This document provides a geospatial analysis of Amendment 2, known as the Safe Harbor Act, which passed overwhelmingly in Georgia in November 2016. The analysis examines the spatial relationships between voting results, locations of strip clubs, and addresses of registered sex offenders to determine if the funding sources identified in the amendment are appropriate. Three hypotheses are tested: 1) Voting changed in areas with more strip clubs, 2) Voting changed in areas with more crime, and 3) Areas with more strip clubs have more crime. The analysis finds some support for hypotheses 1 and 2 but not 3. It concludes that while sex offender penalties are fair, strip clubs are penalized unfairly, and resources would be better allocated in lower-income areas with more

![Acknowledgements:
Data providedbyFultonCounty[GeoPortal],the Secretary of State [Elections Page], Georgia Bureau of
Investigation, (GBI), American FactFinder, and the Atlanta Regional Commission (ARC)
Shapefiles provided by Fulton County [GeoPortal]
Addresses verified by ‘GEOBATCH’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-2-2048.jpg)
![Abstract:
ThisanalysisisbasedonAmendment2,legallyknownasthe Safe Harbor forSexuallyExploitedChildren
Fund, which was on the November 2016 general election ballot in the State of Georgia. It proposed to
add the Safe Harbor Fund to the state constitution, collecting funds from: additional penalties on
convicted sex traffickers, and a new fee on the adult entertainment industry.
This Amendment passed overwhelmingly - 85 percent ‘Yes’ in across the State of Georgia.
This analysis serves as a supplement for the lack of available research provided on either the Safe
Harbor Ballot Committee webpage.
I determined if the Safe Harbor Act Fund is focused on the correct variables, specifically the convicted
sex traffickersandthe adultentertainmentindustry. Thisanalysis focuses on crimes [referred to in this
analysisas‘Sex Offenders’]specificallyrelatedtosex traffickingof minors under 17 years of age, and on
strip clubs in the adult entertainment industry.
I did this through spatial correlation between the following data sets: 2016 General Election Results –
FultonCounty,FultonCounty[andCityof Atlanta] StripClubLocations, Georgia Bureau of Investigation
Sex Offenders List 2005 – 2015, and 2010 Decennial Income for Fulton County [and City of Atlanta].
By focusing on Fulton County and the City of Atlanta, I was able to provide a sample for discussion to
answerthe following questions: Are the variables from which the Fund is sourced appropriate? If not,
what would be an appropriate source? Is this Amendment truly serving children who have the most
need?
The hypothesis were as follows:
1) Voting Changes in locations with Strip Clubs – Where there are more, there is more voting
against the amendment
2) Voting Changes in locations with more crime – Where there is more crime, there is more
voting against the amendment
3) Where there is more strip clubs, there is more crime.
Based on the outcome provided in Maps A – L, my hypothesis 1 and 2 were both correct that voting
changed in relation location of strip club and sex offenders [by permanent registered addresses].
However,basedonmapsE and F, where there ismore crime there wasmore supportforAmendment2.
This part of Hypothesis #2 was incorrect. Lastly, Hypothesis 3 was incorrect. Based on maps G and H,
there is not a significant correlation between the two variables.
Therefore mydiscussionfocusedonwhythe Amendment’svariables,crime andstripclubvariables,do
not correlate;whatwasa more significantrelationship?MyfindingsinmapsKandL show a significant
correlationbetweencrime andincome levelsinFultonCounty[andthe Cityof Atlanta].Iquestioned
where the resourceswill be allocatedspecifically,asthe amendmentdoesnotprovide specificlocations.
Thisledme to the followingconclusions:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-3-2048.jpg)
![1) The AdultEntertainmentIndustry[specificallyStripClubs] isbeingpenalizedunfairly.
2) ConvictedSex Offendersare beingpenalizedfairly.
3) Resourceswouldbe betterallocatedinareasof lowerincome,wherethere are more
incarcerations.
4) While Amendment2overwhelminglypassed,therewasnotsignificantresearchorspatial
analysistosupportitsissue(s).Itisapartial moralityadditiontothe Constitutionof Georgia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-4-2048.jpg)

![ Safe Harbor Act refers to ‘Adult Entertainment’ for taxable locations and ‘Crime Rates’ for
trafficking locations. For data attainment, in this analysis:
o Strip Clubs addresses will be used for ‘Adult Entertainment’.
o Registered addresses of Sex Offenders will used for ‘Crime’.
