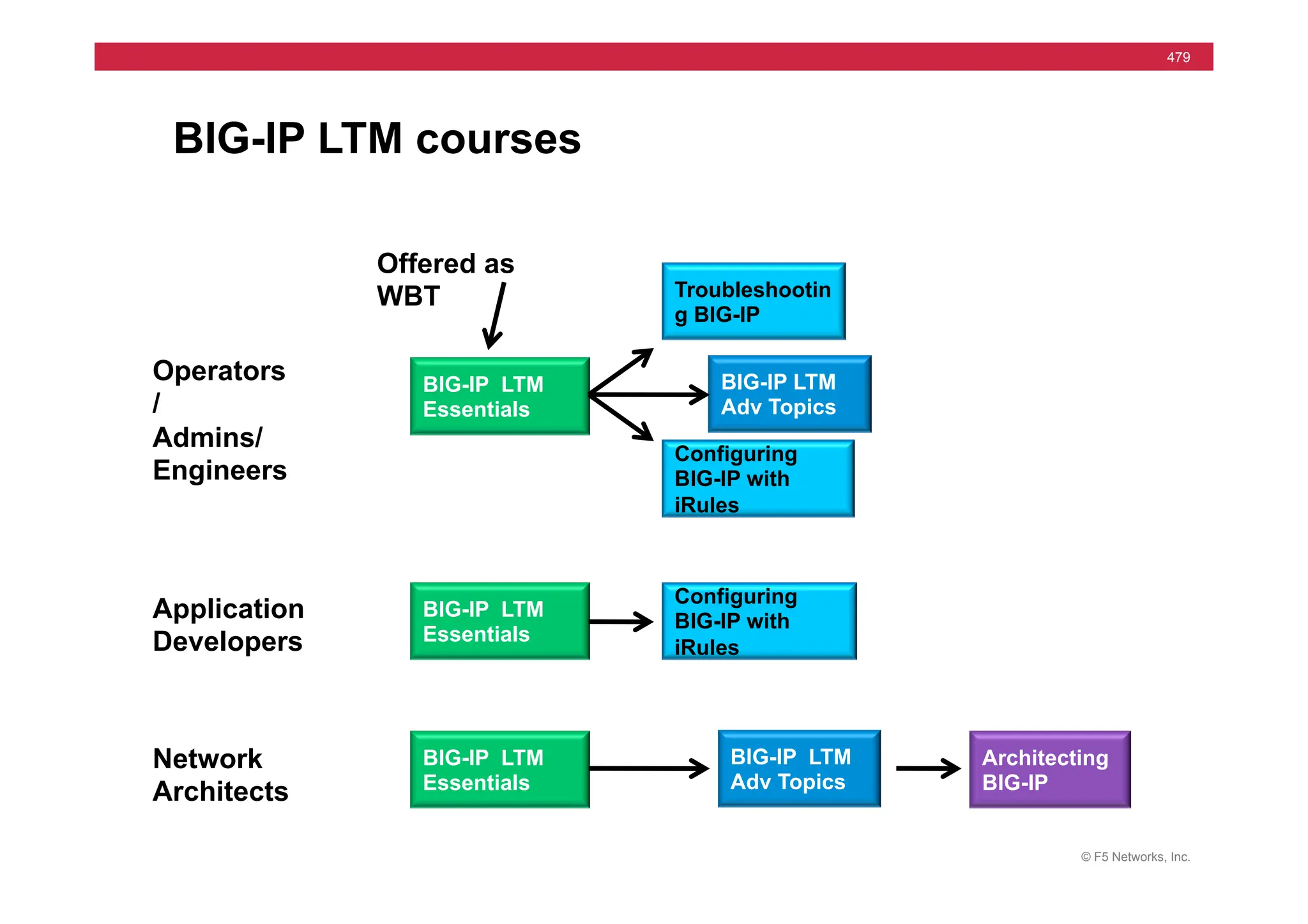
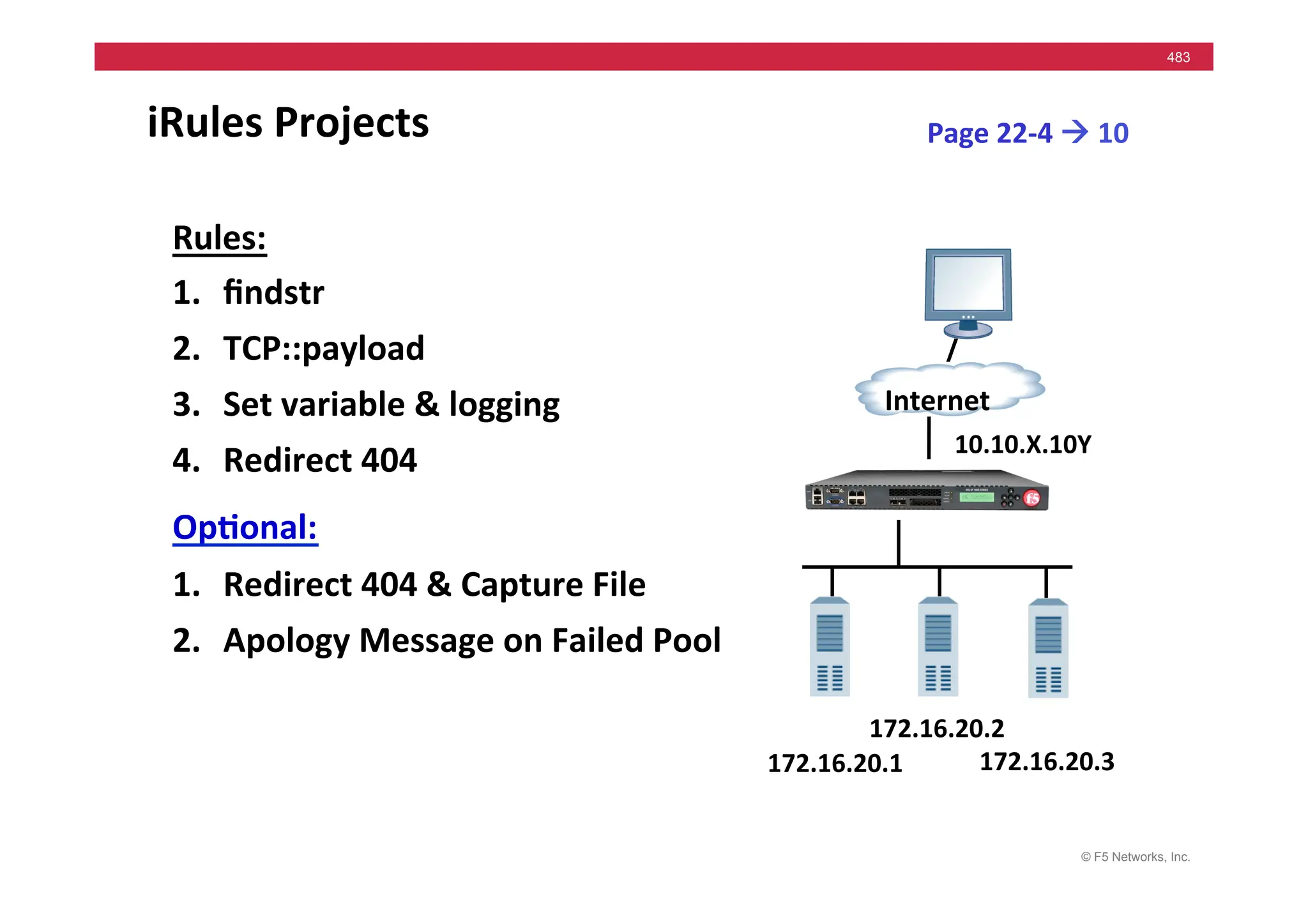
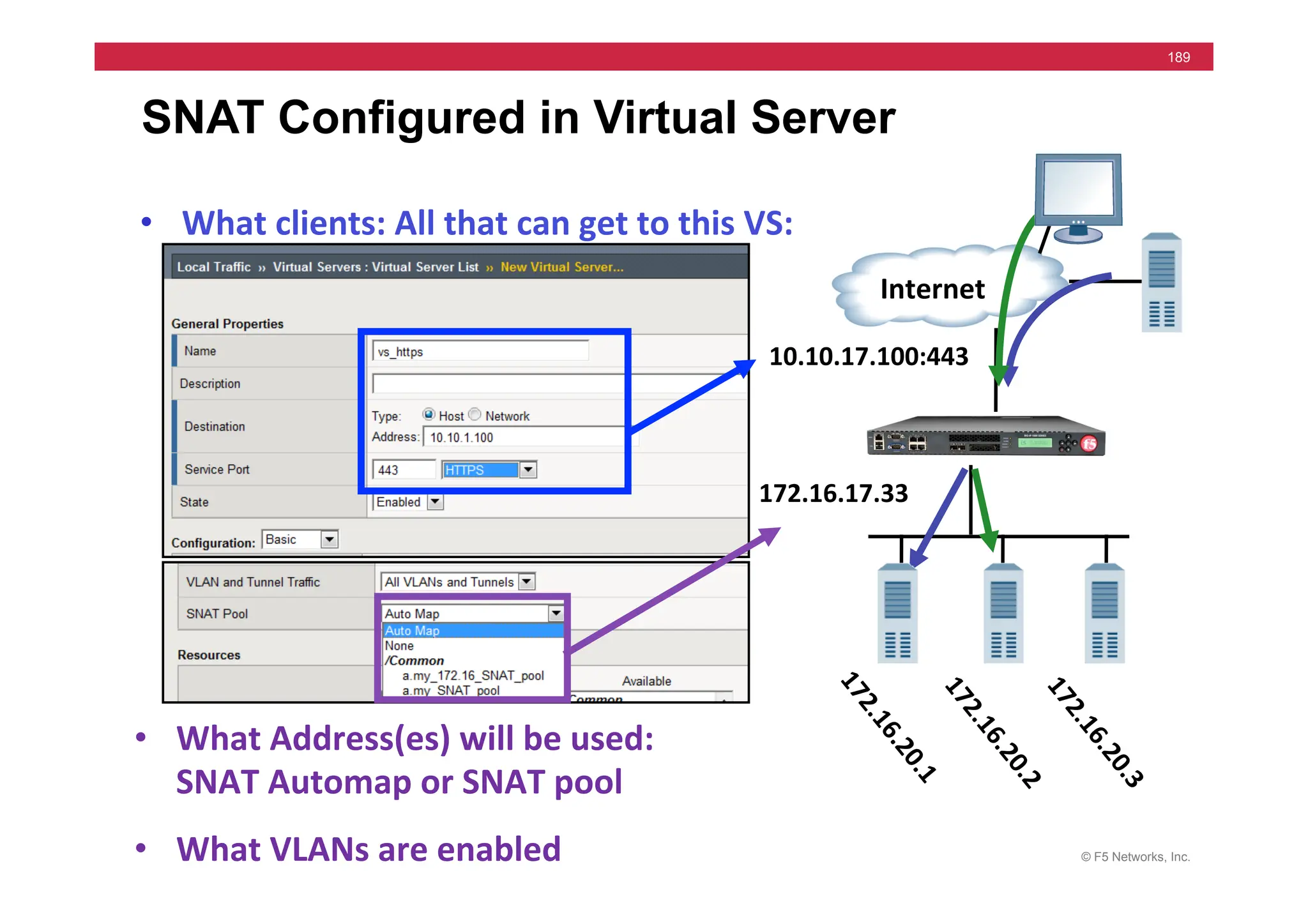
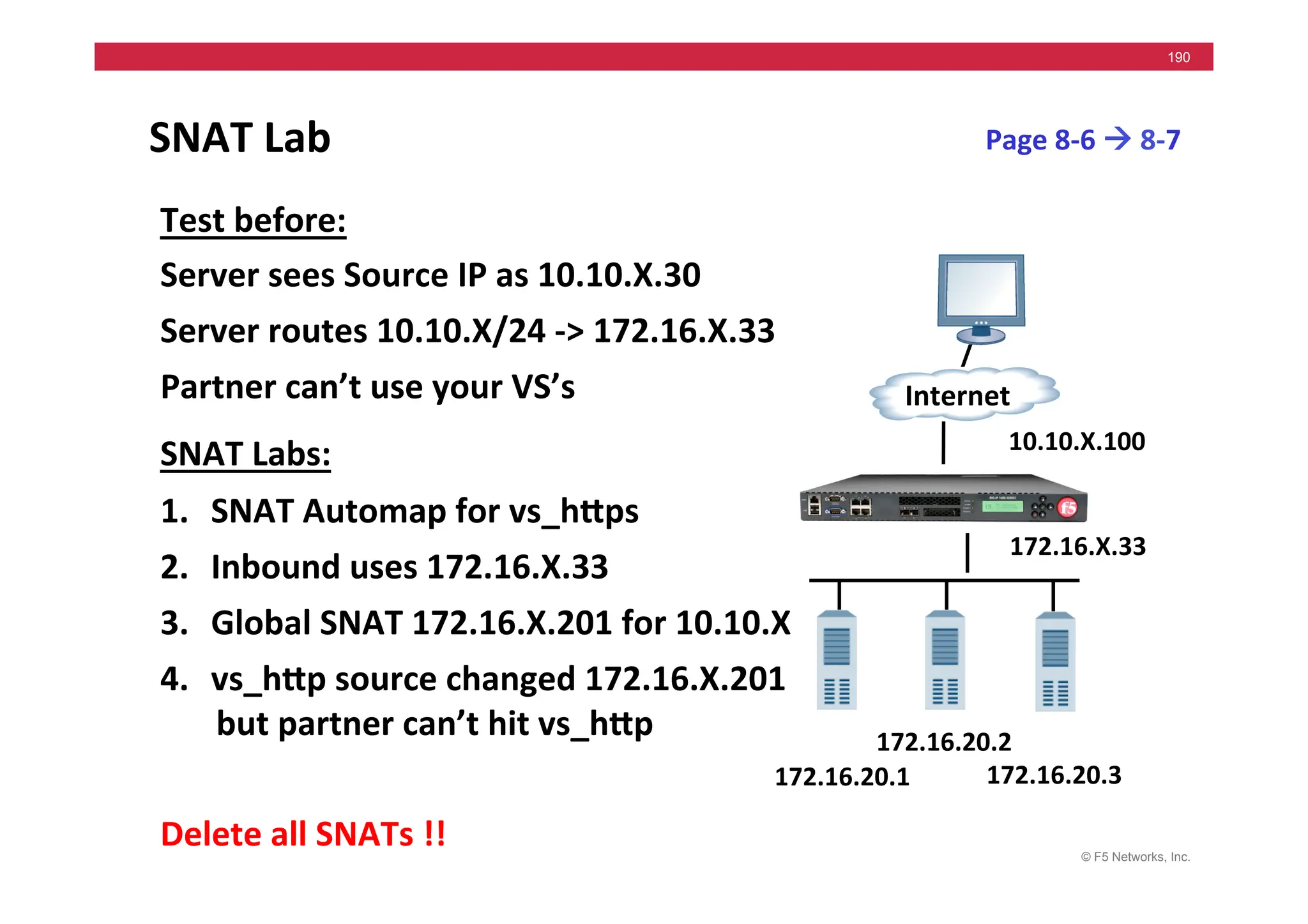
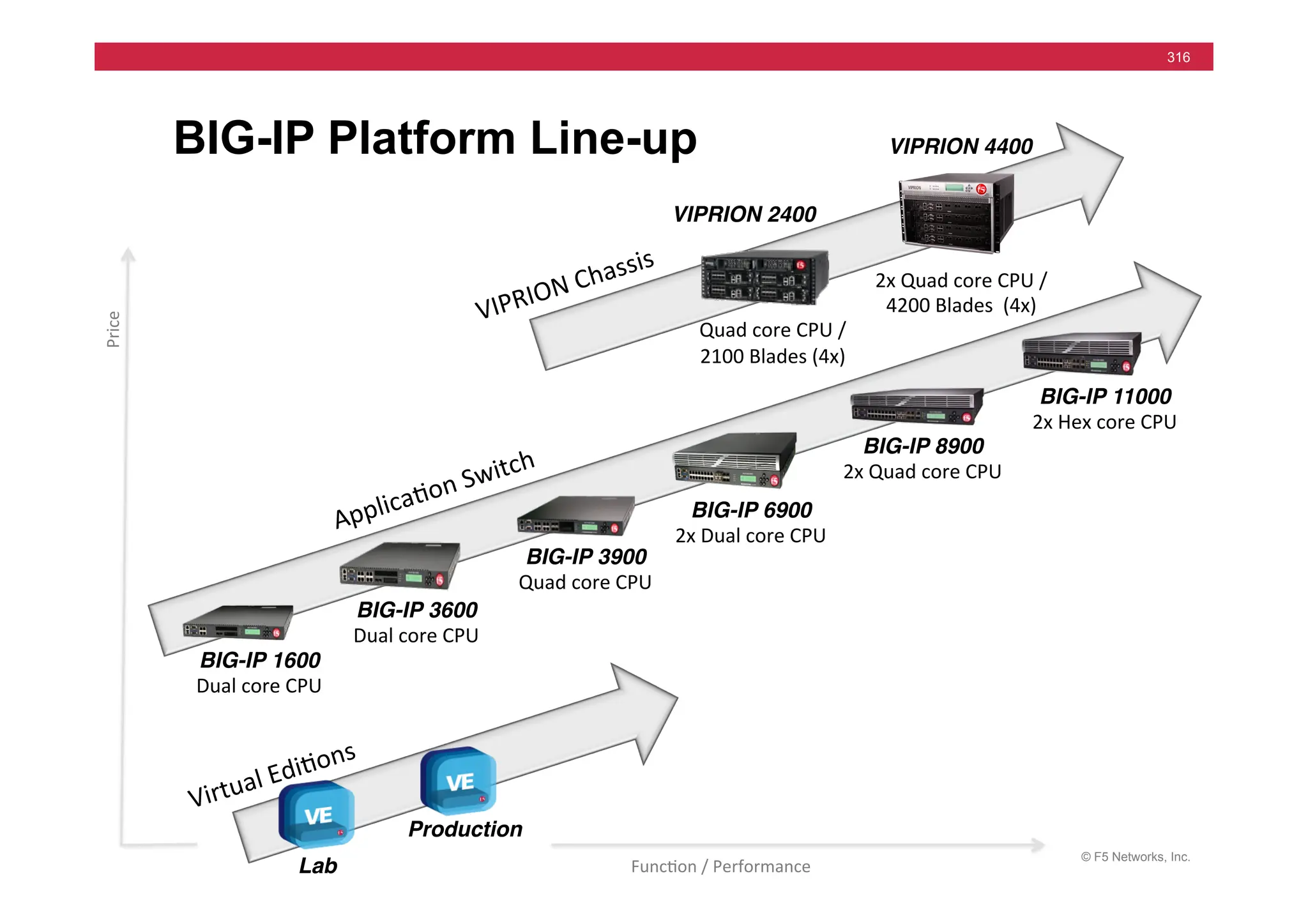
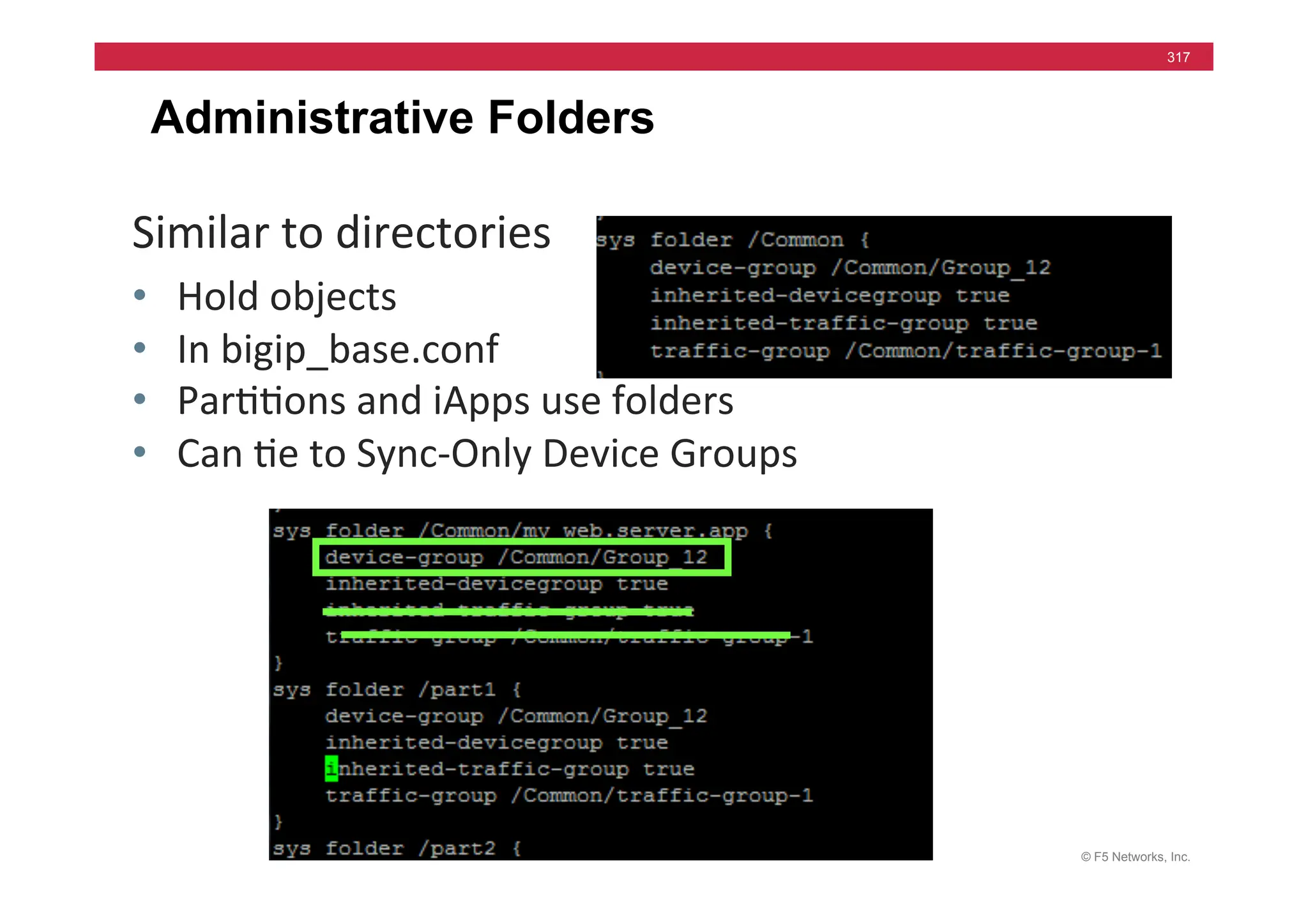
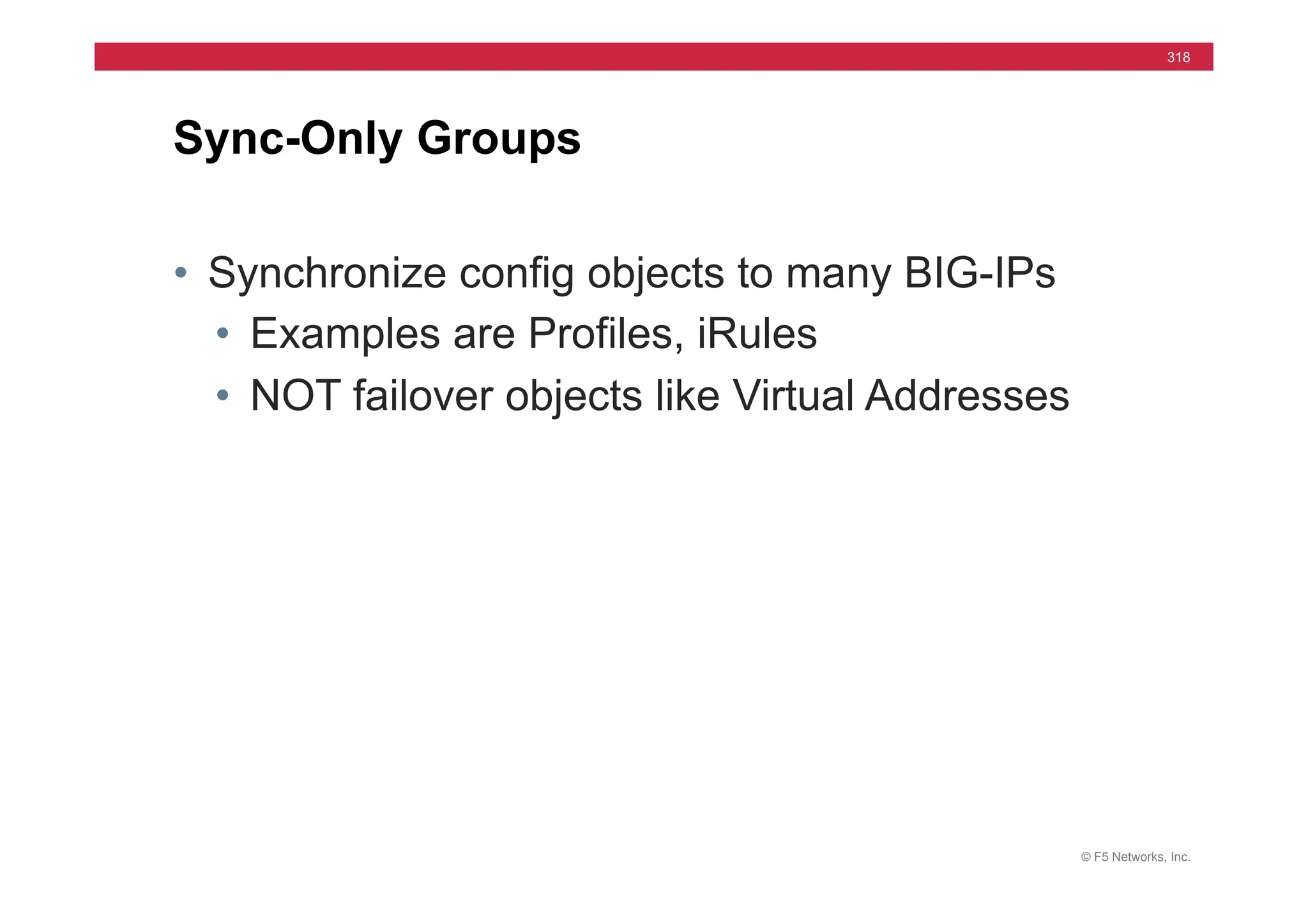
