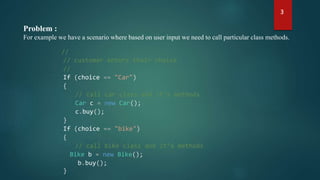
The document discusses the factory design pattern, highlighting its utility in decoupling systems and minimizing client exposure to instantiation logic. It provides code examples demonstrating how to implement a factory pattern to create objects like cars and bikes based on user input. Additionally, it introduces the concept of replacing 'if' statements with polymorphism to improve design flexibility.




![RIP (Replace IF with Polymorphism)
public class FactoryChoice
{
private IDictionary<ChoiceType, IChoice> _choices;
public FactoryChoice()
{
_choices = new Dictionary<ChoiceType, IChoice>
{
{ChoiceType.Bike, new clsBike() },
{ChoiceType.Car, new clsCar()}
};
}
static public IChoice getChoiceObj(ChoiceType choice)
{
var factory = new FactoryChoice();
return factory._choices[choice];
}
}
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factorypatternwithrip-151112005603-lva1-app6892/85/Factory-pattern-with-rip-6-320.jpg)
![Factory pattern contd.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Client class
IChoice objInvoice;
objInvoice = FactoryChoice.getChoiceObj(ChoiceType.Bike);
Console.Write(objInvoice.Buy());
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factorypatternwithrip-151112005603-lva1-app6892/85/Factory-pattern-with-rip-7-320.jpg)