I only used Safe Harbor Priority offenses: Sodomy, Rape, Molestation,
Trafficking,Prostitution,andSex withaMinor.All othercharges were removed.
Step 2: Clean up the data so that ArcGIS can interpret and analyze the data. This includes removing
unnecessary fields and symbols that clutter and confuse the software. Finally convert GeoID2 on the
Census data for Income to text so that it joins to the Census tracts layer in GIS.
Voting Data:
o Election results downloaded were strictly Amendment 2 voting ‘Yes’ or ‘No’
o Any blank votes i.e. an individual did not vote for the Amendment were removed for
analysis.
o See Table A for a look at Voting Results Data.
o See Step 7 below: Voting data was joined to Fulton County Voting Precinct shapefile
based on Precinct ID which was included in Voting Results Data file from Secretary of
State webpage.
GBI Sex Offender Data:
o All names, personal information, and incarceration information was removed.
o Streetnumbersandaddresseswere mergedintoone column(fromtwo) titled ‘GEOID2’
for address locator.
o Any ‘unknown’ addresses or addresses not reported were removed for purposes of
analysis and ease of matching.
o Address and Offense were remaining.
o See Table B for a look at GBI Data.
o See Table C for ‘repeated’ addresses [which likely skewed the data]
Strip Club locations:
o No AdultEntertainment‘item’ stores are included on this list, as they’re not verifiable
by ARC.
o All locationswere foundon‘Google’andverifiedbyAtlantaRegional Commission (ARC)
Of 41 locations, 20 were verified and matched in GEO Batch.
o Streetnumbersandaddresseswere mergedintoone column(fromtwo) titled ‘GeoID2’
for address locator.
o See Table D for a look at GBI Data.
Step3: Create City of Atlanta VotingPrecinct Layer by clippingthe FultonCounty voting precinct shape
file to fit the City of Atlanta shapefile.
o Use the GeoProcessing Tab to successfully clip the precinct shapefile to fit the City of
Atlanta.
Step 4: Create an Address Locator using the Tiger street shapefile and US Zip Code system. This allows
the sex offender’s and strip club addresses to be placed in their locations on the map.
See Table B and C for Sex Offenders and Strip Club address information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-6-2048.jpg)
![Step 5: Plot the sex offenders and strip clubs using the new address locator.
Remember:
o StripClubsaddresseswillbe usedfor‘AdultEntertainment’.
o Registeredaddressesof Sex Offenderswill usedfor‘Crime’.
Step 6: Relocate/Rematch any missing locations using online resources, such as ‘GeoBatch’ or self-
locating them with visual help from Google Imagery.
All StripClubaddressesverifiedbyAtlantaRegional Commission (ARC)
Step 7: Select by location only those strip clubs and sex offenders that occur in Fulton County and/or
City of Atlanta [based on Map].
To SelectbyLocationfor StripClubs:
o Clickon ‘SelectionTab’
o Choose ‘SelectByLocation’
Selectfeaturesfrom StripClubs
Selectsource layer‘FultonCounty’
o Method:‘Withinthe Source Layer’
o Right-Click‘StripClubs’layerinTable of Contents
Choose Selection
Create Layerfrom SelectedFeatures
o Exportdata from newlayer
Save as ‘FultonCountyStripClubs’
o RepeatthisprocessforCityof AtlantaMaps using‘CityLimits’layerinsteadof ‘Fulton
County’
Repeatthisprocessfor‘Sex Offenders’using‘Sex Offenders’layerinTable of Contents
Remember:Noavailable DekalbCountyVotingPrecinctShapefile.
o Therefore,Cityof Atlantaprecinctshapefile will be visible inMapsB,D, F, H, J, and L.
o Therefore,Sex Offenderlocationswill be visibleinMapsF – L.. Crime Dataas clipping
the Cityof Atlantacrime partiallywasn’tpreferred.
Step 8: Join the Income data from the census to the census tract layer using the common GEOid field.
Also join the voting results from Amendment 2 with the Fulton County voter precinct layer using the
common precinctID field.
Votingjoinstepsare asfollows:
o Rightclickon the Layer File (FultonCounty) andclick‘Join’
o Selectdatafile,andInputthe data file forIncome
o Choose the commonidfield,inthiscase GEOid
Step9: Use Quantitative Symbologyto create a ‘ChloreoplethMap’ of the Income levels in Fulton and
City of Atlanta.