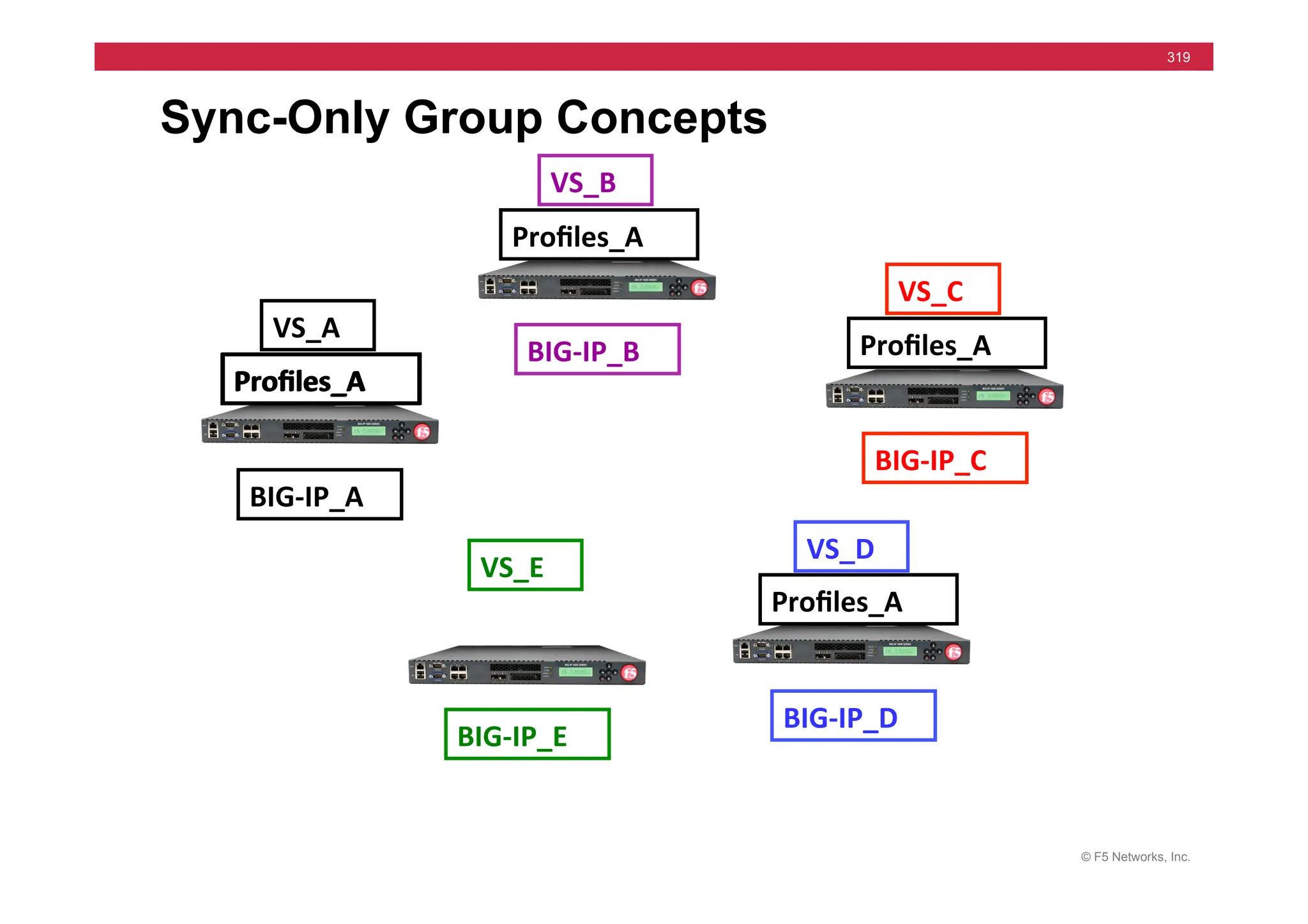
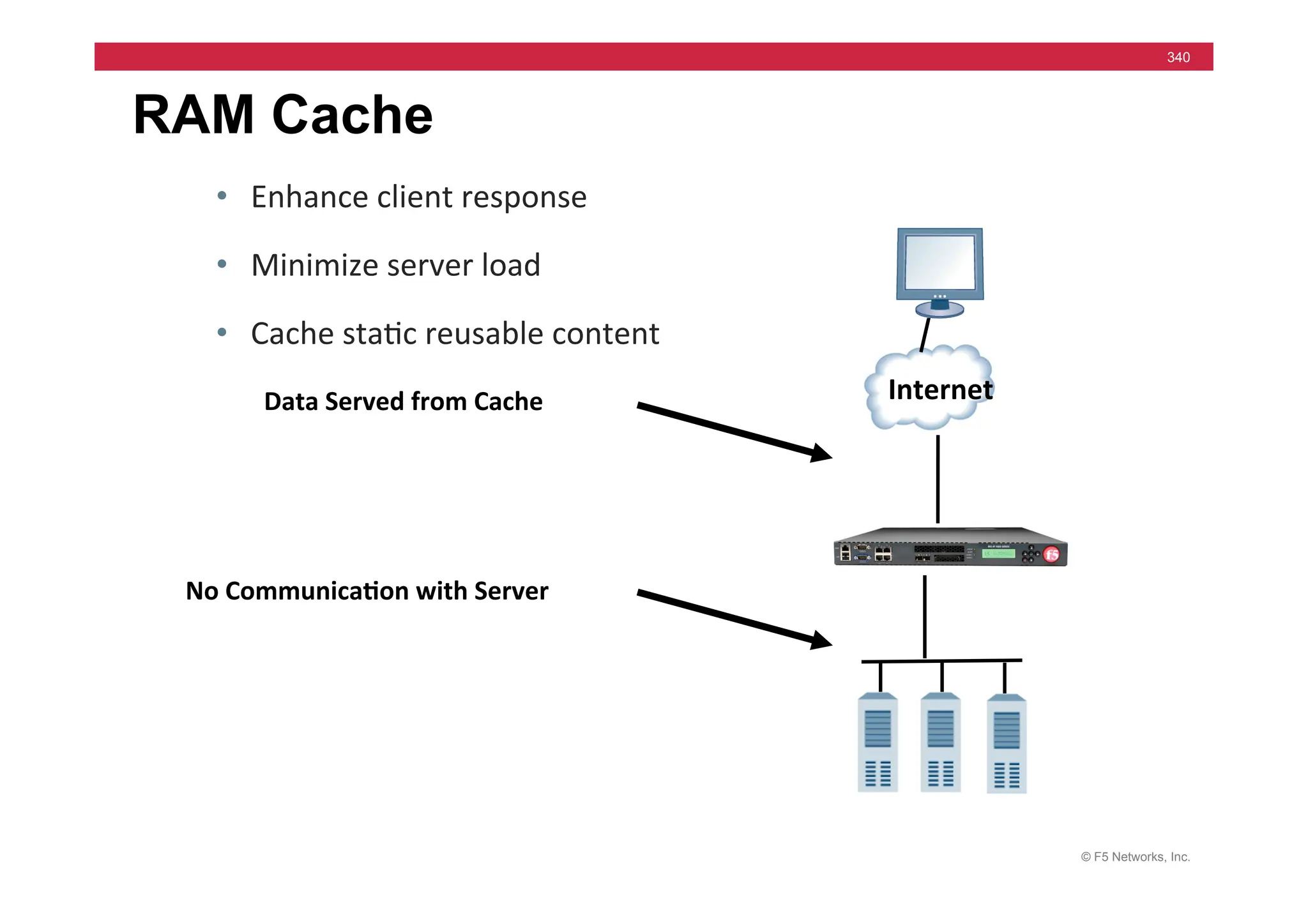
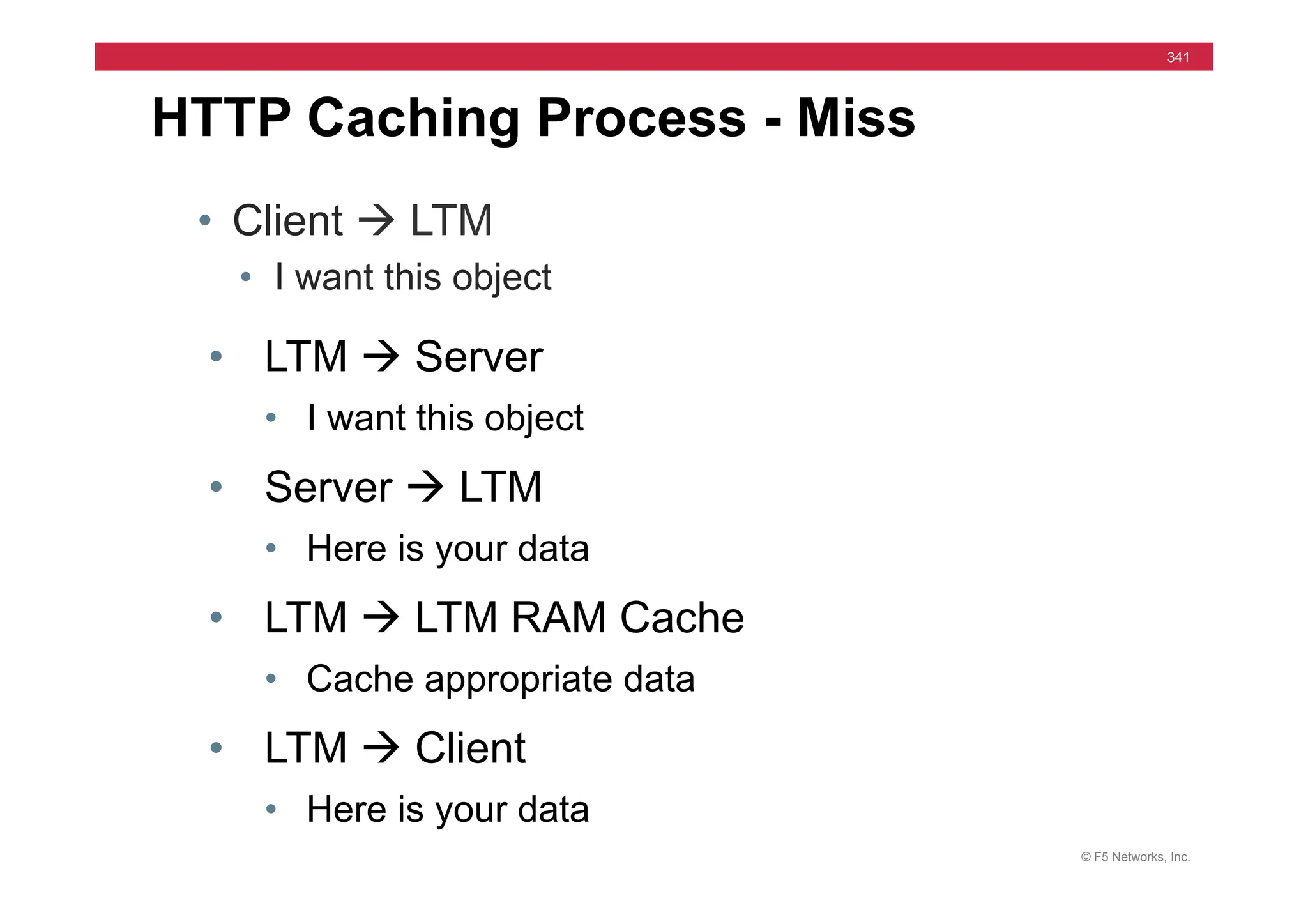
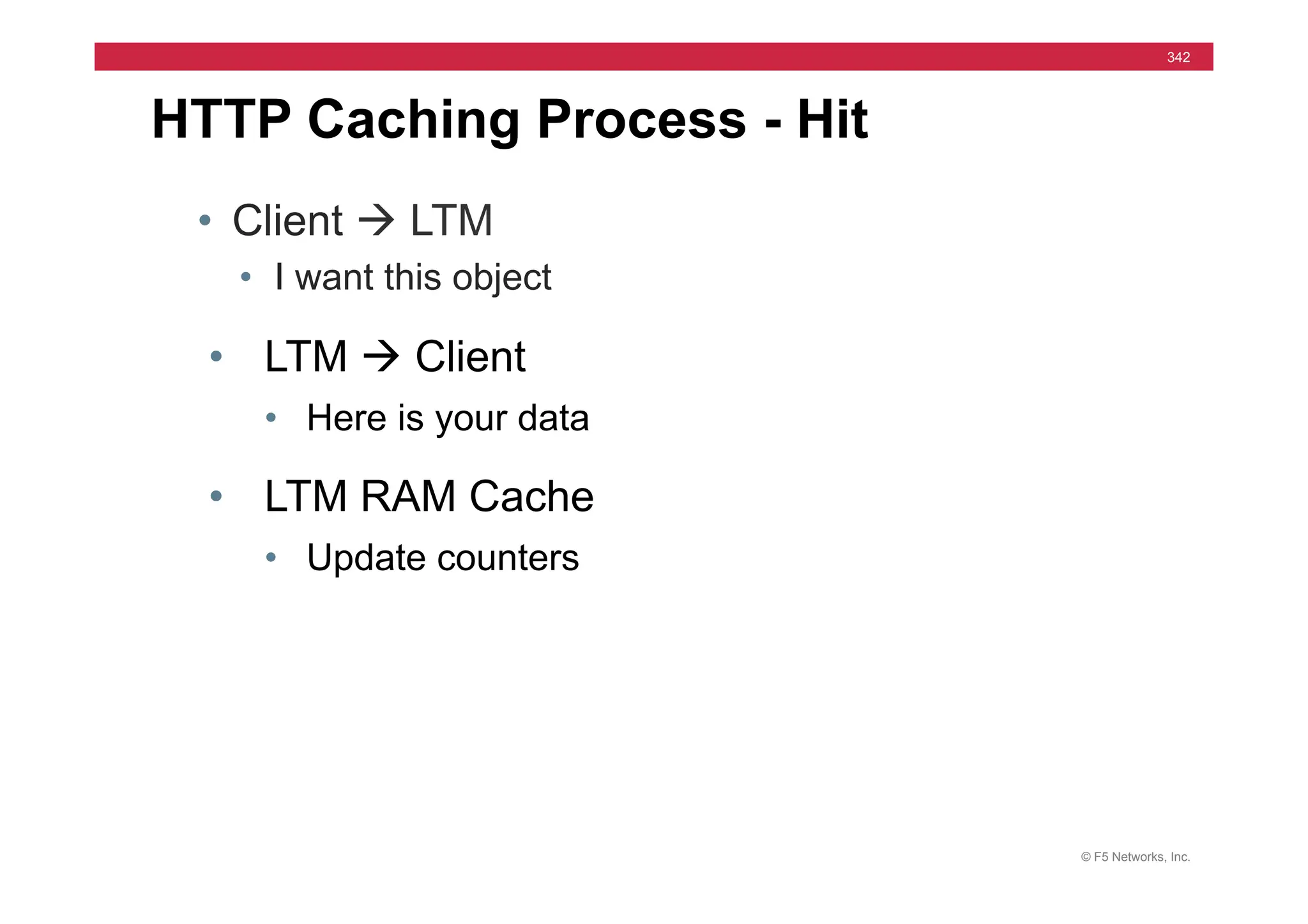
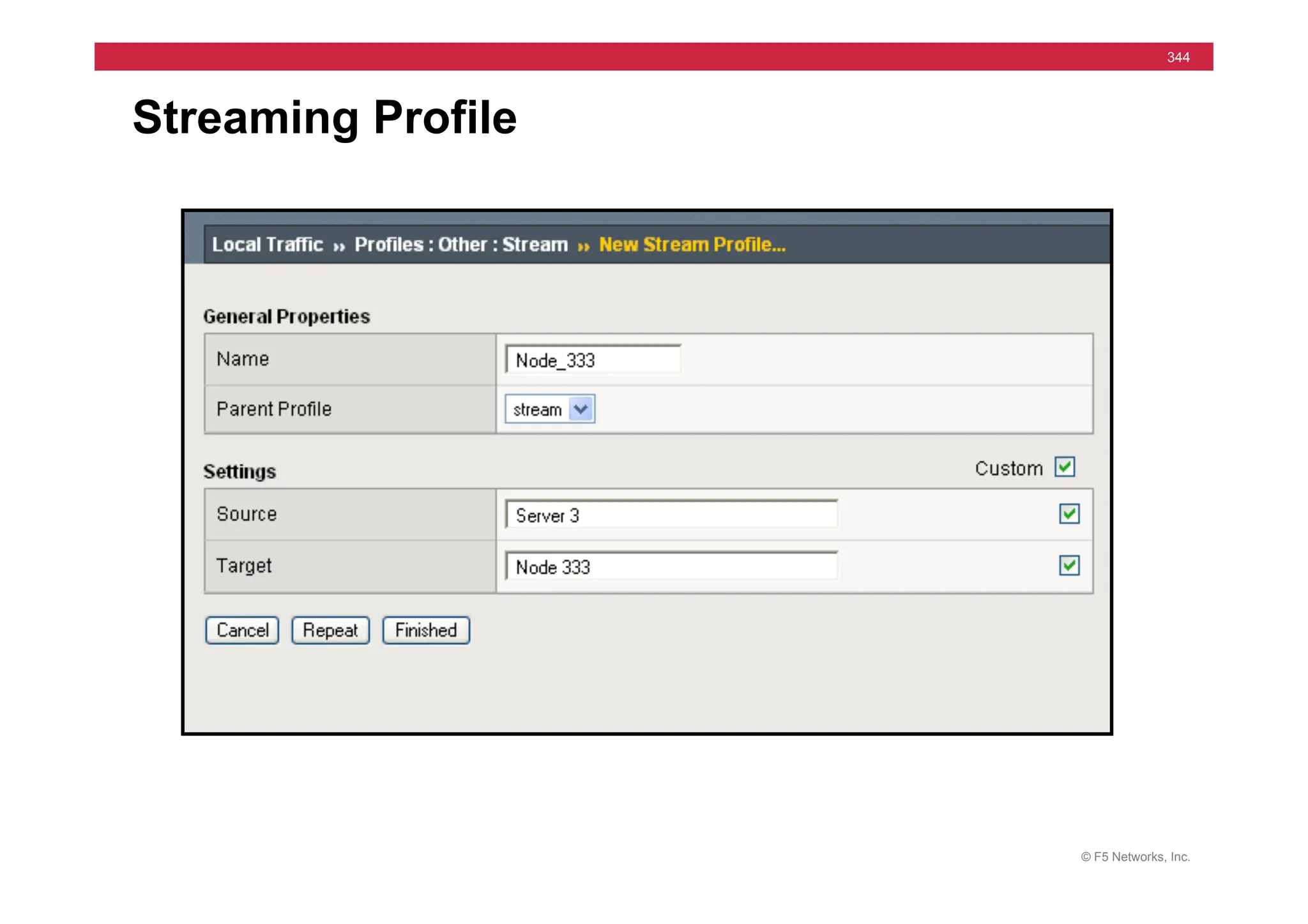
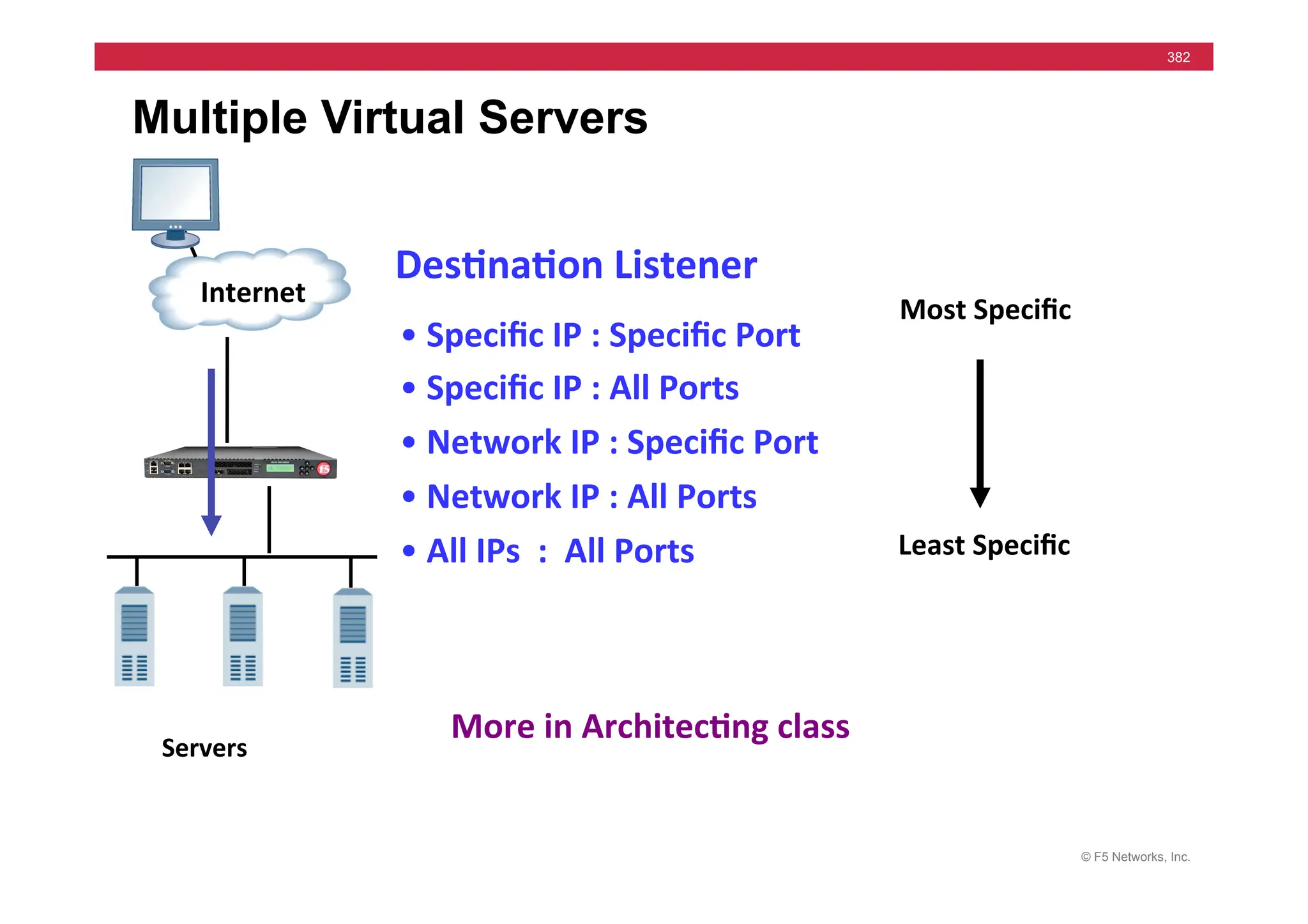
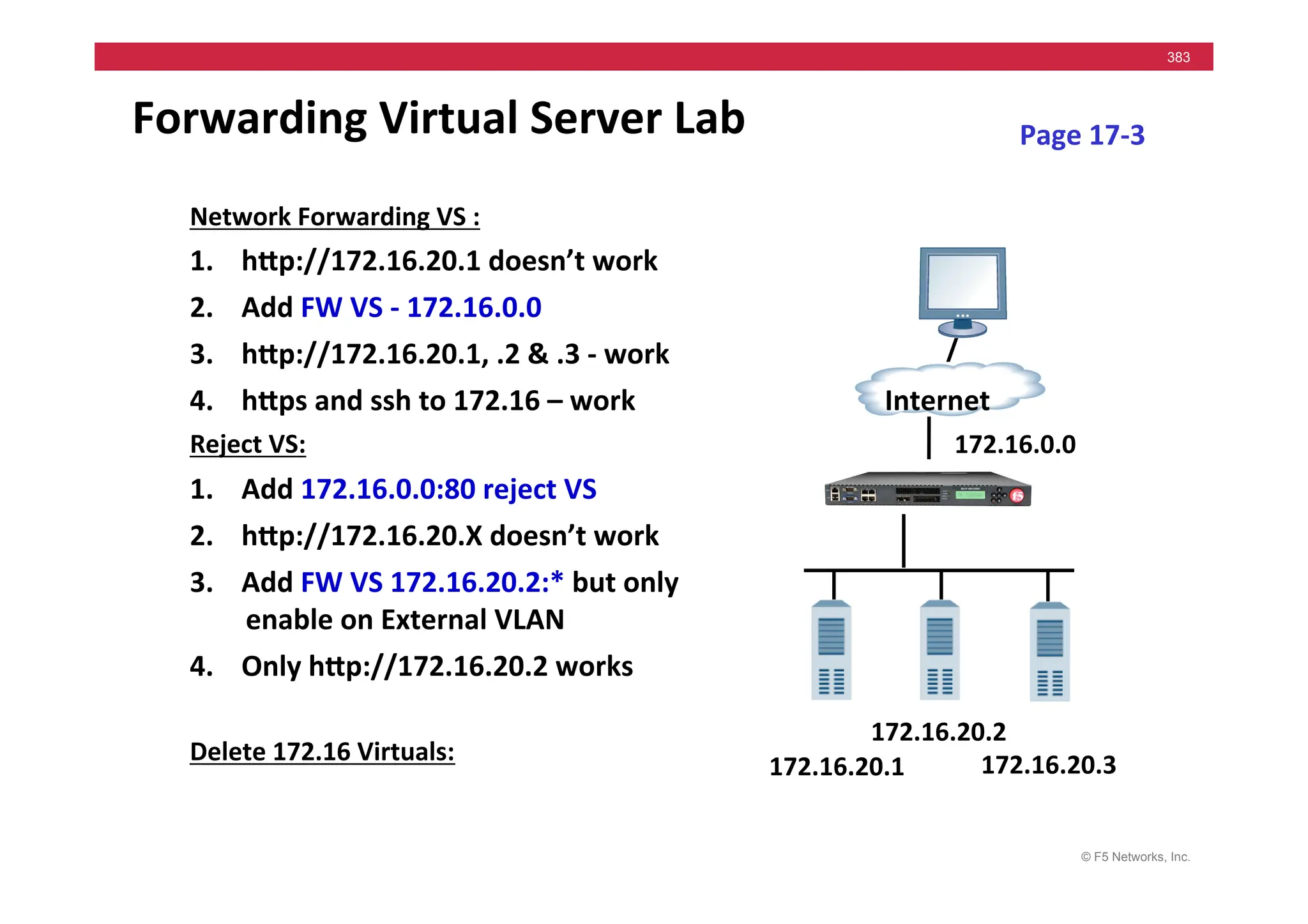
