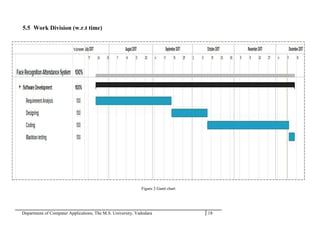
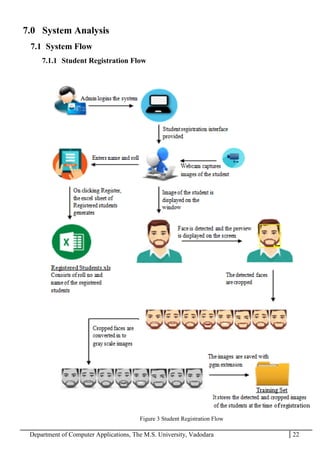
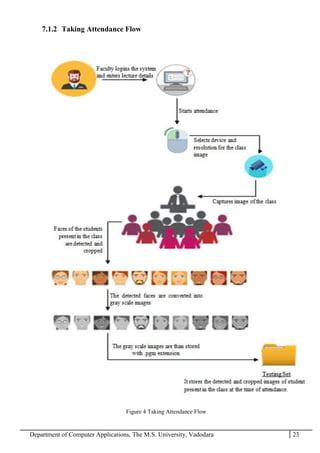
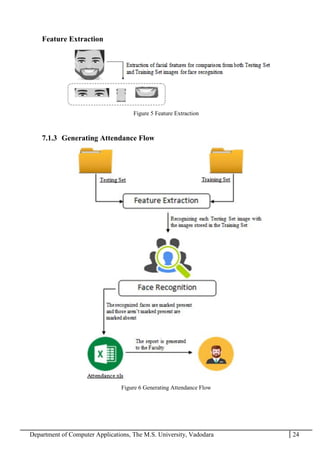
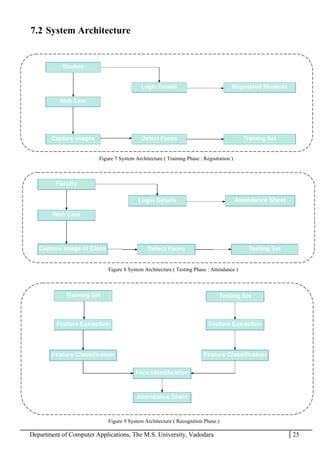
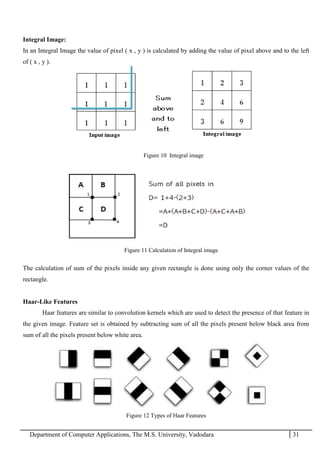
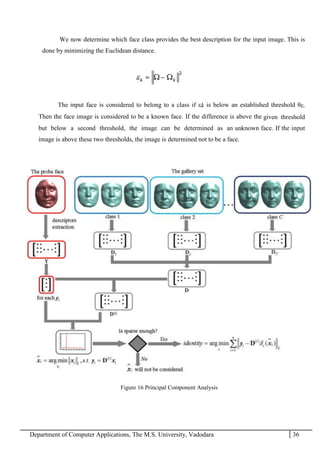
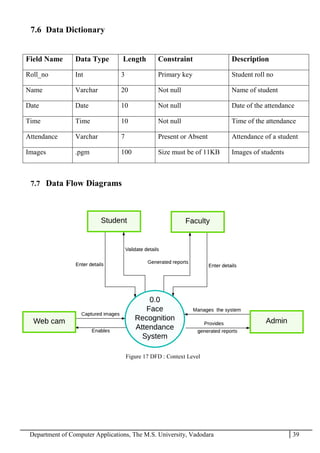
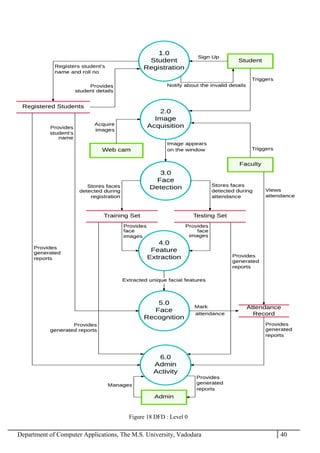
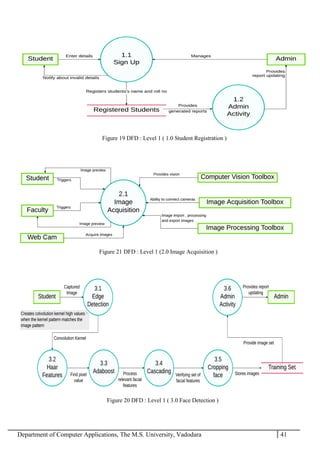
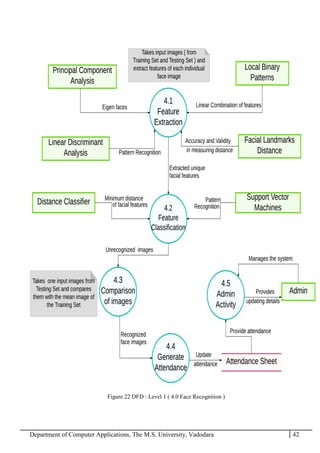
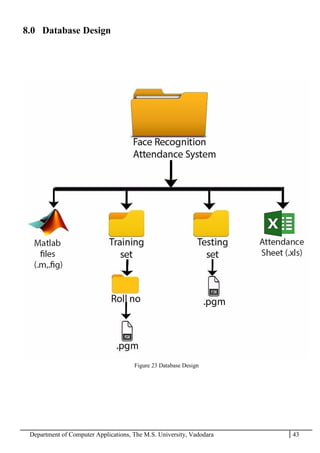
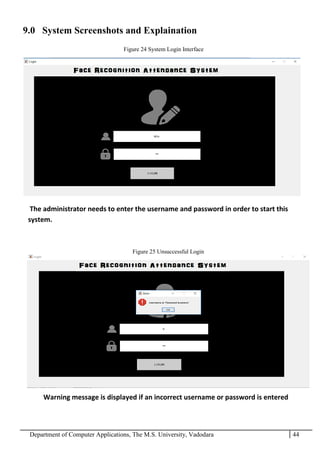
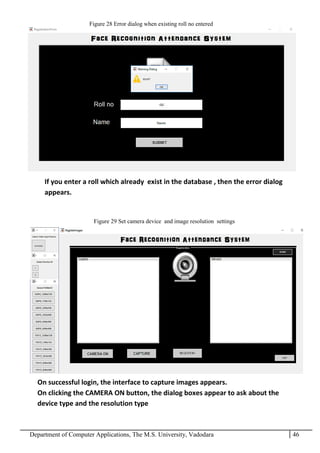
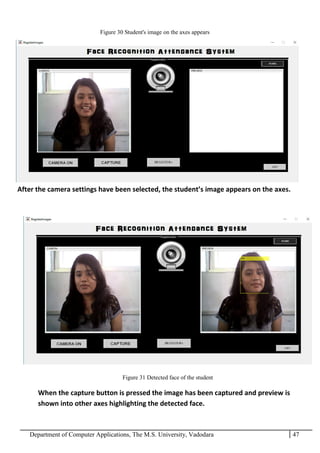
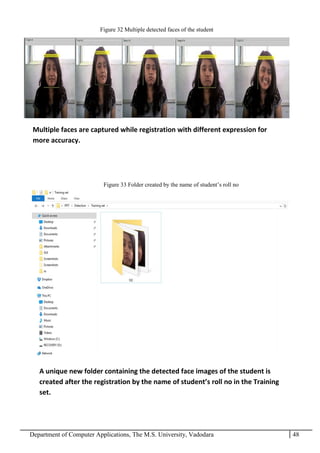
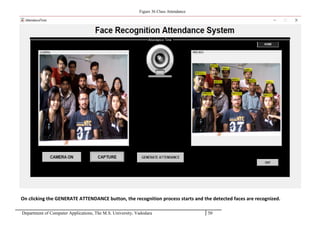
The project report outlines the development of a face recognition attendance system aimed at automating the traditional manual attendance process in educational institutions. The system employs image processing techniques for face detection and recognition to efficiently mark student attendance, addressing time consumption and accuracy issues inherent in existing methods. The report details the project plan, system architecture, and anticipated contributions, emphasizing improvements in speed, usability, and security over conventional attendance systems.