Income joinstepsare as follows:
o Rightclickon the Layer File (Income.XLS) andclick‘Join’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-7-2048.jpg)
![o Selectdatafile,andInputthe data file forIncome
o Choose the commonidfield,inthiscase GEOid
RepeatthisprocessforbothFultonCountyand Cityof Atlantalayers.
ColorsinChloroplethMapchosenbasedonAPA Regulations.
Data:
Geographic Area of Interest:
o Fulton County
o City of Atlanta
o Not Included: Dekalb County [voting precinct file wasn’t available]
Coordinate Systems Used:
o NAD83_Georgia_West_ftUS
MetaData:
o 2010 Tiger Street Shapefile [Decennial Census Data]
o 2010 Fulton County, City of Atlanta, and State of Georgia shapefiles [Fulton GeoPortal]
o 2010 City of Atlanta neighborhood shapefile
o 2016 Amendment 2 Election Results
by Fulton County
o 2010 Voting Fulton County Precinct Shapefile
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex Offenders
o Fulton County Strip Clubs
Analytical Procedures:
(12) Maps createdbasedon:
o Votingprecinctresults:
inFultonCounty [Map A]
inCityof Atlanta[Map B]
o 1st
HypothesisStatement:votingresultsvs.stripclublocations
inFultonCounty [Map C]
inCityof Atlanta[Map D]
o 2nd
HypothesisStatement:votingresultsvs.sex offenderlocations
inFultonCounty [Map E]
inCityof Atlanta[Map F]
o 3rd
HypothesisStatement: variable locations(stripclubsandsex offenders)
inFultonCounty [Map G]
inCityof Atlanta[Map H]
o Votingresultsandvariables
inFultonCounty [Map I]
inCityof Atlanta[Map J]
o Findings:
inFultonCounty [Map K]
inCityof Atlanta[Map L]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-8-2048.jpg)
![ Assumptions basedon:[made priortoIncome correlation]
o Votingprecinctresults: [MapsA and B]
Amendment2will be lessfavoredclosertourbancore,and more favoredin
metro/surburbaregions
Thisassumptionismade priorto knowingwhere anystripcluborsex offender