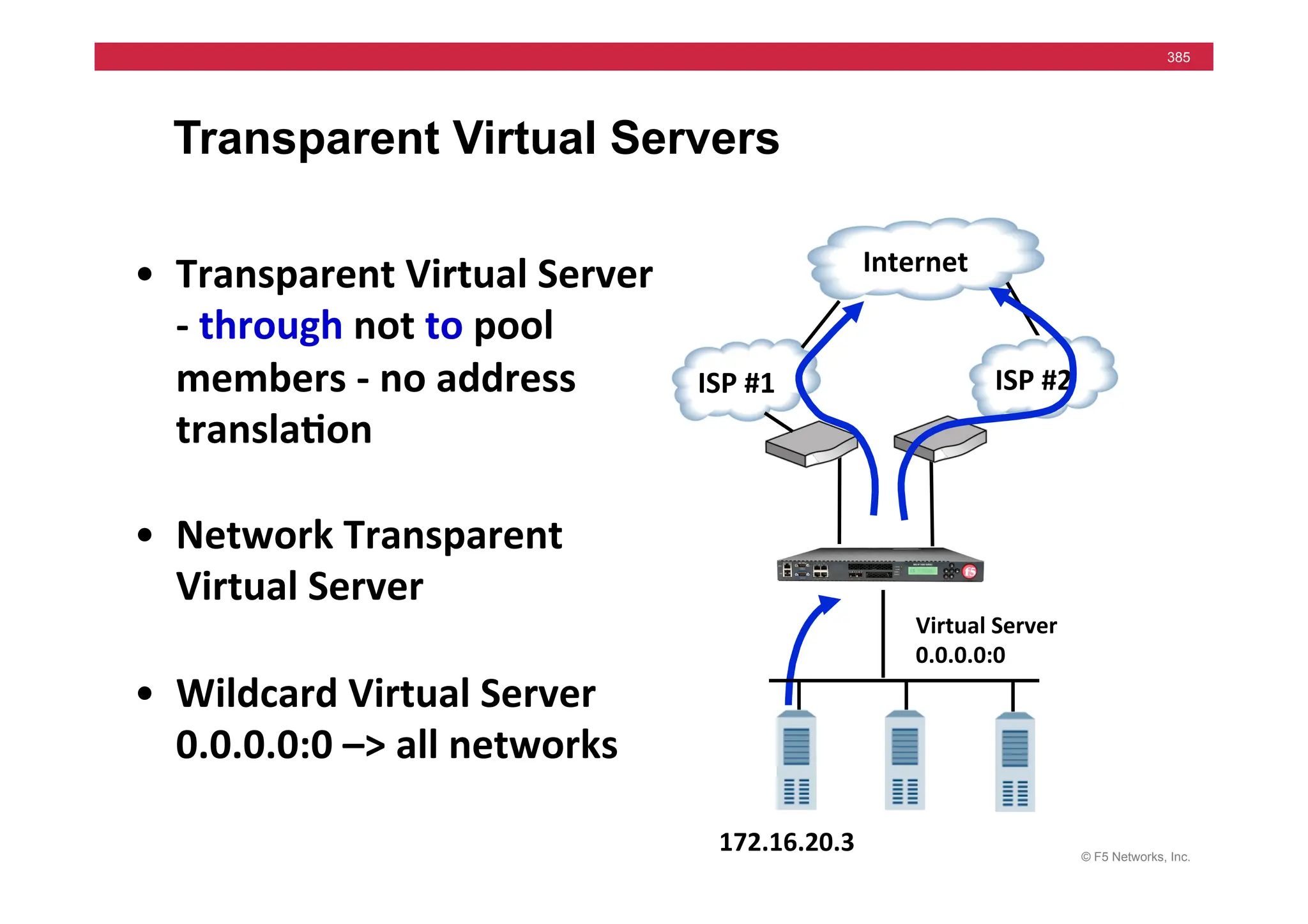
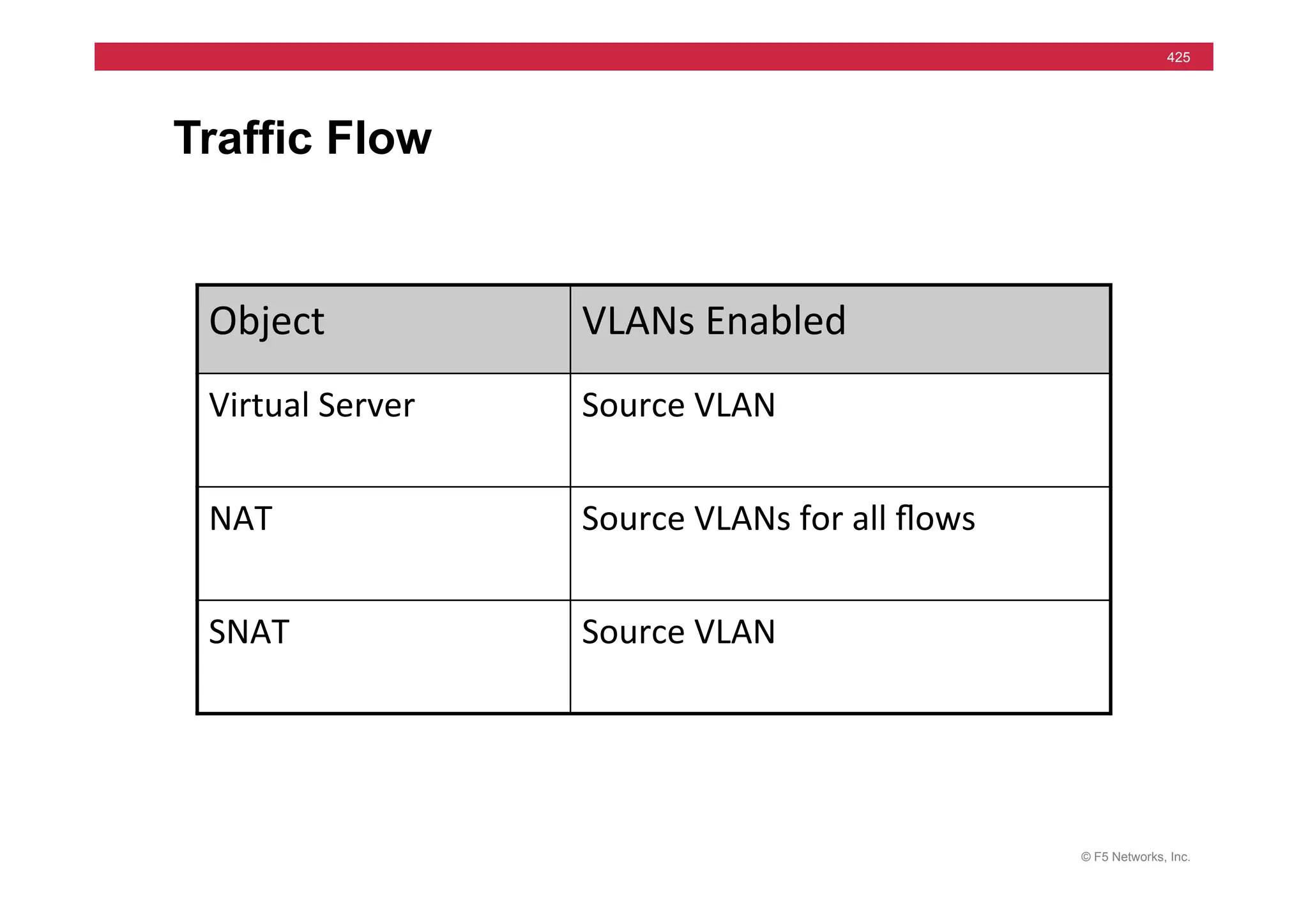
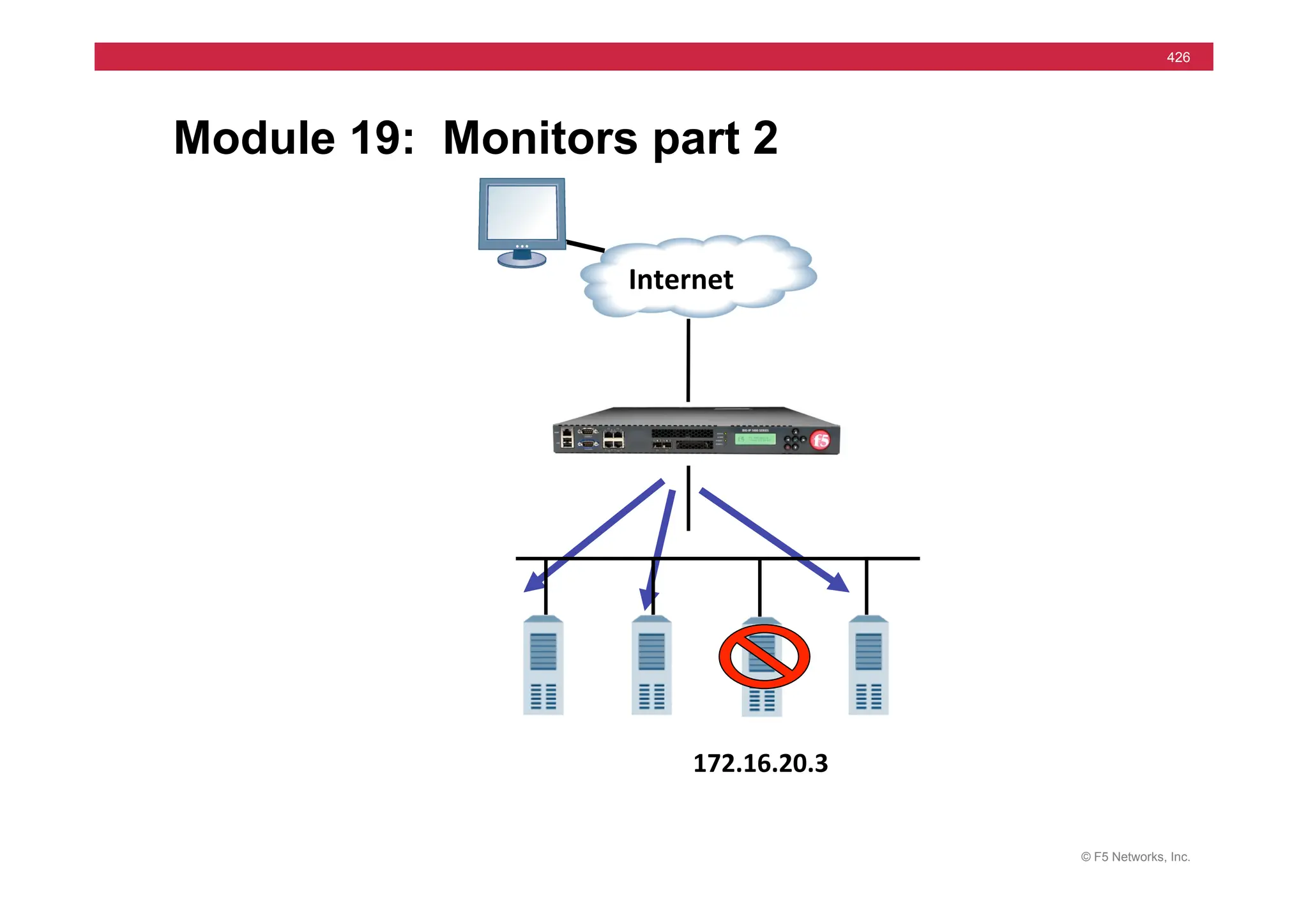
The document provides a detailed overview of configuring F5's BIG-IP Local Traffic Manager (LTM) and associated products, including load balancing, security features, and hardware specifications. It includes information about various modules, installation procedures, and features of the BIG-IP product family, as well as practical labs and administrative tasks. Additionally, it outlines technical support resources and a course structure for training on the system.
















