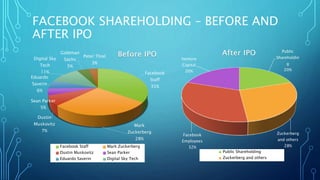
The document analyzes Facebook's 2014 acquisition of WhatsApp for $19 billion, discussing the origins, structures, and objectives of the deal. It highlights both companies' market positions, the regulatory landscape, and potential synergies, including access to new markets and economies of scale. While the acquisition is regarded as significant, it faces criticism regarding data privacy and the challenge of monetizing WhatsApp.