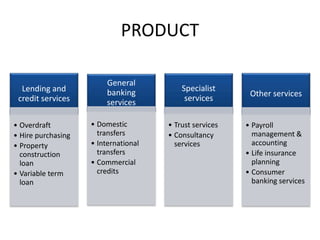
This document discusses marketing of financial services. It defines financial services as professional services involving investment, lending and money management. Some key financial service institutions are listed such as banks, mutual funds, pension funds, and stock exchanges. The marketing mix elements of product, price, promotion, place, physical evidence, people, process, and challenges and trends in financial marketing are then outlined.