locations.
o 1st
Hypothesis:[MapsCand D]
There will be achange invotingbasedonStripClublocations.
Amendment2will be lessfavoredwhere there are StripClubs,andmore
favoredinlocationswithoutStripClubs.
o 2nd
Hypothesis:[MapsEand F]
There will be achange invotingbasedonSex Offenderlocations.
Amendment2will be lessfavoredwhere there are more verifiedSex Offenders.
o 3rd Hypothesis[MapG andH]:
There will be correlationbetweenStripClubsandSex Offenders
Where there isStripClubs,there will be more Crime.
----
Refer to Maps A – L for results of Methodology, Data, and Analytical Procedures.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-9-2048.jpg)
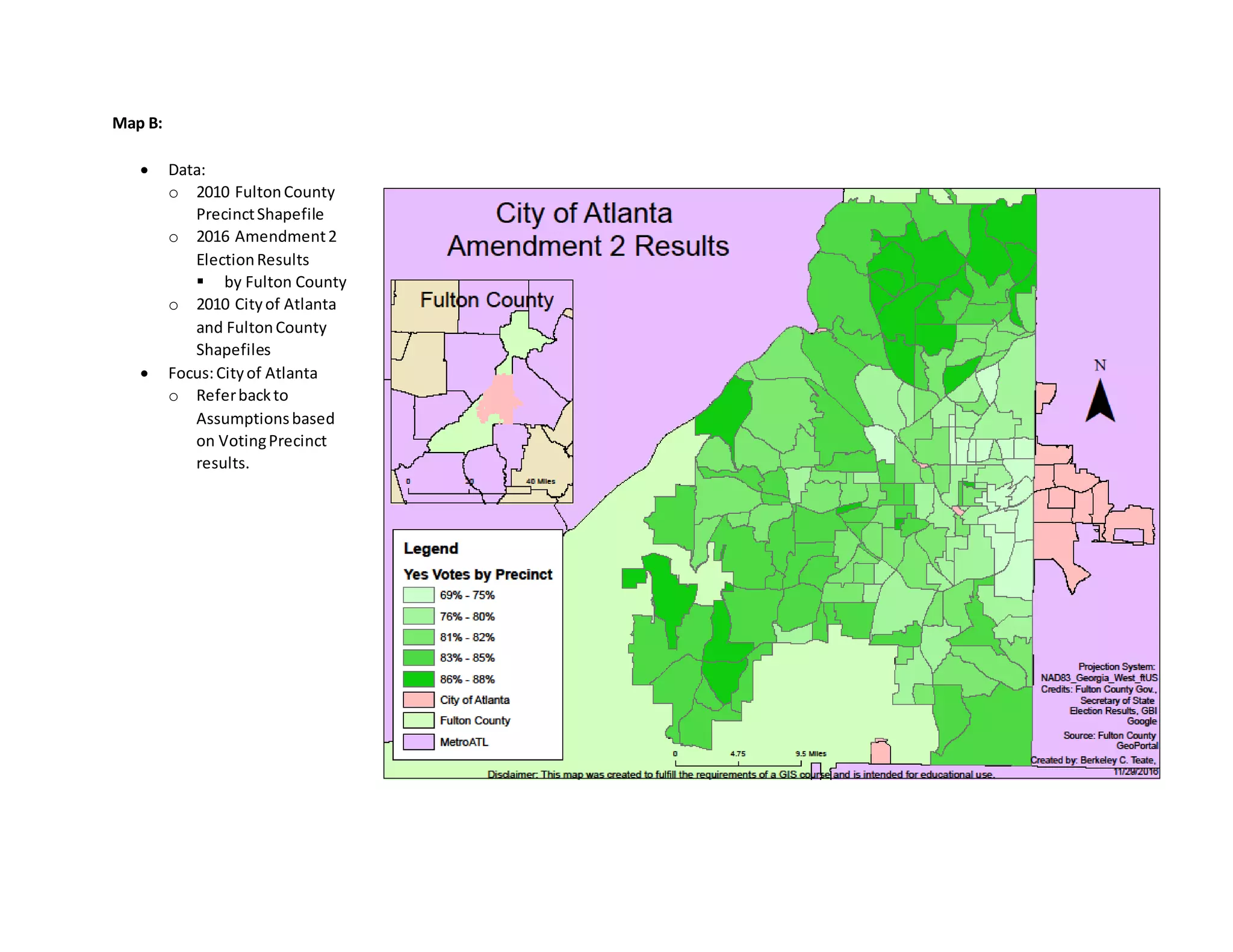
![Maps:
Map A:
Data:
o 2016 Amendment 2 Election Results
by Fulton County
o 2010 Voting Fulton County Precinct Shapfile
o 2010 Fulton County and State of Georgia Shapefiles
Focus:FultonCounty
o Referbackto Assumptions basedonVotingPrecinctresults.
Disclaimer:NoDekalbShapfile[RefertoData,GeographicAreaof Interest]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-10-2048.jpg)
![Map E:
Data:
o 2010 FultonCountyandState of Georgiashapefiles
o 2010 Fulton CountyPrecinctShapefile
o 2016 Amendment2ElectionResults
by FultonCounty
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex Offenders
Focus:FultonCounty
o Referbackto AssumptionsbasedonHypothesisStatement#2
Remember:Addressesare basedonregisteredpermanentaddresses[providedbyGBI],not
locationsof the crime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-14-2048.jpg)
![Map F:
Data:
o 2010 FultonCounty
and Cityof Atlanta
shapefiles
o 2010 FultonCounty
PrecinctShapefile
o 2016 Amendment2
ElectionResults[by
FultonCounty]
o 2005 – 2016 GBI
Sex Offenders
Focus:Cityof Atlanta
o Referbackto
Assumptionsbased
on Hypothesis
Statement#2
Remember:Addresses
are basedonregistered
permanentaddresses