![© F5 Networks, Inc.
191
Module 9 - iRules
Internet
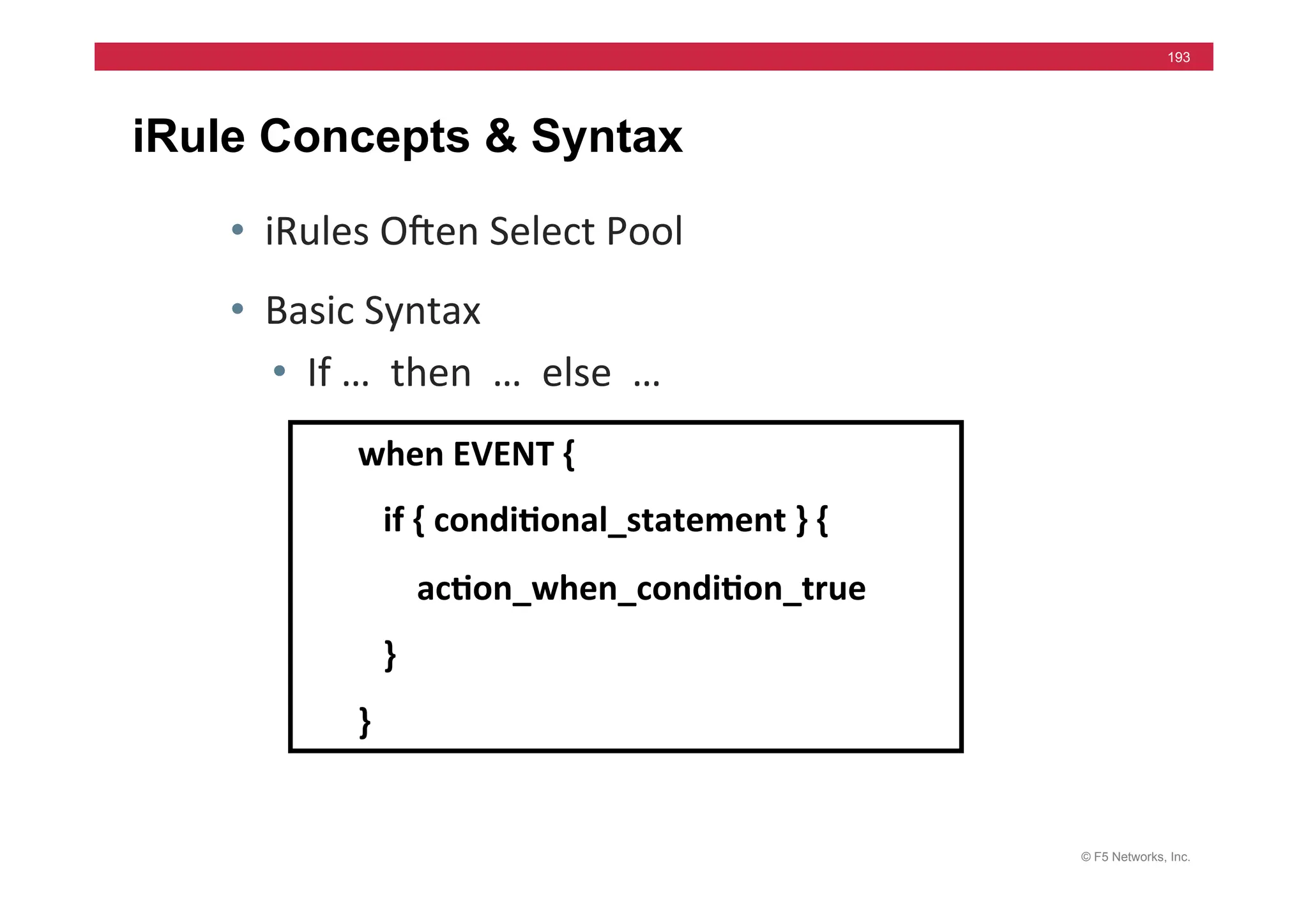
when
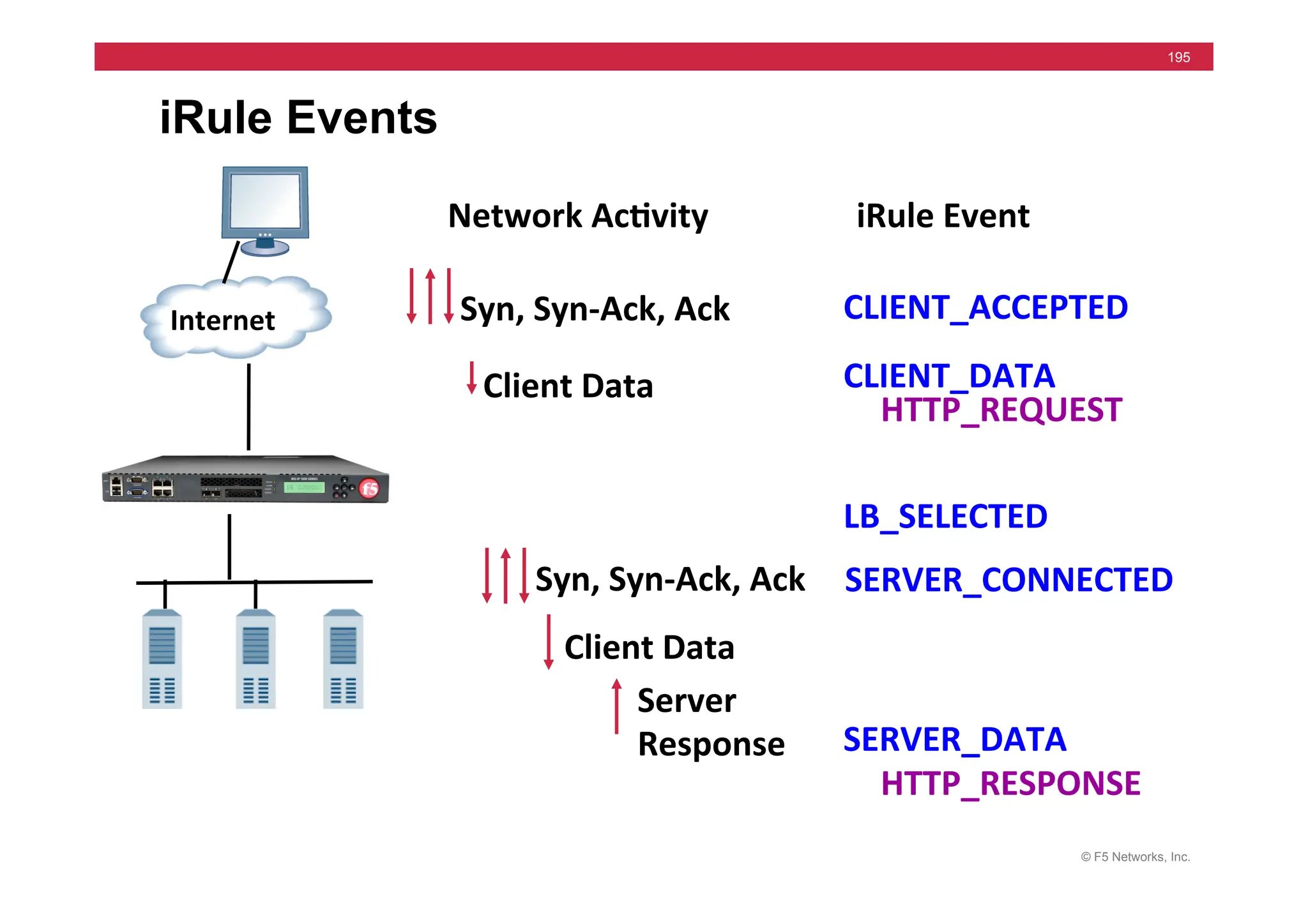
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
if
{
[[IP::remote_addr]
starts_with
“10.”
]
}
{
pool
ten_pool
}
else
{
pool
customer_pool
}
}
ten_pool
customer_pool](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-191-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
196
HTTP Event Example
Pool selection based on Browser
rule
BrowserType
{
when
HTTP_REQUEST
{
if
{
[[HTTP::header
User-‐Agent]
contains
“MSIE”]
}
{
pool
/Common/IE_pool
}
elseif
{
[[HTTP::header
User-‐Agent]
contains
“Mozilla”]
}
{
pool
/Common/Mz_pool
}
}
}
else { /Common/
Other_browser } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-196-2048.jpg)

![© F5 Networks, Inc.
200
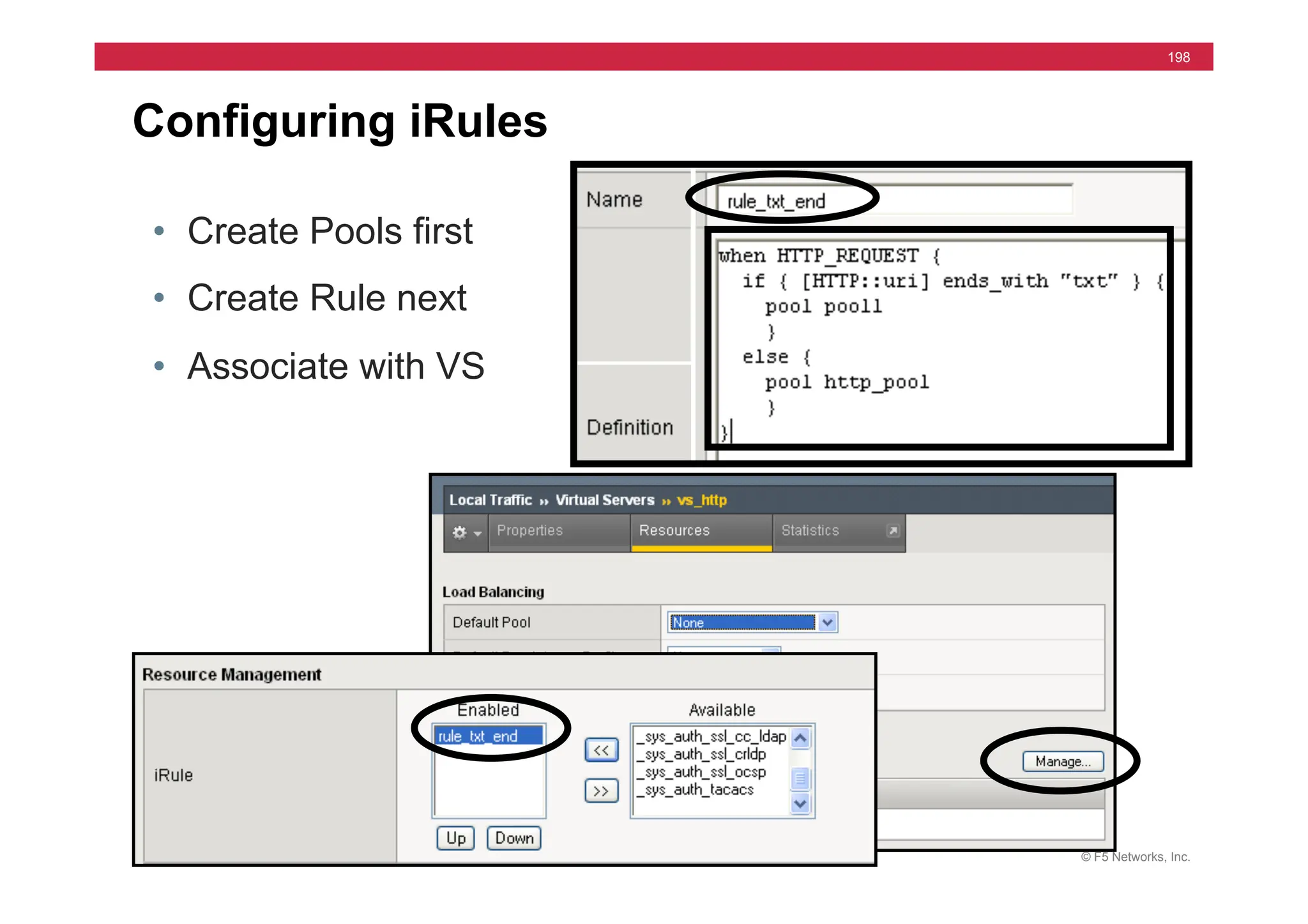
iRules
Labs
Simple
Rule:
1. Pool1,
2,
3
–
only
172.16.20.1,2,3:*
2. rule
–
rule_txt_ends
3.
VS
10.10.X.102:80
-‐>
rule
4. pool3
default,
then
else
leg
Rule
Lab
#2:
1. rule
–
rule_tcp_port
2.
VS
10.10.X.103:*
-‐>
rule
&
pool3
when
HTTP_REQUEST
{
if
{
[HTTP::uri]
ends_with
“txt”}
{
pool
/Common/pool1
}
}
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
if
{
[TCP::local_port]
equals
80}
{
pool
/Common/pool1
}
elseif
{
[TCP::local_port]
equals
443}
{
pool
/Common/pool2
}
}
Pages
9-‐6
!
