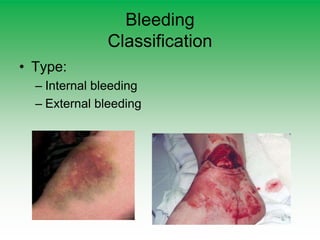
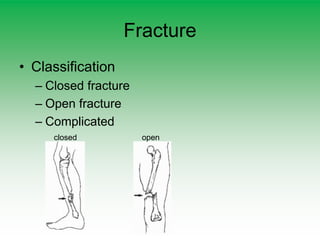
First aid is emergency medical treatment given before full medical attention arrives. The primary survey uses DRABC to assess danger, response, airway, breathing, and circulation. CPR involves chest compressions and rescue breathing if there is no pulse or breathing. Bleeding is managed through direct pressure, elevation, and bandages without removing objects. Fractures are immobilized and head and spinal injuries require maintaining the airway and not moving the victim.