[providedbyGBI],not
locationsof the crime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-15-2048.jpg)
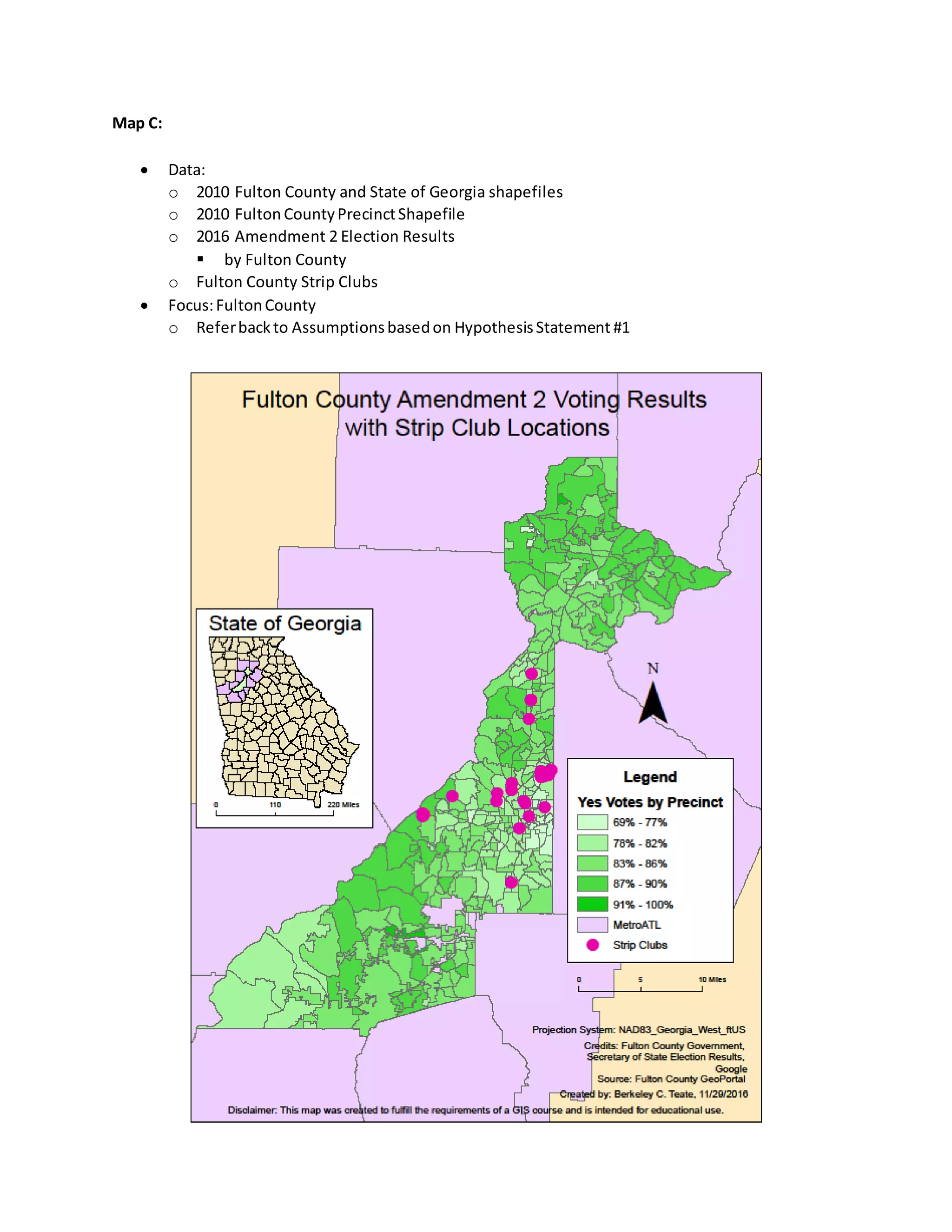
![Map G:
Data:
o 2010 FultonCountyandState of Georgiashapefiles
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex Offenders
o FultonCountyStripClubs
Focus:FultonCounty
o Referbackto AssumptionsbasedonHypothesisStatement#3
Remember:Sex Offendersaddressesare basedonregisteredpermanentaddresses[providedby
GBI],not locationsof the crime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-16-2048.jpg)
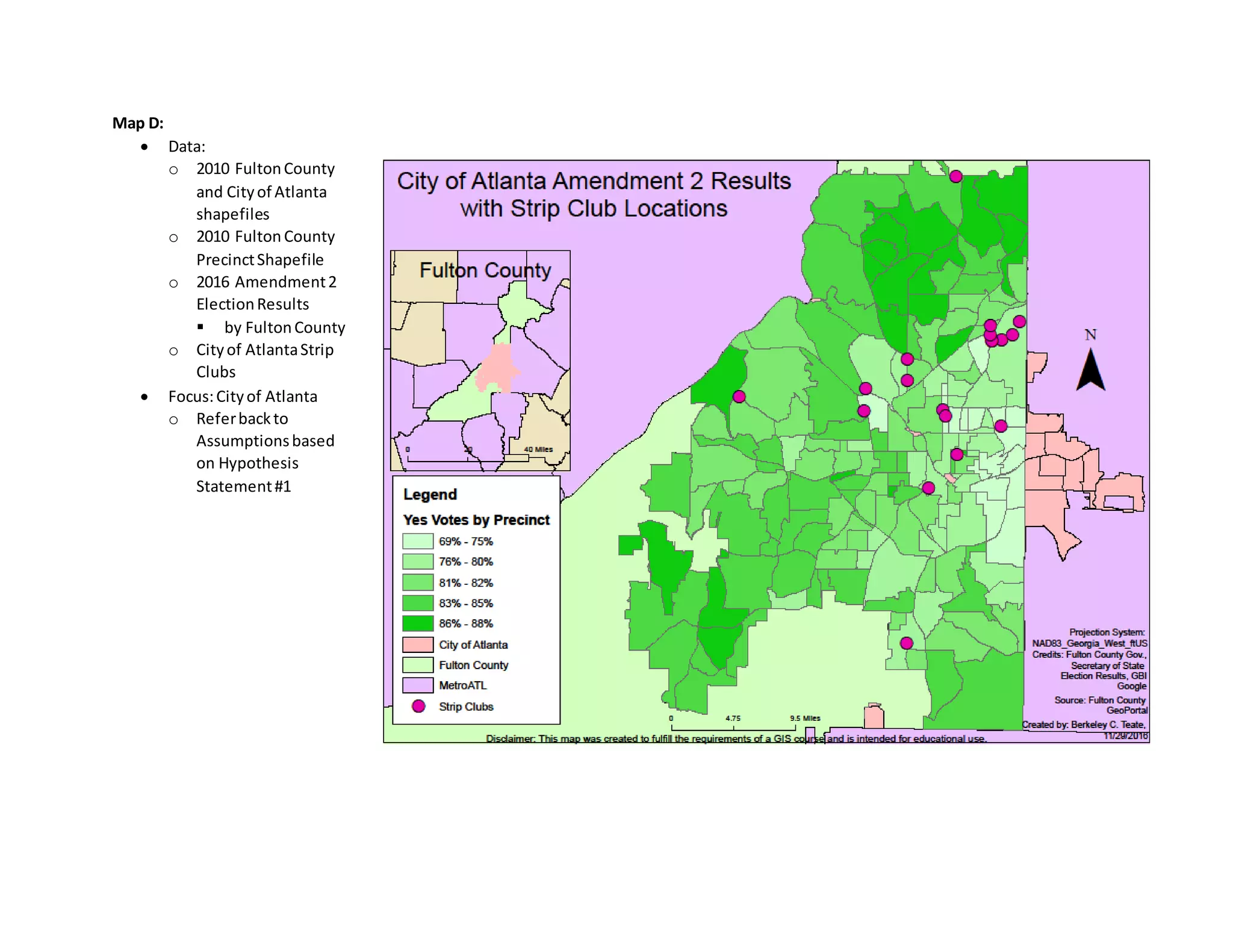
![Map H:
Data:
o 2010 FultonCounty
and State of
Georgiashapefiles
o Cityof Atlanta
neighborhood
shapefile
o 2005 – 2016 GBI
Sex Offenders
o FultonCountyStrip
Clubs
Focus:FultonCounty
o Referbackto
Assumptions
basedon
Hypothesis
Statement#3
Remember:Sex
Offendersaddresses
are basedonregistered
permanentaddresses
[providedbyGBI],not
locationsof the crime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-17-2048.jpg)
![Map I:
Data:
o 2010 FultonCountyandState of Georgiashapefiles
o 2010 FultonCountyPrecinctShapefile
o 2016 Amendment2ElectionResults[byFultonCounty]
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex Offenders
o FultonCountyStrip Clubs
Focus:FultonCounty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-18-2048.jpg)
![Map J:
Data:
o 2010 Fulton
Countyand City
of Atlanta
shapefiles
o 2010 Fulton
CountyPrecinct
Shapefile
o 2016 Amendment
2 ElectionResults
[byFulton
County]
o 2005 – 2016 GBI
Sex Offenders
o FultonCounty
StripClubs
Focus:Cityof Atlanta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-19-2048.jpg)
![Map: K:
Data:
o 2010 Tiger Street Shapefile [Decennial Census Data]
o 2010 Fulton County and State of Georgia shapefiles [Fulton GeoPortal]
o 2010 Voting Fulton County Precinct Shapefile
