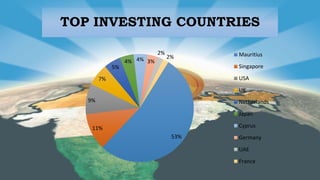
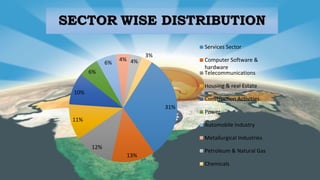
The document discusses foreign direct investment (FDI) in India. It notes that the cabinet approved 51% FDI in multi-brand retail and 100% FDI in single-brand retail. While farmers may benefit, small traders fear they cannot withstand competition. The document provides background on FDI and sectors that attract investment. It also lists factors that attract FDI, such as market size, infrastructure, skilled labor, and a stable political/regulatory environment. Both benefits and concerns of FDI in retail are discussed. The conclusion is that FDI's advantages outweigh disadvantages and it is important for India's economic growth, despite some negative impacts.