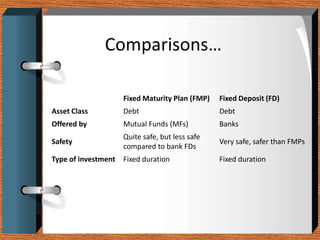
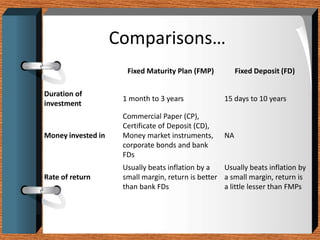
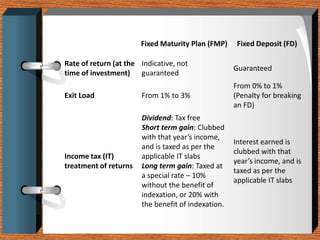
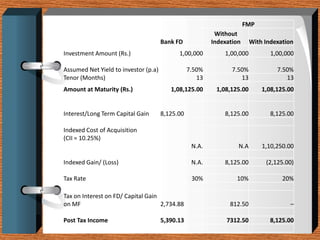
Fixed deposits allow investors to deposit a fixed amount for a fixed duration at a fixed interest rate. With fixed maturity plans, investors' money is invested in close-ended debt schemes with maturity periods ranging from 1 month to 5 years. Both carry credit risk but have predetermined returns. Key differences are that FMPs provide indicative not assured returns and the income is taxed at a lower rate with indexation benefits, making FMPs more tax efficient than fixed deposits.