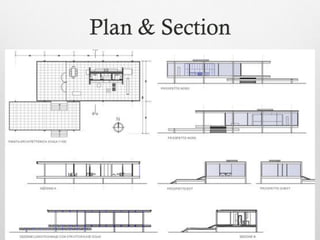
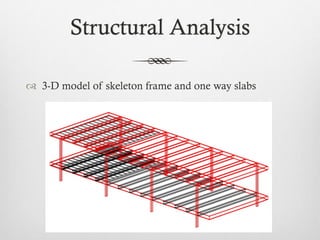
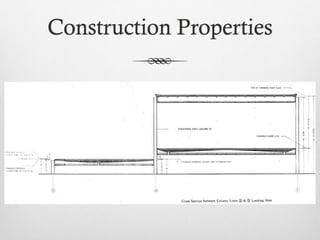
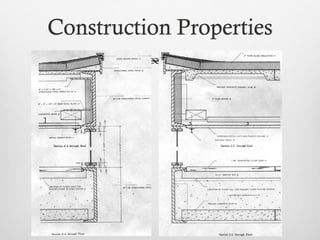
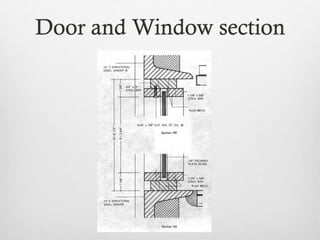
The document summarizes key details about the Farnsworth House, designed by Ludwig Mies van der Rohe in 1945-1951. It is considered an iconic masterpiece of International Style architecture. The steel and glass structure features a minimal framework of eight steel columns supporting two glass-enclosed slabs for the floor and ceiling. It addresses the relationship between individuals and society through its open interior plan enabled by the steel structure and glass walls. The house uses industrial materials like steel and glass that are factory produced.