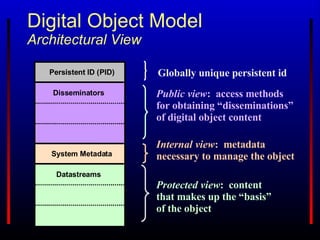
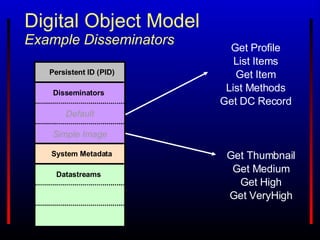
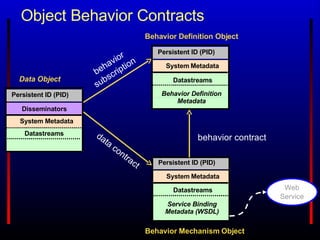
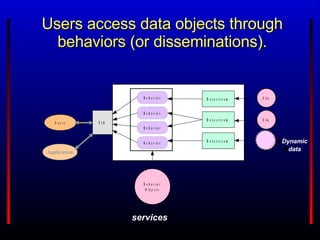
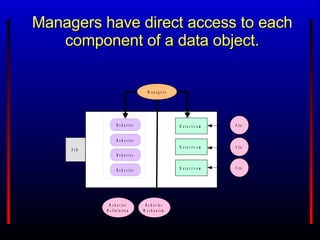
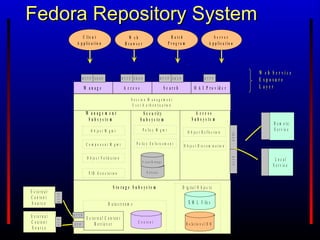
The Fedora Project provides an open source digital object repository system with extensible models and scalable storage. It exposes repository functions via web service APIs and supports use cases in content management, digital libraries, asset management, and scholarly publishing. Prior commercial systems had narrow focuses and lacked interoperability and extensibility. Fedora aims to overcome these shortcomings through its flexible data model, web services approach, and ability to associate behaviors and services with digital objects.