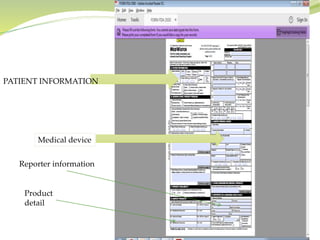
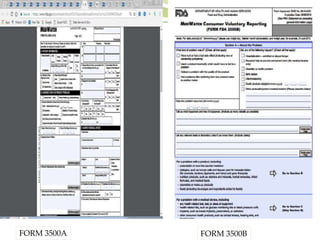
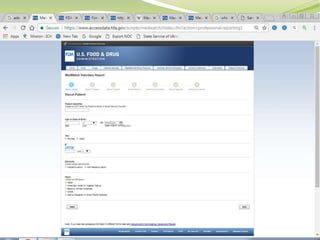
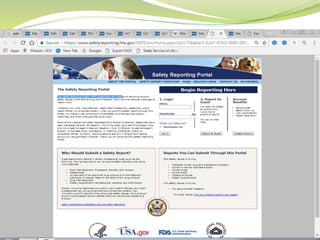
MedWatch is the FDA's program for monitoring the safety of medical products. It allows voluntary reporting of adverse events by the public and healthcare professionals. Reports are collected in a database and monitored by FDA professionals. The FDA uses these reports to identify safety issues, communicate new safety information to the public and healthcare providers, and take regulatory actions like requiring label changes or product recalls when needed. The goal is to help protect public health by ensuring the safety of drugs, medical devices and other medical products.