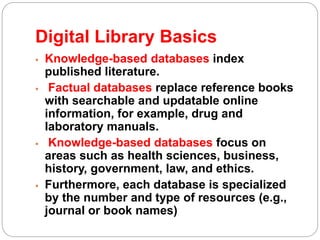
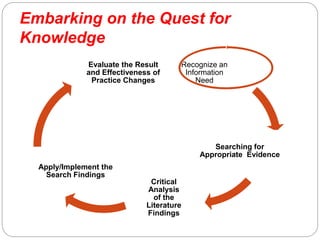
This document outlines finding knowledge in digital libraries for nursing. It defines digital libraries and describes their advantages over traditional libraries. It discusses personal reference managers, library guides, and bibliographic databases useful for nursing research, including CINAHL, MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, and PsycINFO. The document describes embarking on a quest for knowledge through questioning practice, searching evidence, analyzing literature, applying findings, and evaluating outcomes. It also discusses challenges to adopting evidence-based nursing.