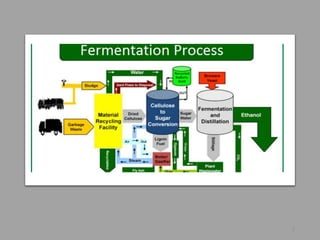
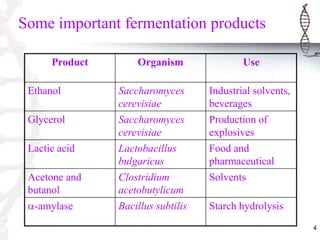
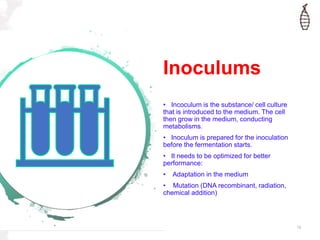
Fermentation is a form of metabolism where organic compounds are broken down without oxygen. Common fermentation products include ethanol, glycerol, lactic acid, acetone, and butanol. Fermenters are bioreactors used to carry out fermentation on an industrial scale, ranging in size from liters to hundreds of cubic meters. Important components of fermentation include the fermentation medium, which provides nutrients, and inoculum, cells introduced to initiate growth. Rates of substrate consumption and product formation are important for mass balances in fermenters. Catabolism generates energy for anabolism and maintenance through electron donor-acceptor couples.