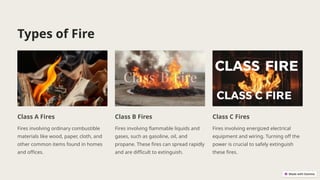
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to fire safety management, detailing the importance of preventing, detecting, and mitigating fire risks to ensure safety for people and property. It distinguishes between different fire types (Class A, B, and C) and provides methods for fire prevention, suppression, and safety training. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for regular inspections, emergency planning, and the use of advanced monitoring technologies to enhance fire safety practices.