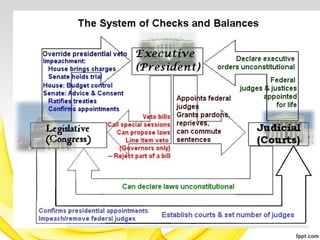
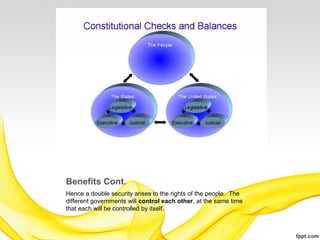
The document discusses the implementation of federalism, highlighting Madison's views on the compound republic, the necessary and proper clause, and the principles of checks and balances within government structures. It emphasizes the importance of dividing power among different branches and between state and federal governments to prevent tyranny and protect individual rights. Additionally, it argues that the extended republic of the United States helps to diminish factional power and promote greater justice and moderation.