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex Offenders
Focus:FultonCounty](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-20-2048.jpg)
![Map L:
Data:
o 2010 TigerStreet
Shapefile[Decennial
CensusData]
o 2010 FultonCounty
and State of Georgia
shapefiles[Fulton
GeoPortal]
o 2010 VotingFulton
CountyPrecinct
Shapefile
o 2005 – 2016 GBI Sex
Offenders
Focus;Cityof Atlanta](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-21-2048.jpg)
![Tables
Table A: VotingPrecincts inFultonCounty
Precincts[348] Yes No Total
Raw Vote Count 350,007 70,067 420,074
Percentage 83.32 percent 16.67 percent 100.00 percent
Table B: GBI Data inFultonCounty
Top Crime Charged ConcentratedZip Code: Total Offenses:
ChildMolestation 30303 [Downtown] 1800 [Clean]
Table C: GBI Data, RepeatedLocations
Name: Address: Zip: Total Repeats:
Homeless –Pine Street
Shelter
447 Peachtree Street
NE
30308 20
Homeless –Gateway
CenterShelter
275 PryorSt SW,
Atlanta
30303 59
DekalbCoJail 0 DekalbCoJail,
Decatur GA
30035 2
FultonCoJail 0 FultonCoJail,Atlanta
GA
30318 9
State Prison 0 State Prison 30032 5
Table D: StripClubLocations
Name: Street: City: State: Zip:
ClubBabes 304 FultonIndustrial CirSW Atlanta GA 30336
ClubWax 4375 Commerce Dr SW Atlanta GA 30336
Hunk – O – Mania Male Strip Club 85 Peachtree Pl NW Atlanta GA 30309
Onyx Atlanta 1888 Cheshire Bridge RdNE Atlanta GA 30324
ClermontLounge 789 Ponce De LeonAve NE Atlanta GA 30306
FanniesCabaret 4401 FultonIndustrial BlvdSW Atlanta GA 30336
StilettosGentleman’sClub 806 MariettaSt SW Atlanta GA 30318
V Live Atlanta 1271 Marietta St NW Atlanta GA 30318
SwingingRichards 1400 Northside DrNW Atlanta GA 30318
Magic City 241 ForsythSt SW Atlanta GA 30303
GoldrushShowBar 2608 MetropolitanPkwySW Atlanta GA 30315
Flashers 6420 Roswell Rd Atlanta GA 30328
Blue Flame Lounge 1097 Harwell RdNW Atlanta GA 30318