9-‐10
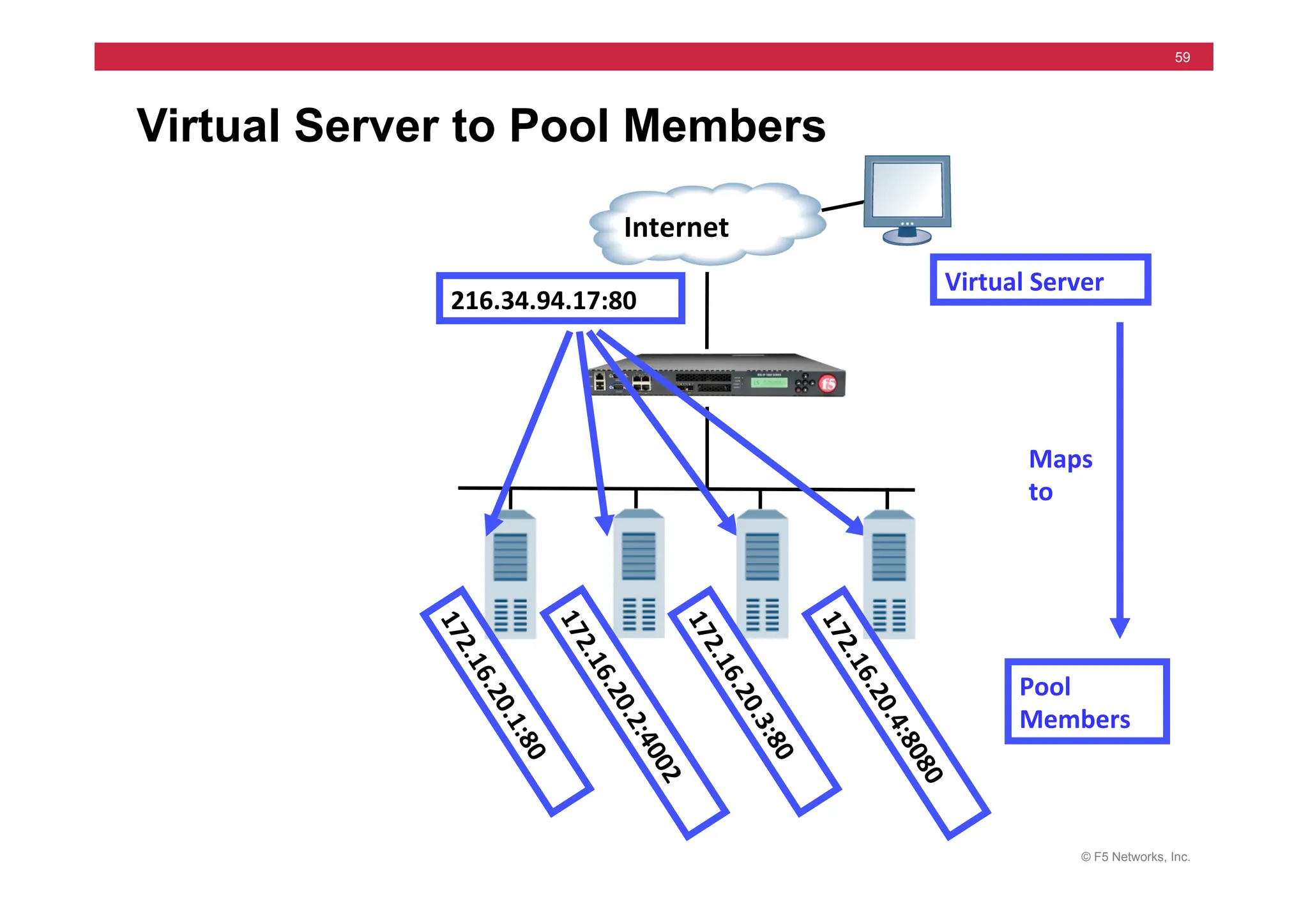
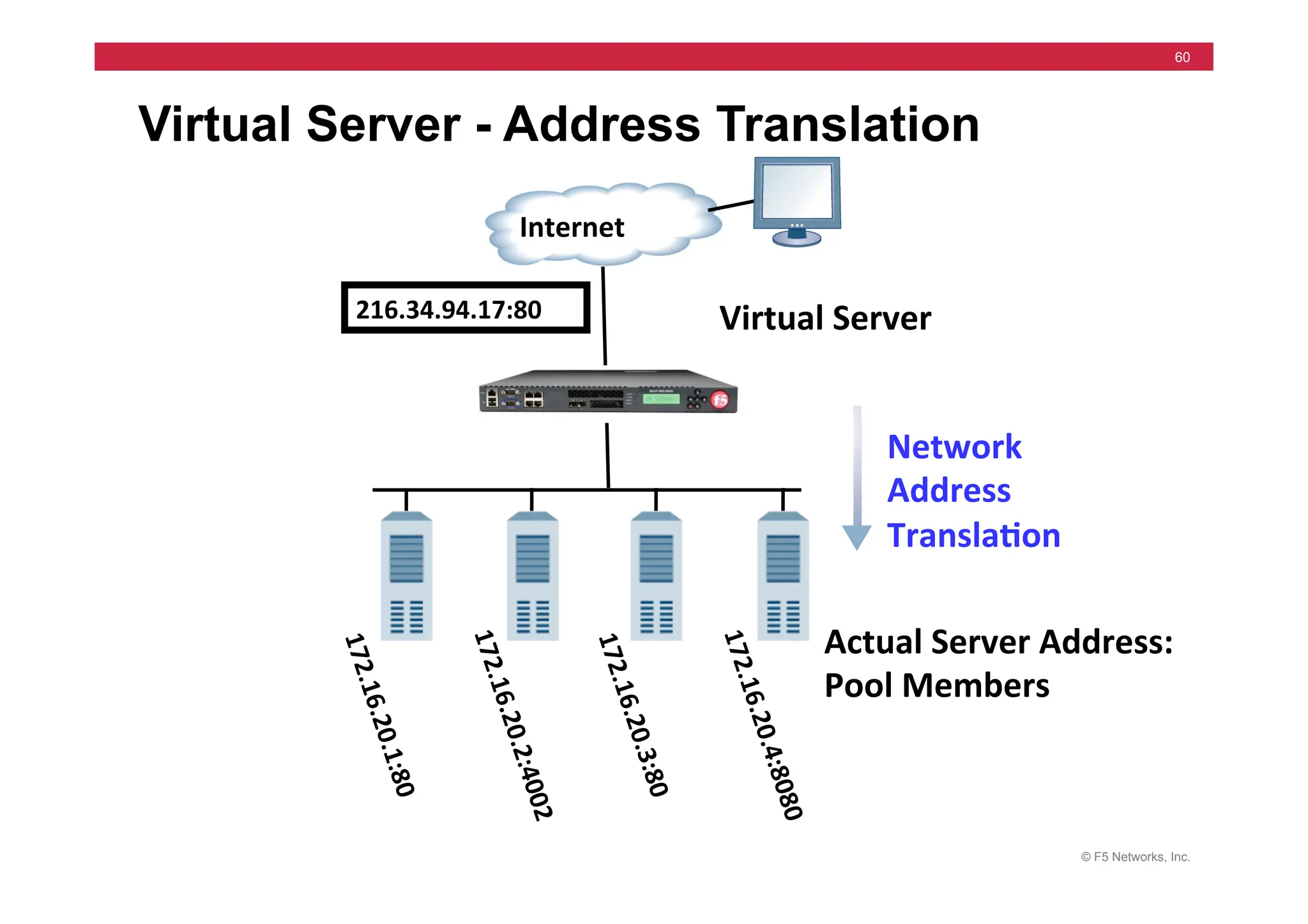
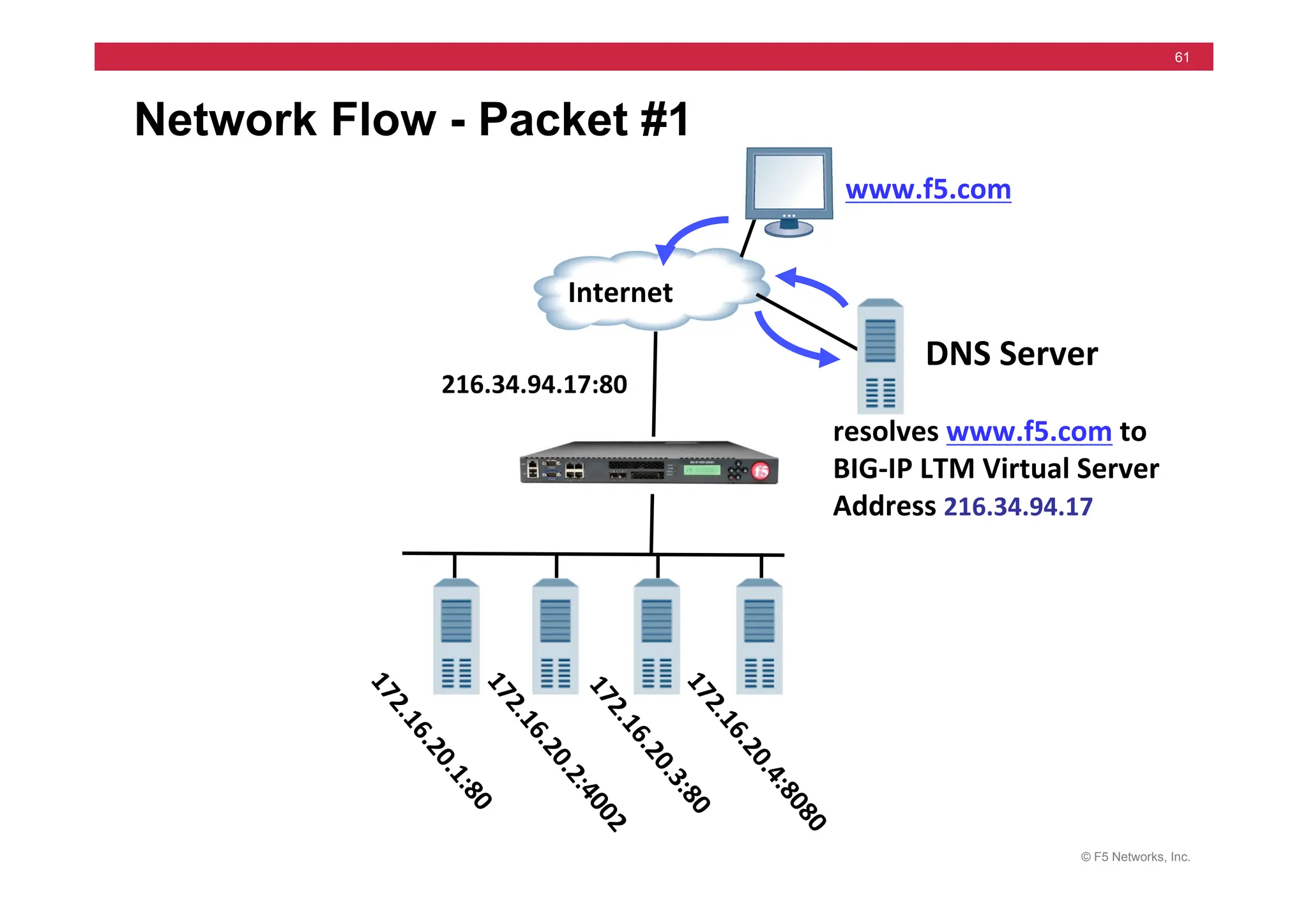
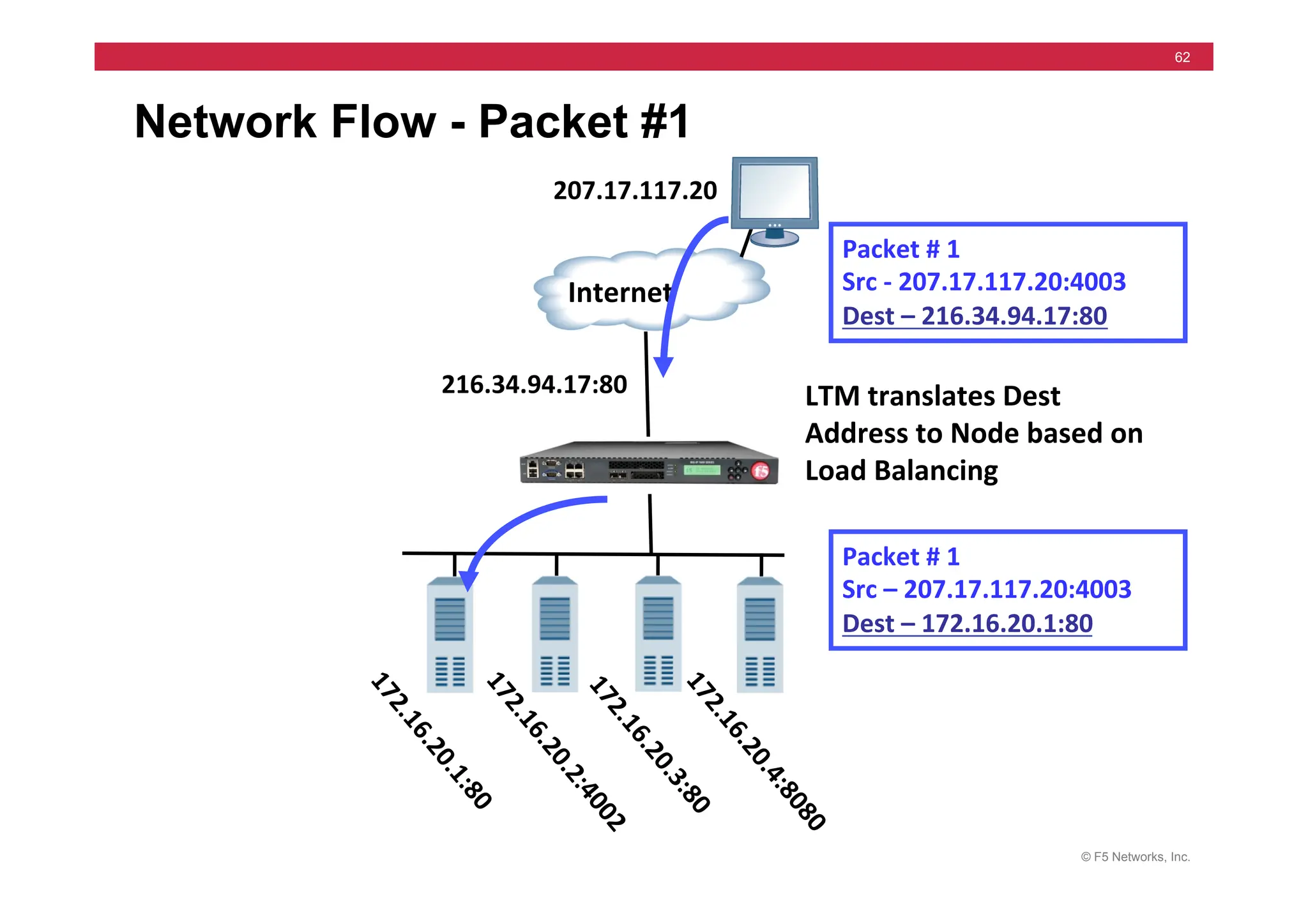
172.16.20.1
Internet
172.16.20.3
172.16.20.2
10.10.X.100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-200-2048.jpg)








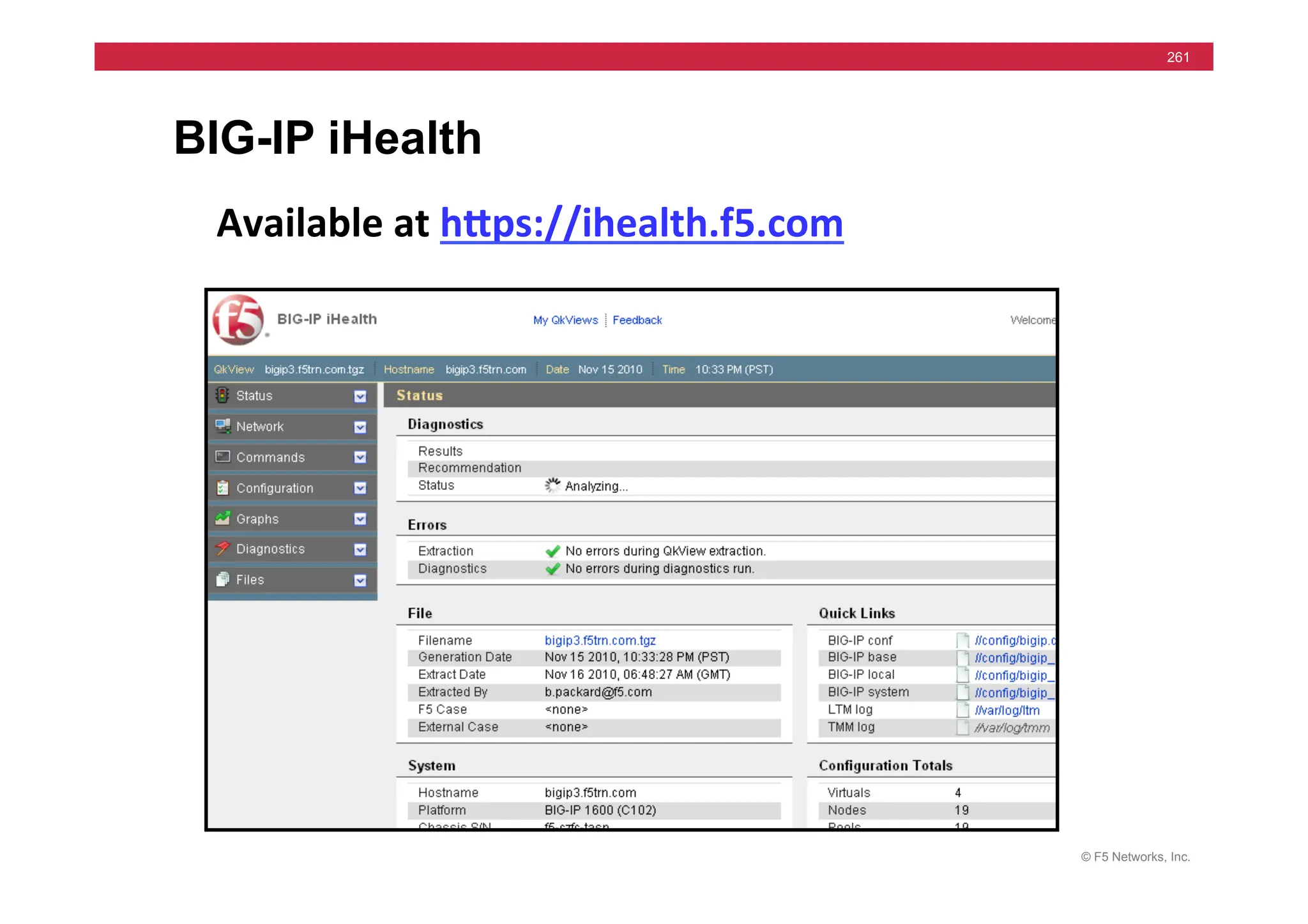

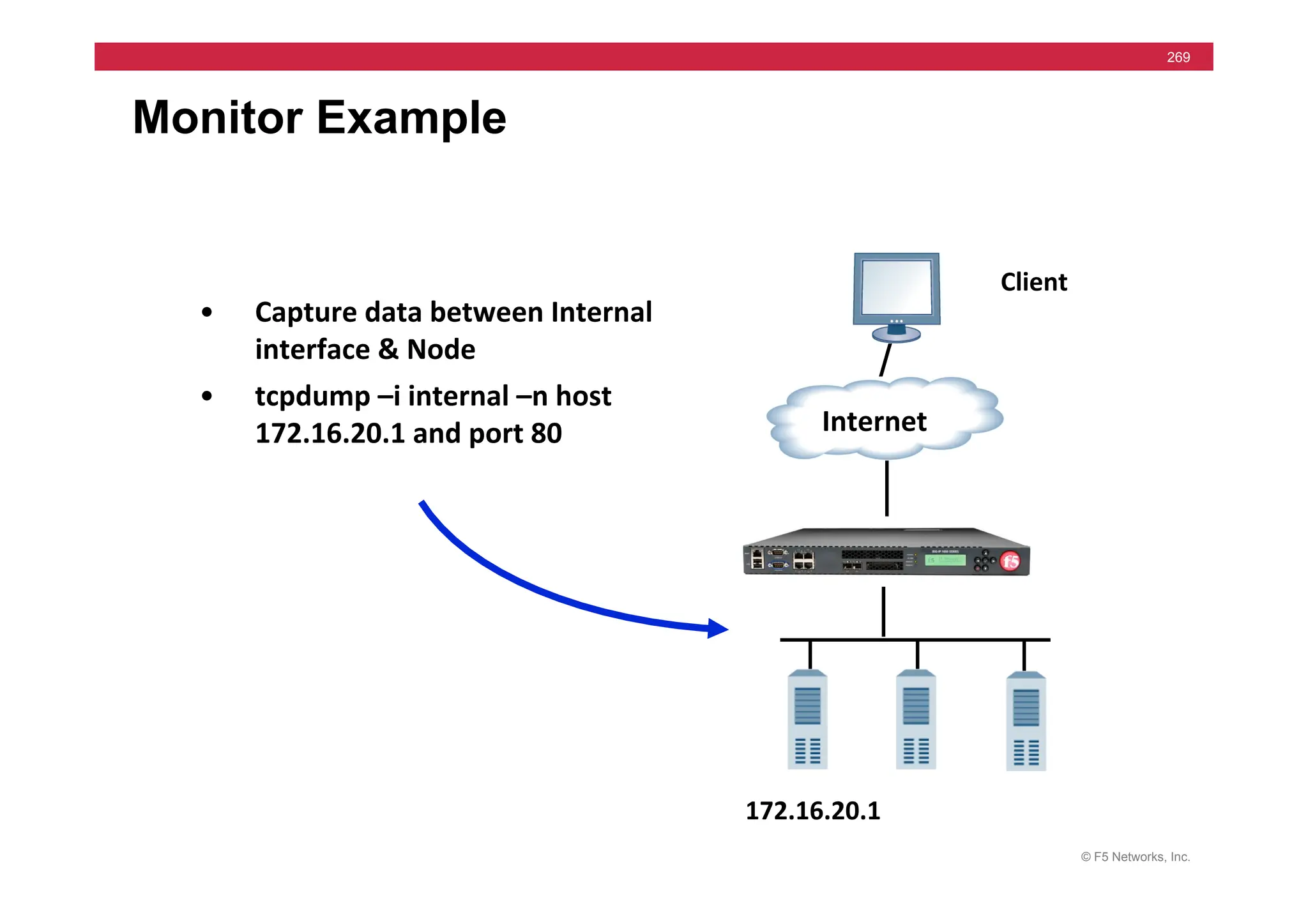
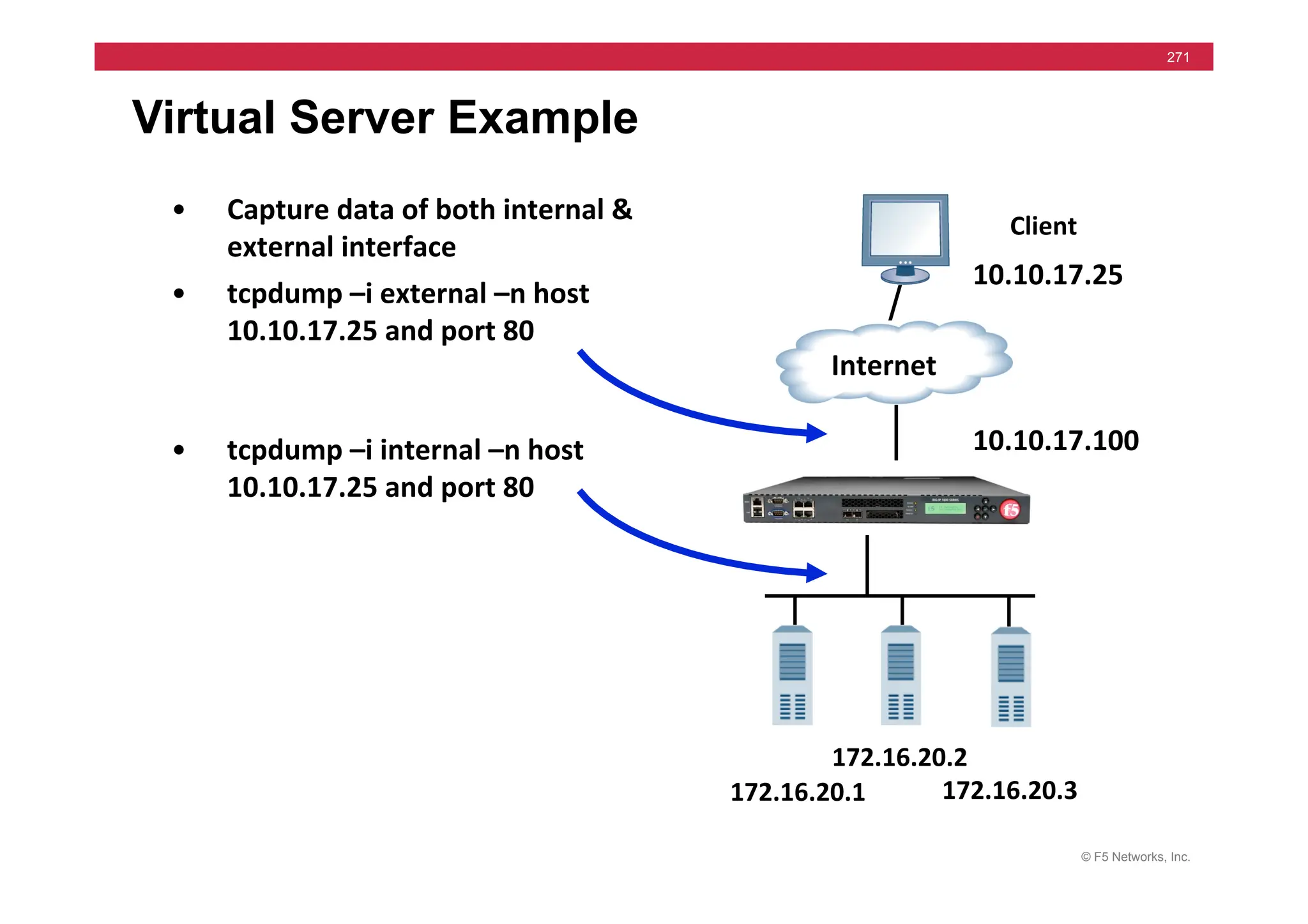
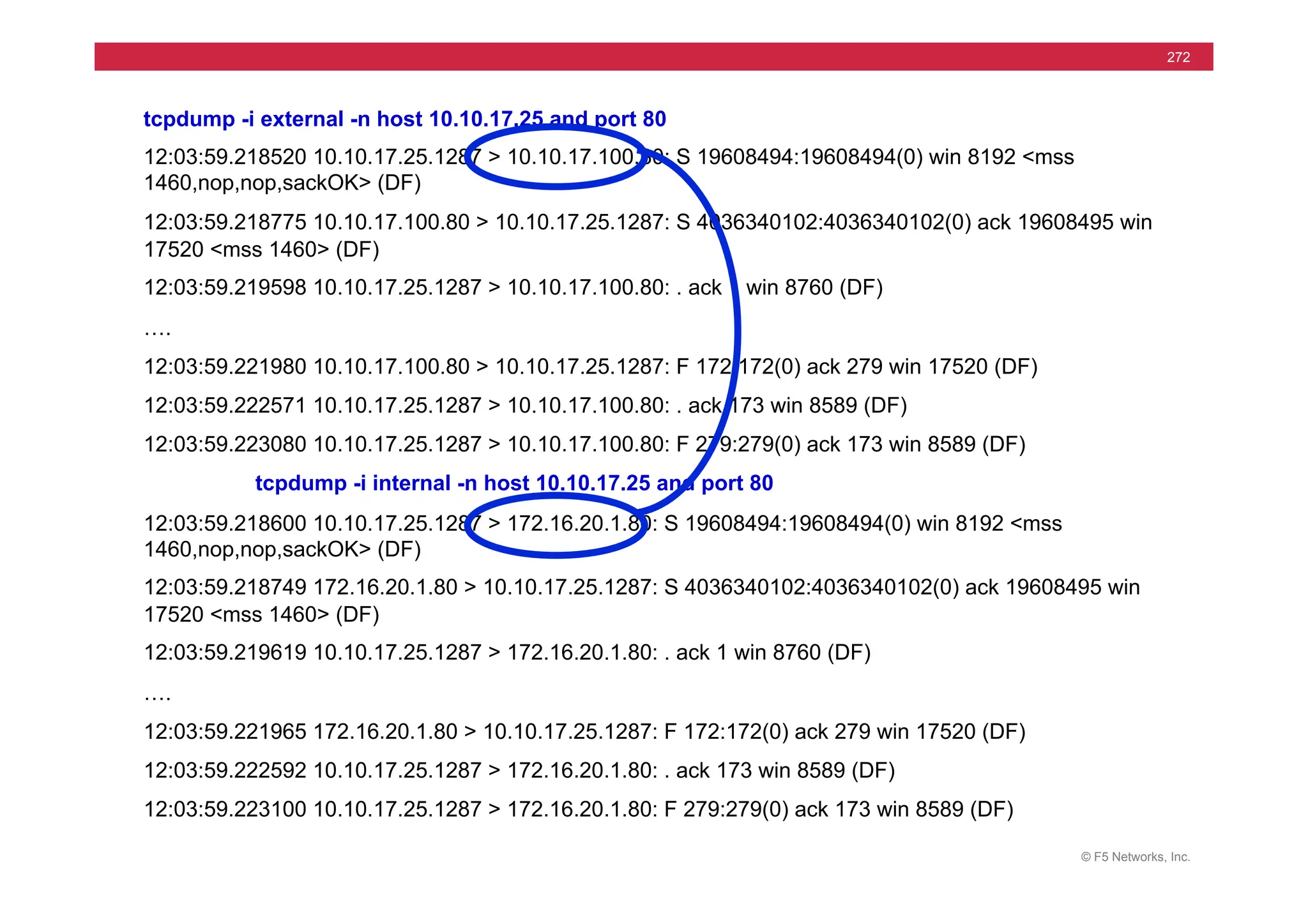
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
270
tcpdump -i internal -n host 172.16.20.1 and port 80
09:50:32.811118 172.16.17.31.39613 > 172.16.20.1.80: S 444272268:444272268(0) win
