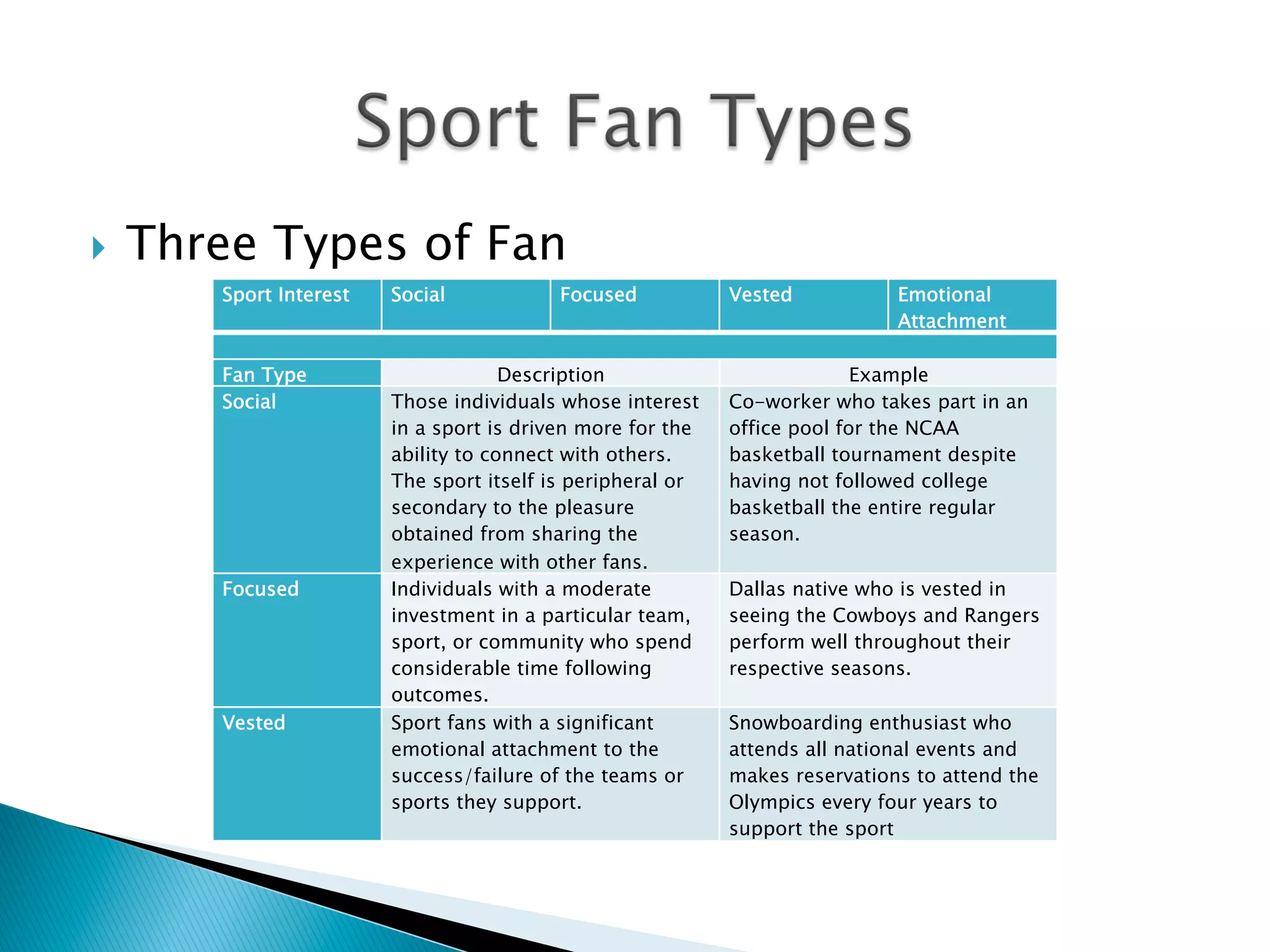
This document discusses the phenomenon of sports fandom. It defines the differences between spectators and fans, with fans having a stronger devotion to a team or sport. Fans can range from fair-weather fans who only follow when a team is winning, to die-hard fans deeply invested in a team's success or failure. The document also categorizes fans into social, focused, and vested types based on their level of emotional attachment. It explores the rituals and performances of fandom, as well as the six main motivations that drive fans' connections to sports such as aesthetic beauty, achievement, drama, escape, knowledge and social connection.