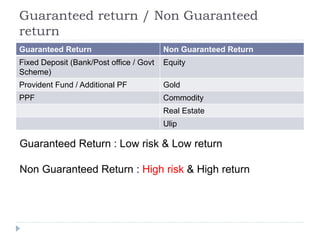
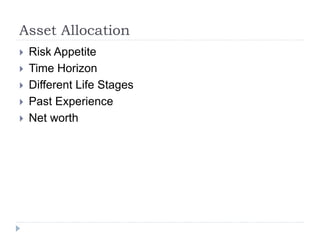
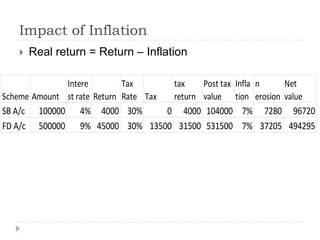
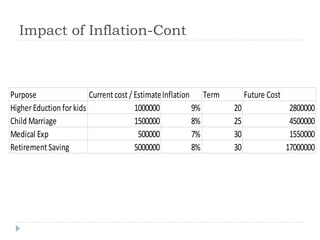
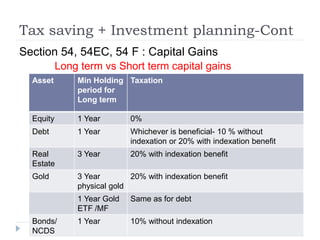
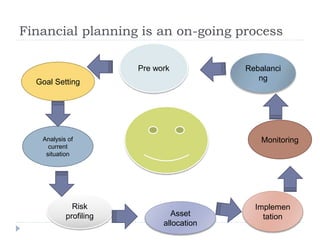
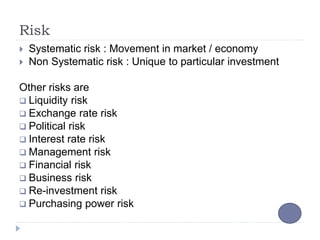
Financial planning is the process of achieving life goals through proper money management and disciplined use of investment options and current resources. It involves setting financial goals, analyzing one's current financial situation, creating a budget, and allocating assets across categories like protection, emergency funds, investments, taxes, retirement, and estate planning. Regular monitoring and adjustments are needed as one's situation changes over time to ensure goals remain on track.