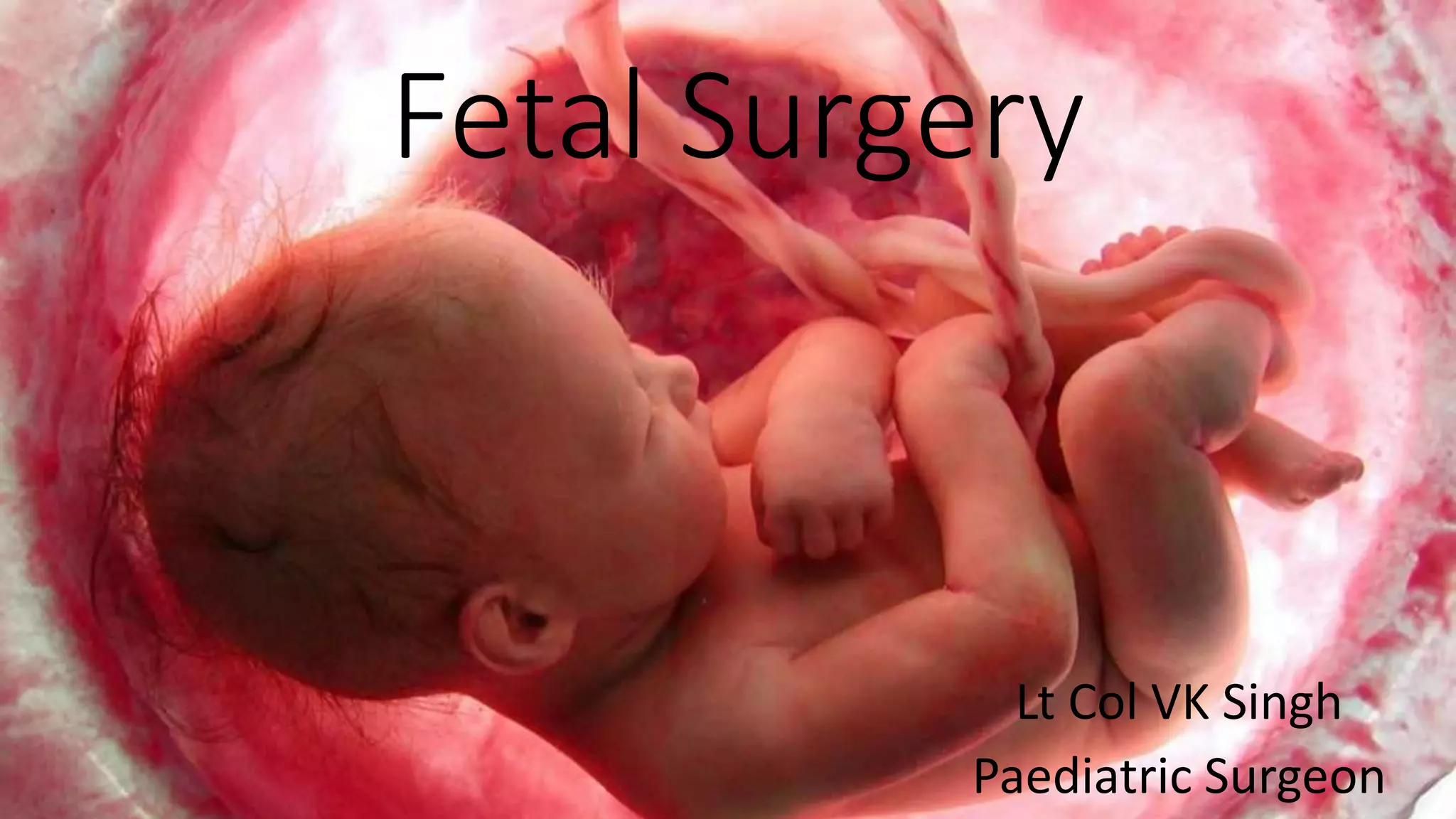
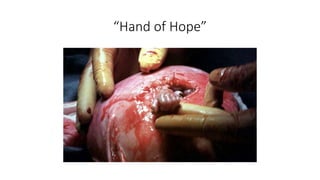
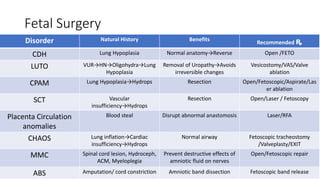
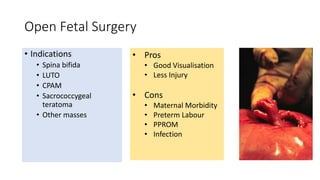
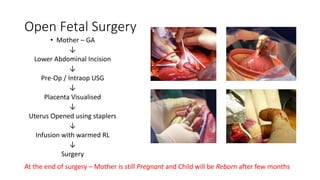
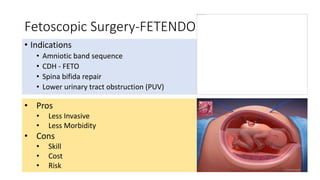
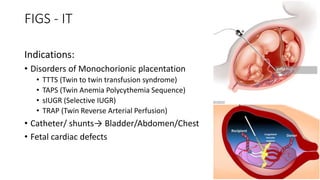
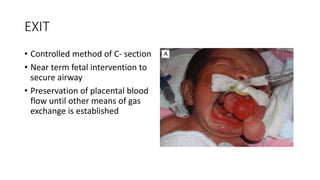
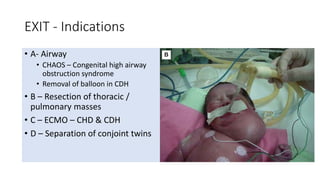
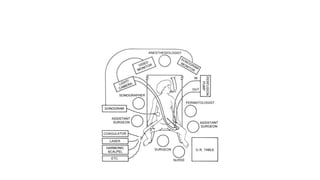
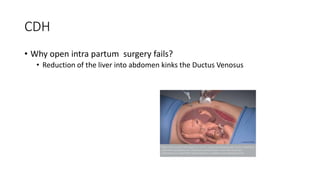
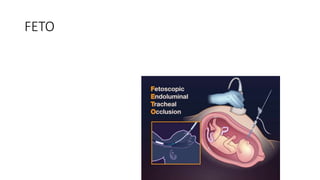
Fetal surgery has evolved significantly, enabling interventions on congenital anomalies that could lead to severe disabilities or death if untreated, with careful risk-benefit analysis for both mother and fetus. Types of fetal surgery include open surgery, fetendo (fetal endoscopic surgery), and EXIT (ex utero intrapartum treatment), each with specific indications and advantages. The document discusses various surgical techniques, outcomes of studies, and future possibilities for treating genetic conditions, emphasizing the necessity of competent fetal lungs for successful postnatal outcomes.