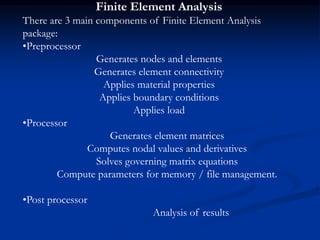
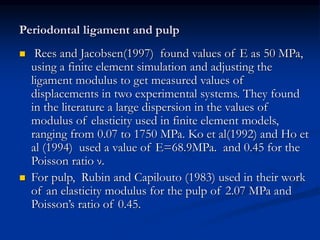
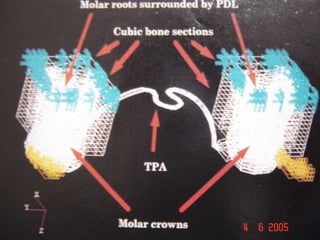
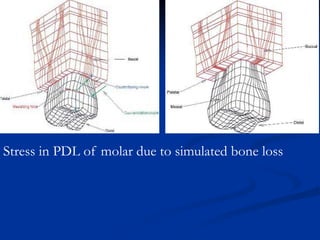
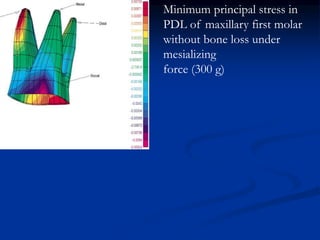
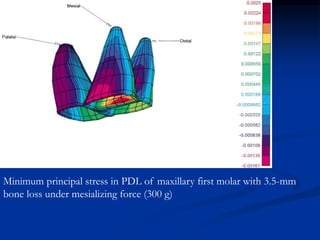
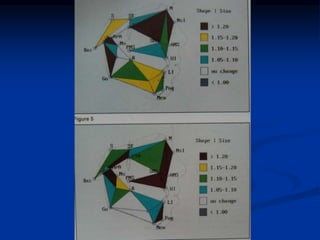
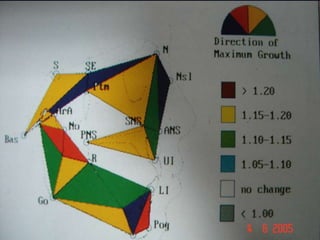
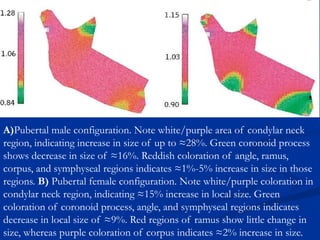
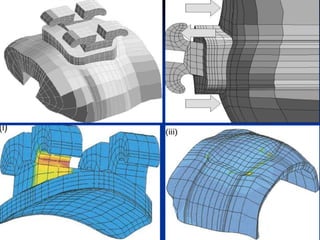
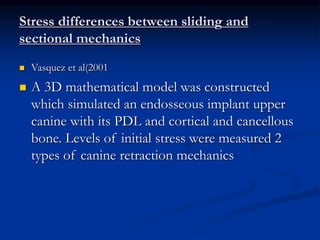
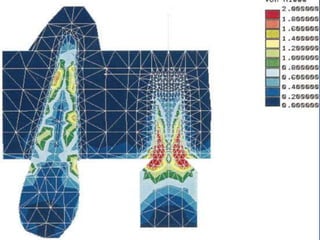
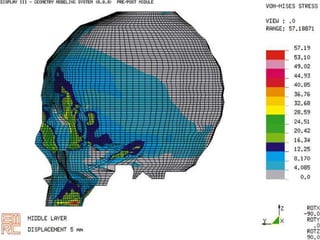
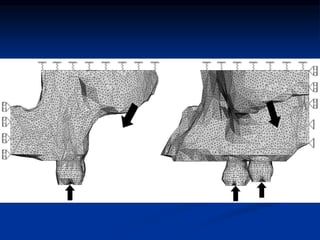
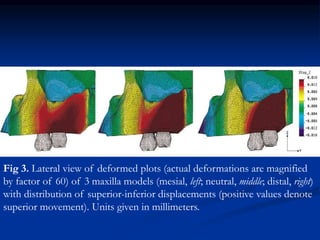
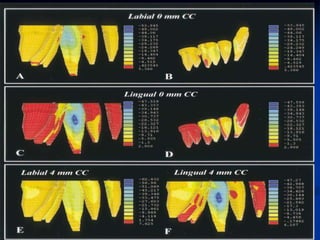
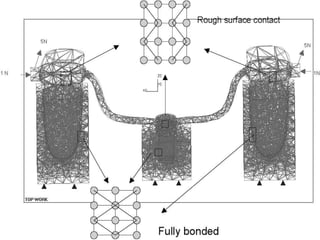
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) was developed in the 1960s to solve aerospace structural problems. It has since been introduced to orthodontics and other dental fields. FEA involves dividing a complex problem into smaller, simpler elements and using shape functions to interpolate variables. Each element is assigned material properties. The computer program then calculates element stiffness, solves matrix equations, and outputs displacement, stress, and other results. FEA allows modeling of complex biological structures like teeth and bone. It has provided insights into stress distributions and tooth movement from various orthodontic appliances and mechanics.