The Cheetah 887 SpringStNW Atlanta GA 30308
CoronetClub 5275 Roswell RdNE Atlanta GA 30342
Tease AdultEntertainmentClub 2284 Cheshire Bridge RdNE Atlanta GA 30324
DreamsGentlemen’sClub 1715 Northside DrNW Atlanta GA 30318](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-22-2048.jpg)
![Kamal’s21 1905 PiedmontRdNE Atlanta GA 30324
Tattletle Lounge 2075 PiedmontRdNE Atlanta GA 30324
Doll House 5275 Roswell RdNE Atlanta GA 30324
GentlmensClub 91 W WieucaRd NE Atlanta GA 30342
BuffBoyzzGayStripClub 2069 Cheshire Bridge RdNE Atlanta GA 30324
XTC 2159 PiedmontRdNE Atlanta GA 30324
Trapeze 4470 Commerce Dr SW Atlanta GA 30336
Discussion:
Let’s briefly review each set of maps to either approve or disprove the hypothesis laid out in the
Introduction.
It isclear in Maps A and B, focusing specifically on voting in Fulton County and the City of Atlanta, that
Mid to NortheastAtlantasupportsAmendment 2 less than its counterparts. This is without either strip
club or crime locations create a strong argument. The major cities in this area are Brookhaven,
Buckhead,Downtown Atlanta, and Midtown Atlanta. Refer to Table A for a snapshot of the Fulton and
Atlanta voting results.
In Maps C and D, an argument can be made which supports my first hypothesis that stated voting in
these geographic areas changes in relation to strip club locations. It is clear in both maps that in
proximitytostripclubs,there islesssupportforAmendment2.The area of highest congestion, the City
of Buckhead,there are approximately 6 out of the 20 strip club locations [in Fulton County]. In the two
shared voting precincts, there was 76 – 80 percent ‘Yes’ votes in comparison to the majority 91 - 100
percentinFulton County. Refer to Table D for Strip Club locations and addresses [provided by Google,
verified by ARC, matched with GEOBatch, joined with Address Locator].
