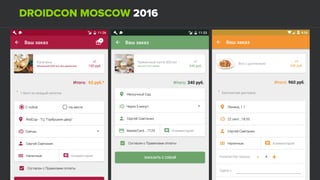
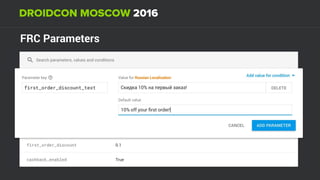
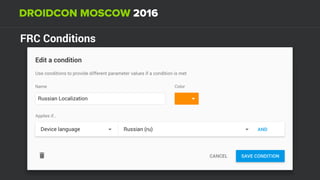
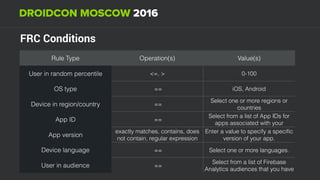
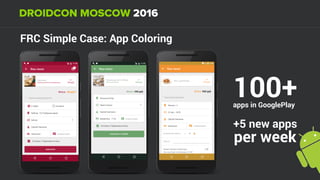
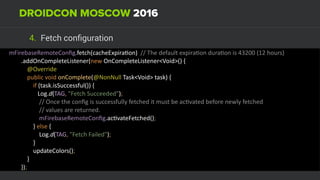
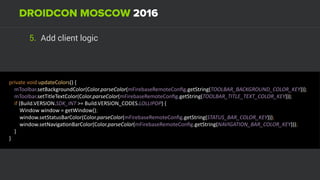
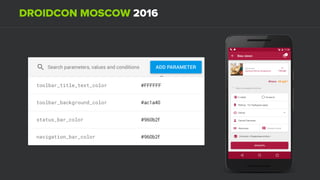
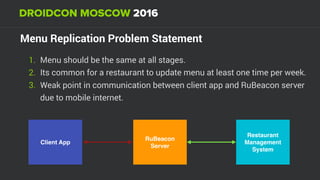
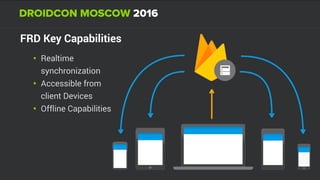
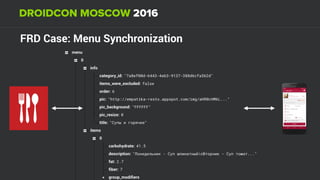
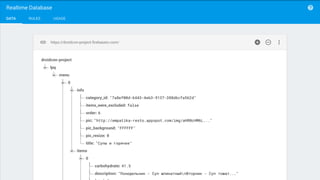
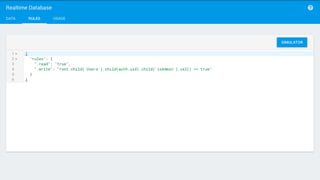
The document discusses using Firebase Realtime Database and Remote Config in a pattern-based mobile app for food ordering. Firebase Remote Config allows modifying app configuration like colors, text and features without an app update. Firebase Realtime Database provides real-time synchronization of data like menus across client and server to avoid out of sync issues during intermittent connectivity. Both services help reduce developer workload and speed up new feature deployment and A/B testing.


















![References
1. "Have you met the Realtime Database?", The Firebase Blog, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://
firebase.googleblog.com/2016/07/have-you-met-realtime-database.html. [Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].
2. "Firebase Realtime Database | Firebase", Google Developers, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://
firebase.google.com/docs/database/. [Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].
3. "Firebase Remote Config | Firebase", Google Developers, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://
firebase.google.com/docs/remote-config/. [Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].
4. "Firebase: Now with more querying!", The Firebase Blog, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://
firebase.googleblog.com/2014/11/firebase-now-with-more-querying.html. [Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].
5. "Queries, Part 1: Common SQL Queries Converted for Firebase", The Firebase Blog, 2016. [Online].
Available: https://firebase.googleblog.com/2013/10/queries-part-1-common-sql-queries.html.
[Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].
6. "Queries, Part 2: Advanced Searches with Firebase, made Plug-and-Play Simple", The Firebase Blog,
2016. [Online]. Available: https://firebase.googleblog.com/2014/01/queries-part-2-advanced-
searches-with.html. [Accessed: 18- Sep- 2016].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2017-06-2113-170621104221/85/Firebase-Realtime-Database-and-Remote-Config-in-Practice-DroidCon-Moscow-2016-32-320.jpg)
