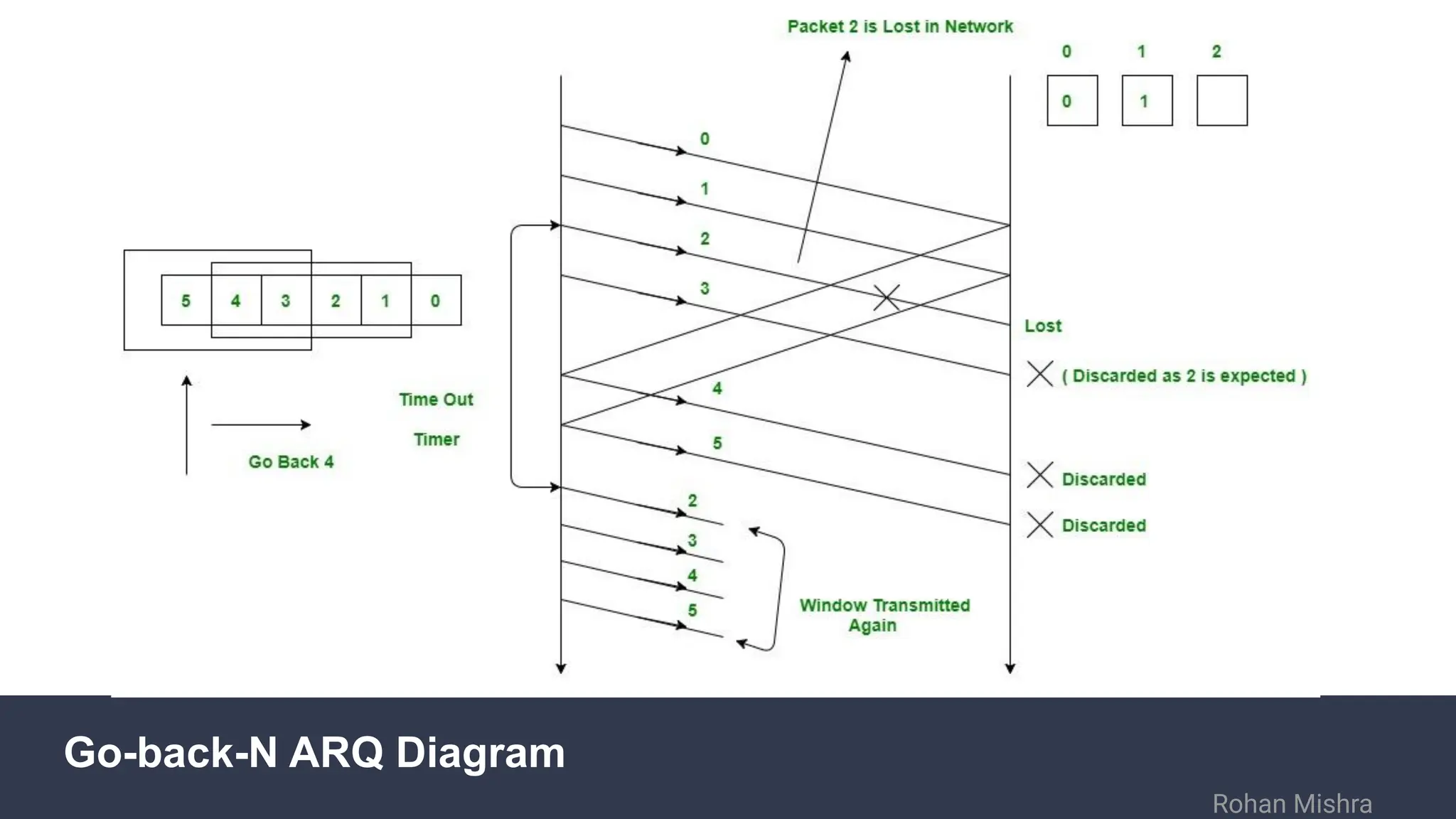
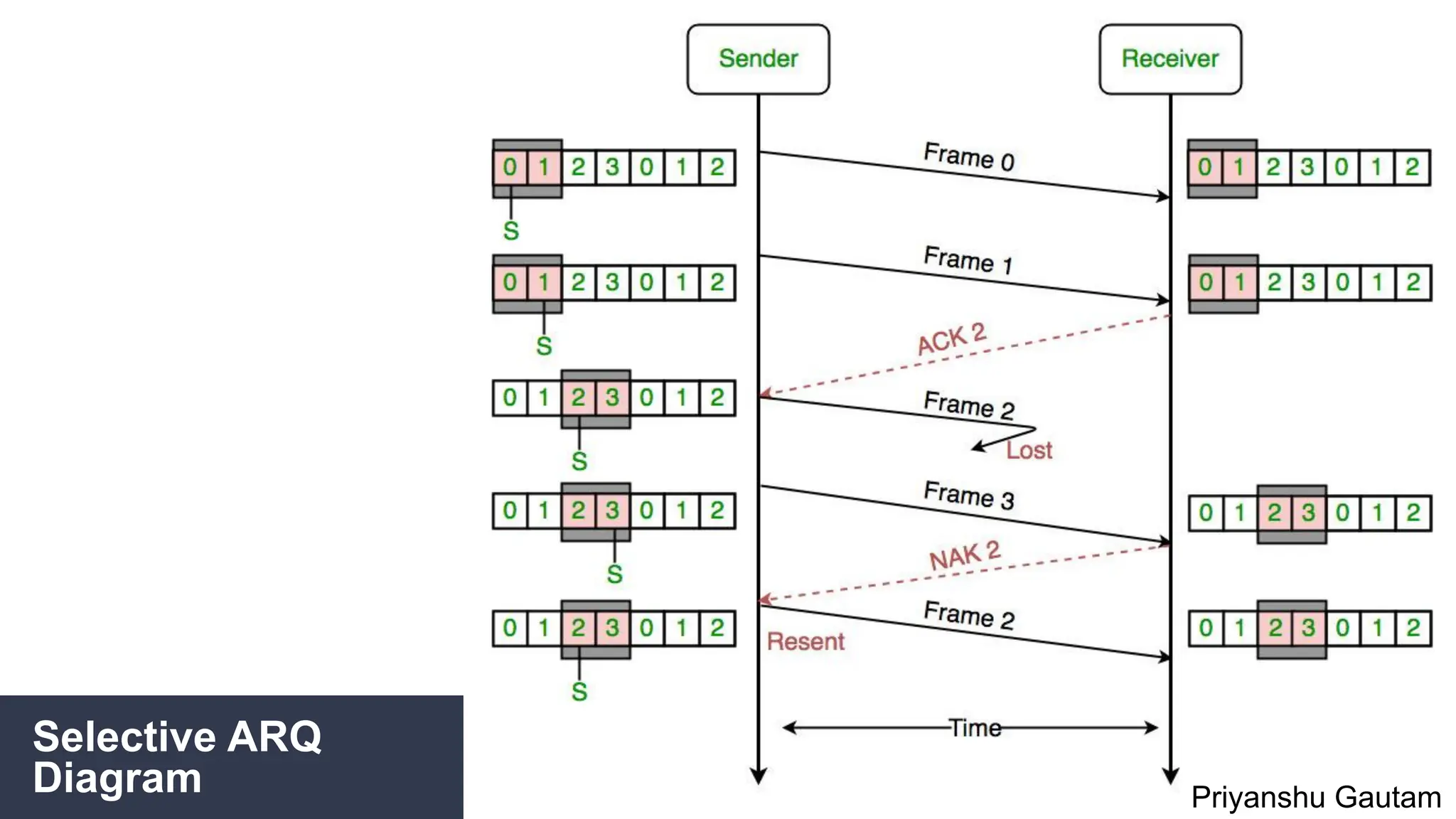
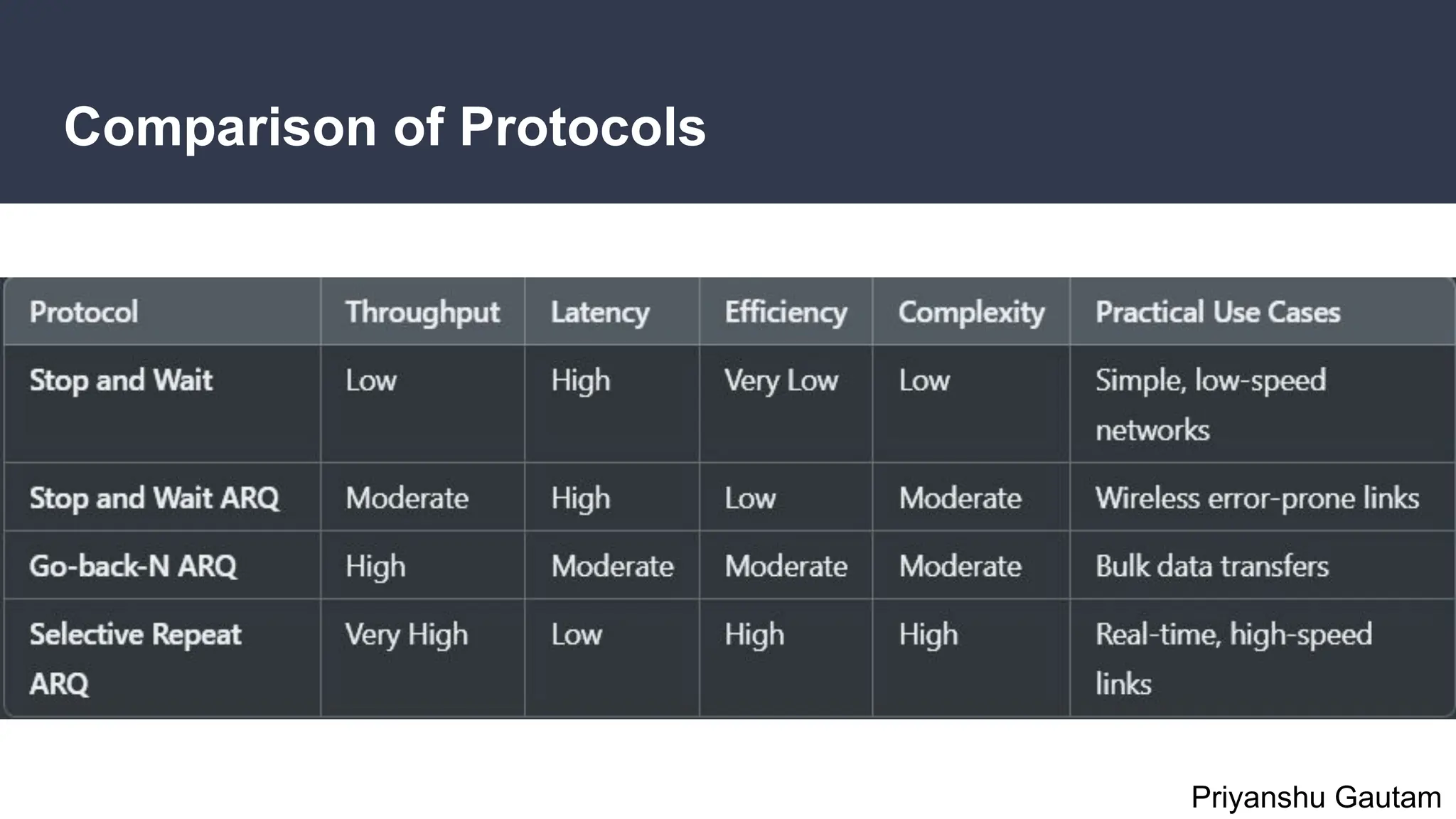
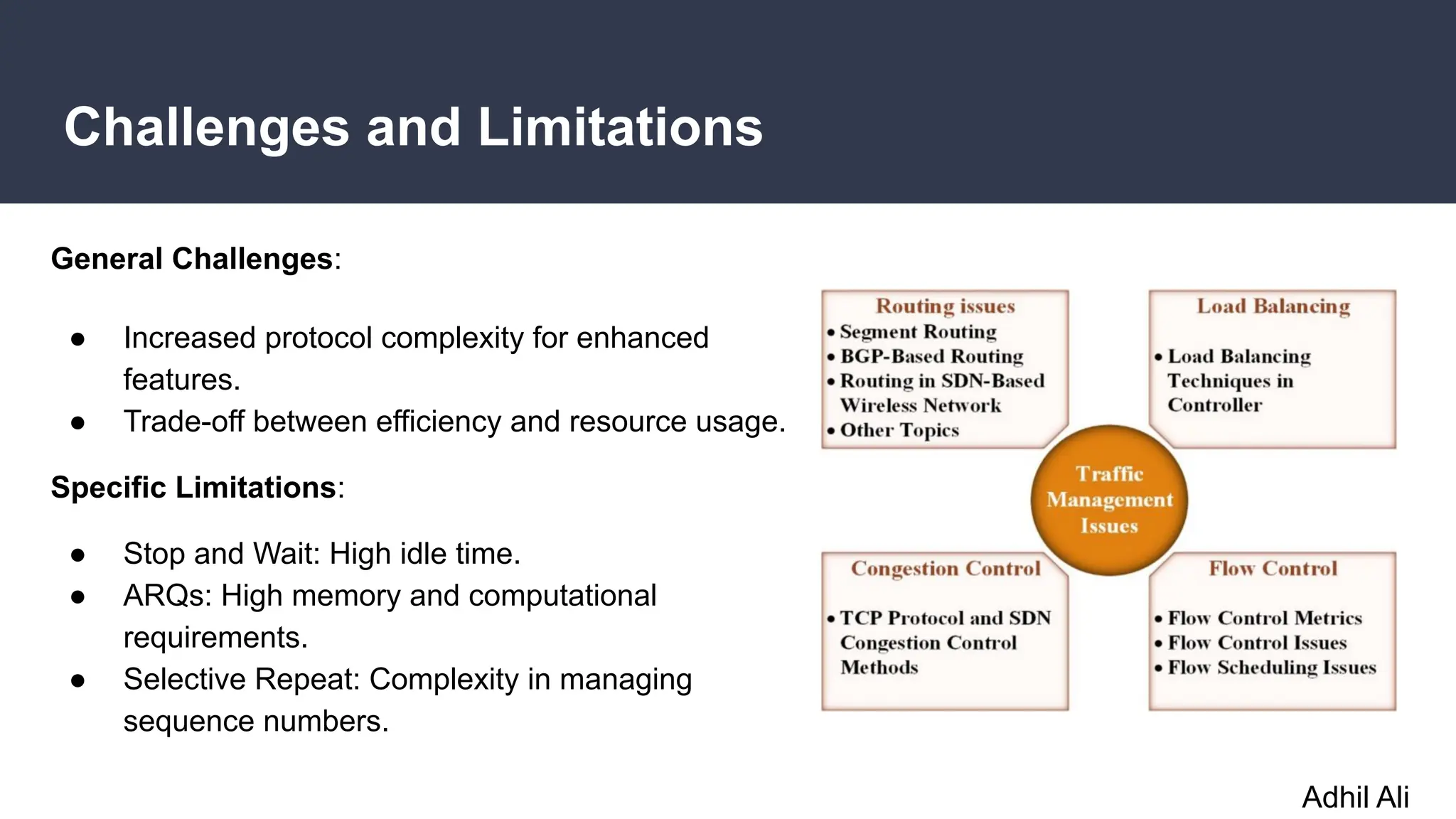
The document discusses flow and error control protocols, including stop and wait, stop and wait ARQ, go-back-n ARQ, and selective repeat ARQ, focusing on their mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages. These protocols are essential for reliable communication in networks, each suited to different conditions and requirements. Challenges include increased complexity and resource utilization, with future trends pointing towards adaptive mechanisms and AI integration.