In Maps E and F, an argument can also be made which partially supports my second hypothesis that
stated voting in these geographic areas changes in relation to registered Sex Offenders [addresses].
However,Istatedthat crime wouldbe higherinareasof lesssupport for Amendment 2. In fact, there is
clearlymore supportforAmendment2inareas of highercrime.Inthe Mid to East Atlanta region where
support was 69 – 75 percent,there is significantly less crime than West to South Atlanta. I looked back
at my GBI Sex Offenders data [cleaned], and discovered a significant reason – the City of Atlanta jail,
Metro Atlanta Jail, Fulton County Jail, Georgia Department of Corrections, and (2) major homeless
shelters are located in these voting precincts that show higher crime rates. Refer to Table C for these
locationsandaddresses,whichwere repeated nearly 200 times based on the GBI data collected. Refer
to Table B for a snapshot of the GBI collected overall.
In maps G and H, which support my third hypothesis that stated there is a correlation between Strip
Club locations and Sex Offender locations [addresses], the analysis clearly shows there is little if any
correlation.The stripclublocationsare inMid – NortheastAtlantaandsex offenderlocations are in Mid
– SouthwestAtlanta.There islittle of eitherthe further out into Fulton County you look. Based on this,
my third hypothesis is incorrect. Maps I and J add voting results into these results, to add a layer of
confirmation to this statement.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-23-2048.jpg)
![So why do the Amendment’s variables, crime and strip club variables, not correlate; what is a more
significantrelationship? Having lived in the City of Atlanta my entire life, I came to the conclusion that
level of income must be a factor in this disparity. My findings in maps K and L show a significant
correlation between crime and income levels in Fulton County [and the City of Atlanta]. Each voter
precinctwasassignedanincome level basedonjoiningthe income datatothe votingprecinctshapefile.
This correlation is perhaps stronger than any of the other maps thus far. Looking specifically at Map L,
the red precincts have [majority] poverty ratings 26,929 USD or below [i.e. poverty line]. The
overwhelming majority of registered Sex Offender addresses are located within these precincts. It is
importantto rememberthatthisareadoescontain the majority of jails, homeless shelters and the GBI
in Fulton County [and the State of Georgia].
Concluding these findings, there is clear disparity between north and south Fulton regarding both
variables, voting results, as well as income. There is a strong correlation between Sex Offenders and
Income [Poverty Level]. My hypothesis 1 and 2 were both correct that voting changed in relation
locationof stripcluband sex offenders[bypermanentregisteredaddresses].However,basedonmaps E
and F,where there ismore crime there wasmore support for Amendment 2. This part of Hypothesis #2
was incorrect. Lastly, Hypothesis 3 was incorrect. Based on maps G and H, there is not a significant
correlation between the two variables.
Limitations for this analysis include the following:
o I did not have a Dekalb County Voting Precinct Shapefile
o I had to use the 2010 FultonCounty VotingPrecinctshapefile with2016 FultonCounty
Votingresults.
o Sex OffenderDatamay be skewedbasedonhomelessindividualsthatwere registered
at the addressesof jails,homelessshelters,andstate agencies.
o I strictlyfocusedonSex Offendersprovidedbythe GeorgiaBureauof Investigation.Idid
not include reportedcrimesoutsideof the State [of citizensof the State of Georgia],nor
didI use incarceratedindividualswhowere notplacedonthe Sex Offenderslist.
It’simportantto lookat whatwouldbe the nextstepsof thisanalysis.If alterationscouldbe made inthe
future,I would look more closely at the areas of crime in comparison to the locations of rehabilitative
industriesinthe region(s).Iwouldalsolookatthe locationsof crime incidents,rather than where these
Sex Offendersare permanentlyaddressed.Lastly,Iwouldlookatrehabilitativeindustries in comparison
to the addresses or reported crimes of the victims.
In conclusion, let’s reflect on the conclusion that there was little correlation between the adult film
industry and crime in Fulton County or the State of Georgia. My findings concluded it is not adult
entertainment, but income, that drives trafficking crimes. Therefore, Amendment 2 is partially a
morality push rather than legislation that wants to enact real effect. If it truly wanted to tackle
traffickingandsex offensesof minors[whichSafe Harborpenalizes],itwouldfocusonpoverty –stricken
areas in Fulton County and the City of Atlanta.
References:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0a2fdc64-8f21-4602-b0a3-c334b59abac2-170106005016/75/FinalPaperBerkeleyTeateDecember072016-24-2048.jpg)