16384 <mss 1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp[|tcp]> (DF)
09:50:32.811383 172.16.20.1.80 > 172.16.17.31.39613: S 1938541816:1938541816(0) ack
444272269 win 17520 <mss 1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp[|tcp]> (DF)
09:50:32.811430 172.16.17.31.39613 > 172.16.20.1.80: . ack 1 win 17520
<nop,nop,timestamp 1162263 3552379> (DF)
09:50:32.811759 172.16.17.31.39613 > 172.16.20.1.80: P 1:8(7) ack 1 win 17520
<nop,nop,timestamp 1162263 3552379> (DF)
09:50:32.844589 172.16.20.1.80 > 172.16.17.31.39613: . 1:1449(1448) ack 8 win 17520
<nop,nop,timestamp 3552379 1162263> (DF)
09:50:32.844714 172.16.17.31.39613 > 172.16.20.1.80: . ack 1449 win 16072
<nop,nop,timestamp 1162263 3552379> (DF)
09:50:32.844851 172.16.17.31.39613 > 172.16.20.1.80: F 8:8(0) ack 1449 win 16072
<nop,nop,timestamp 1162263 3552379> (DF)
09:50:32.845692 172.16.20.1.80 > 172.16.17.31.39613: . 1449:2897(1448) ack 8 win 17520
<nop,nop,timestamp 3552379 1162263> (DF)
09:50:37.757819 172.16.17.31.39621 > 172.16.20.1.80: S 454708950:454708950(0) win
16384 <mss 1460,nop,wscale 0,nop,nop,timestamp[|tcp]> (DF)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-270-2048.jpg)

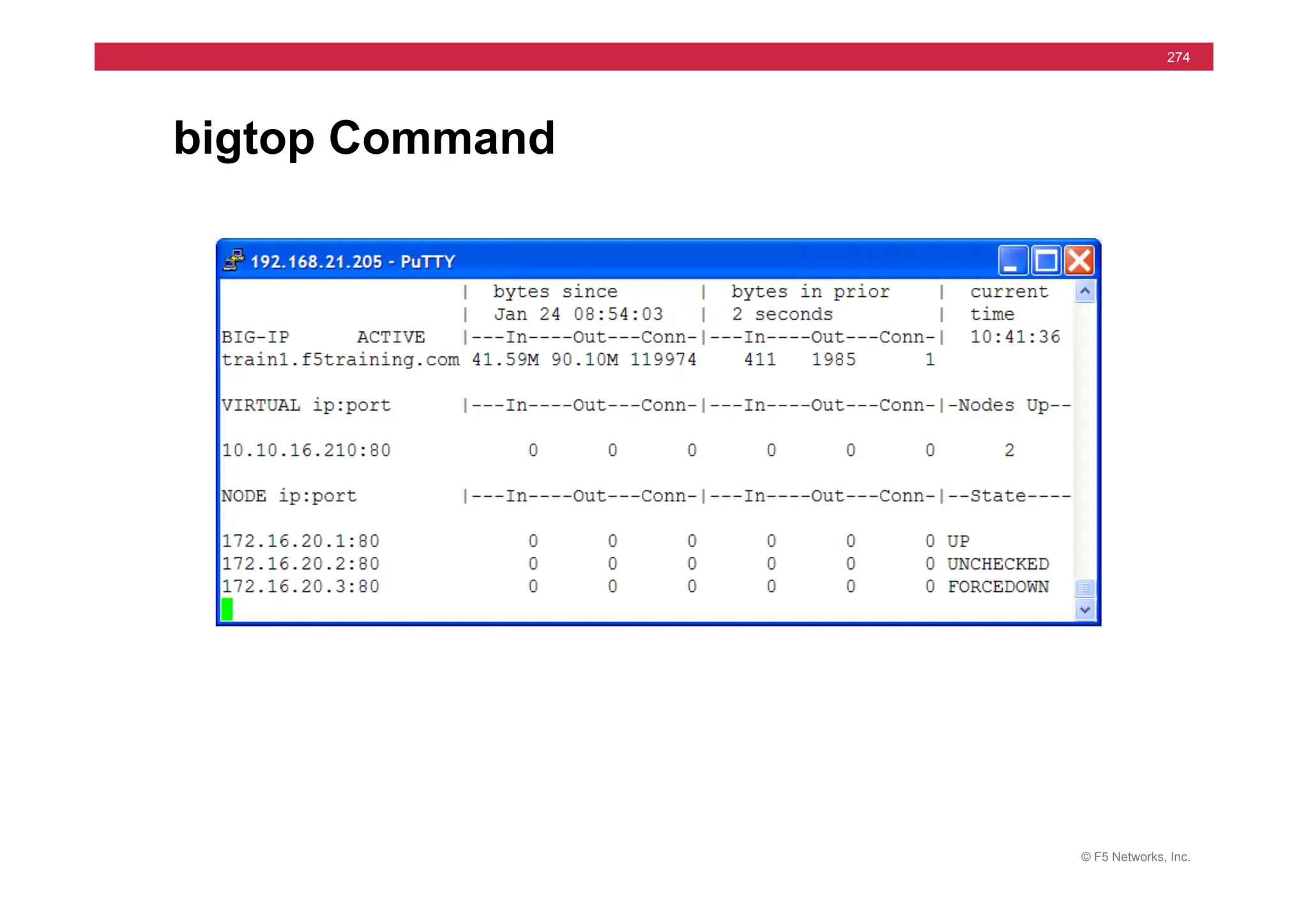

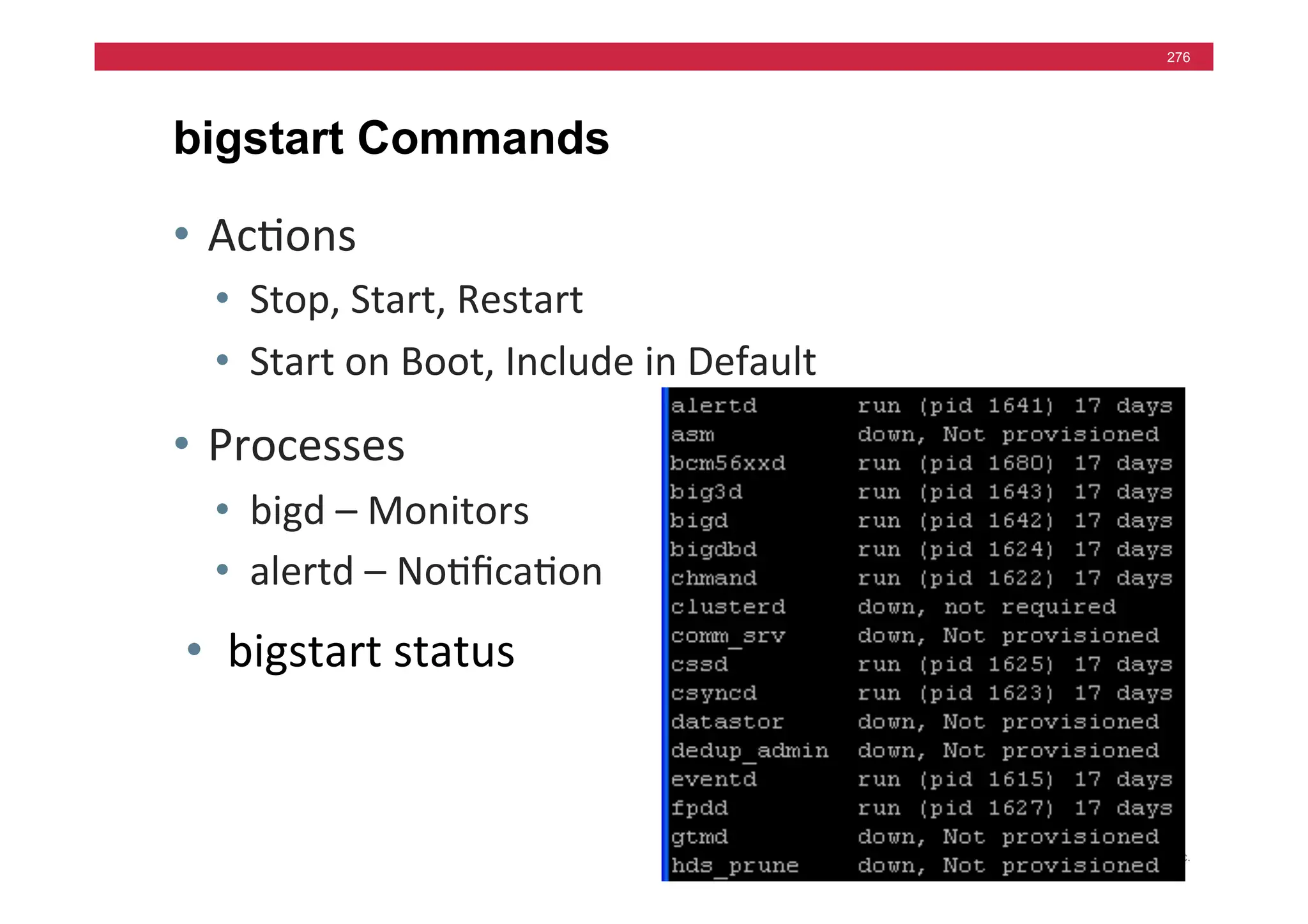
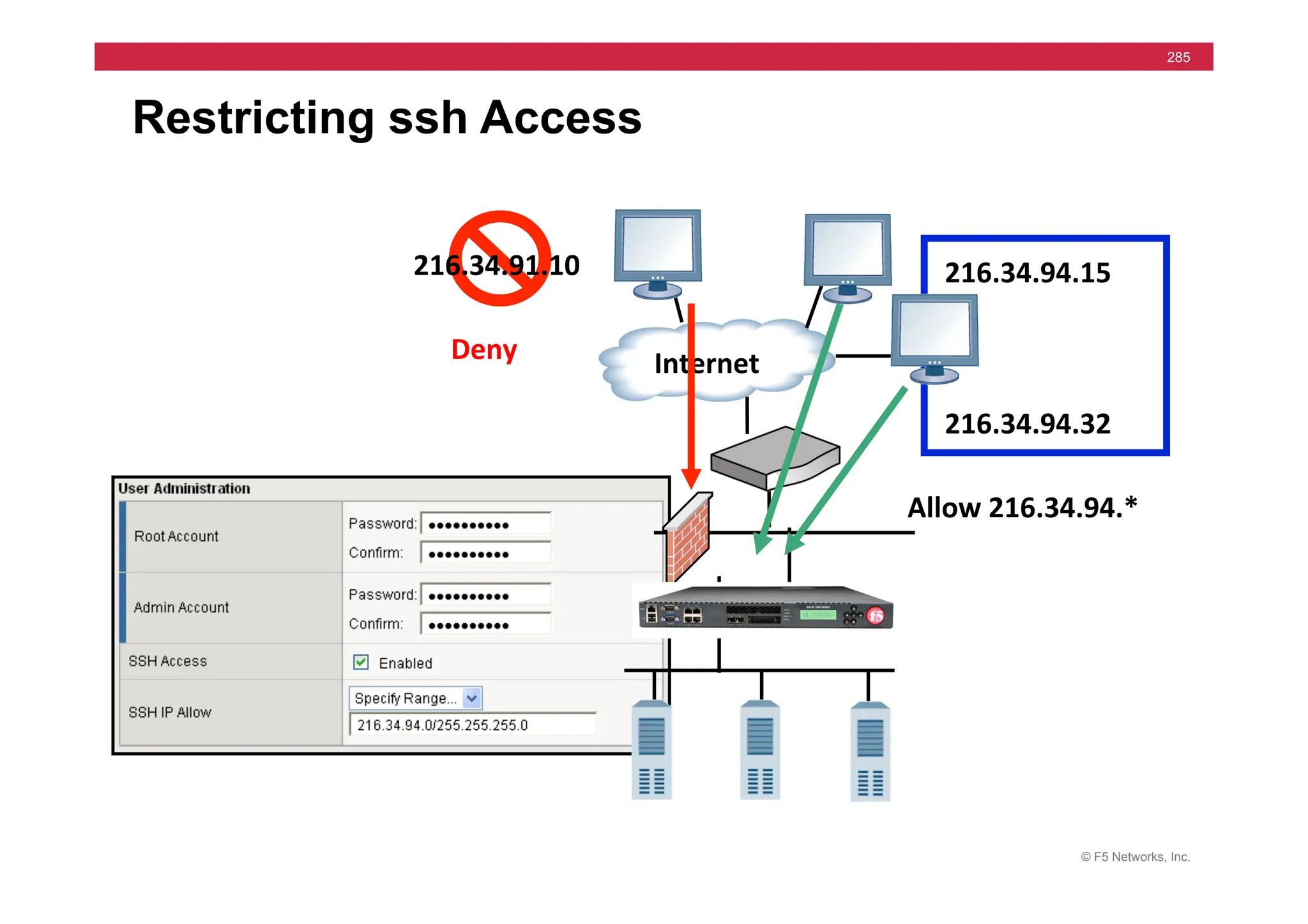
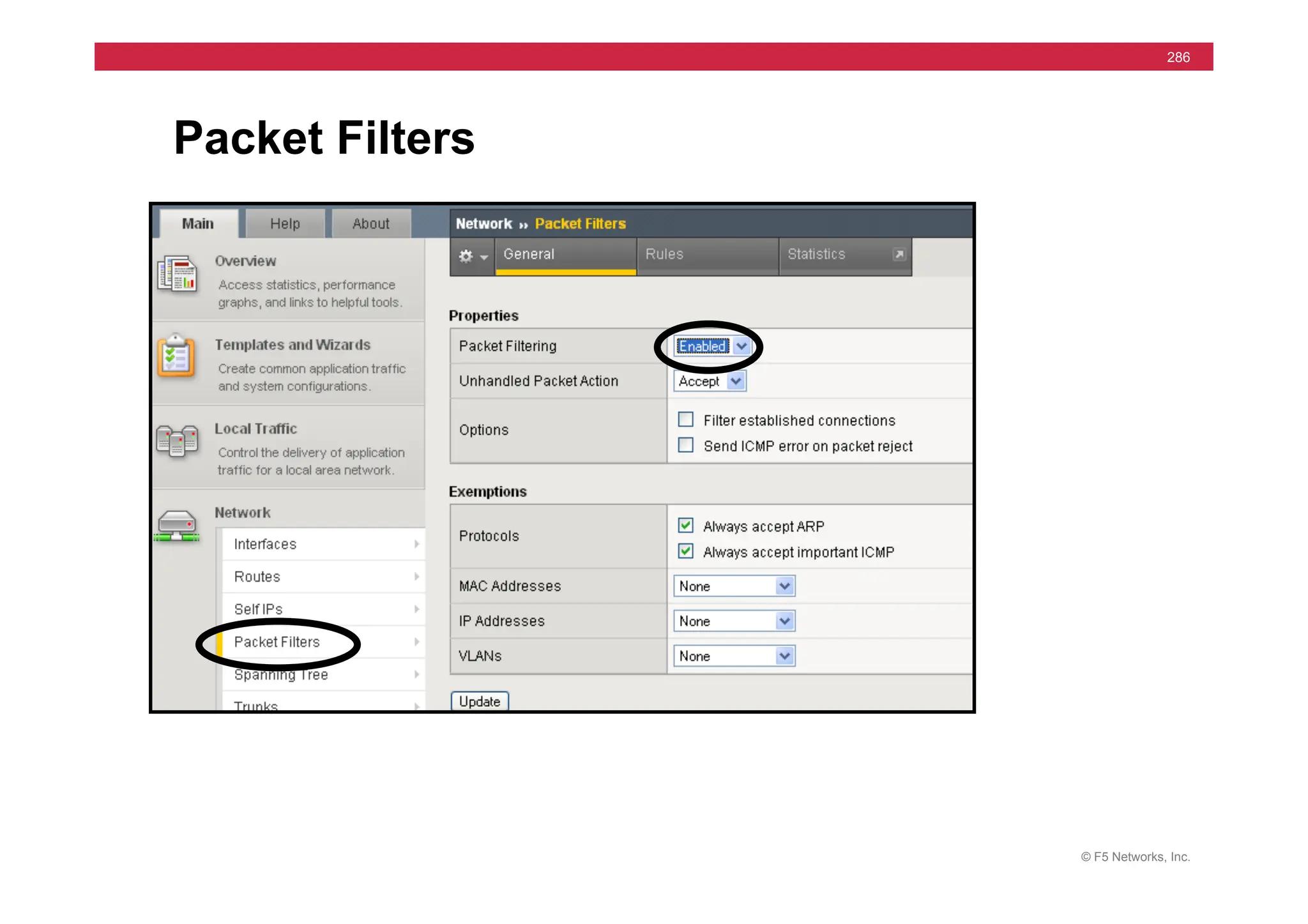
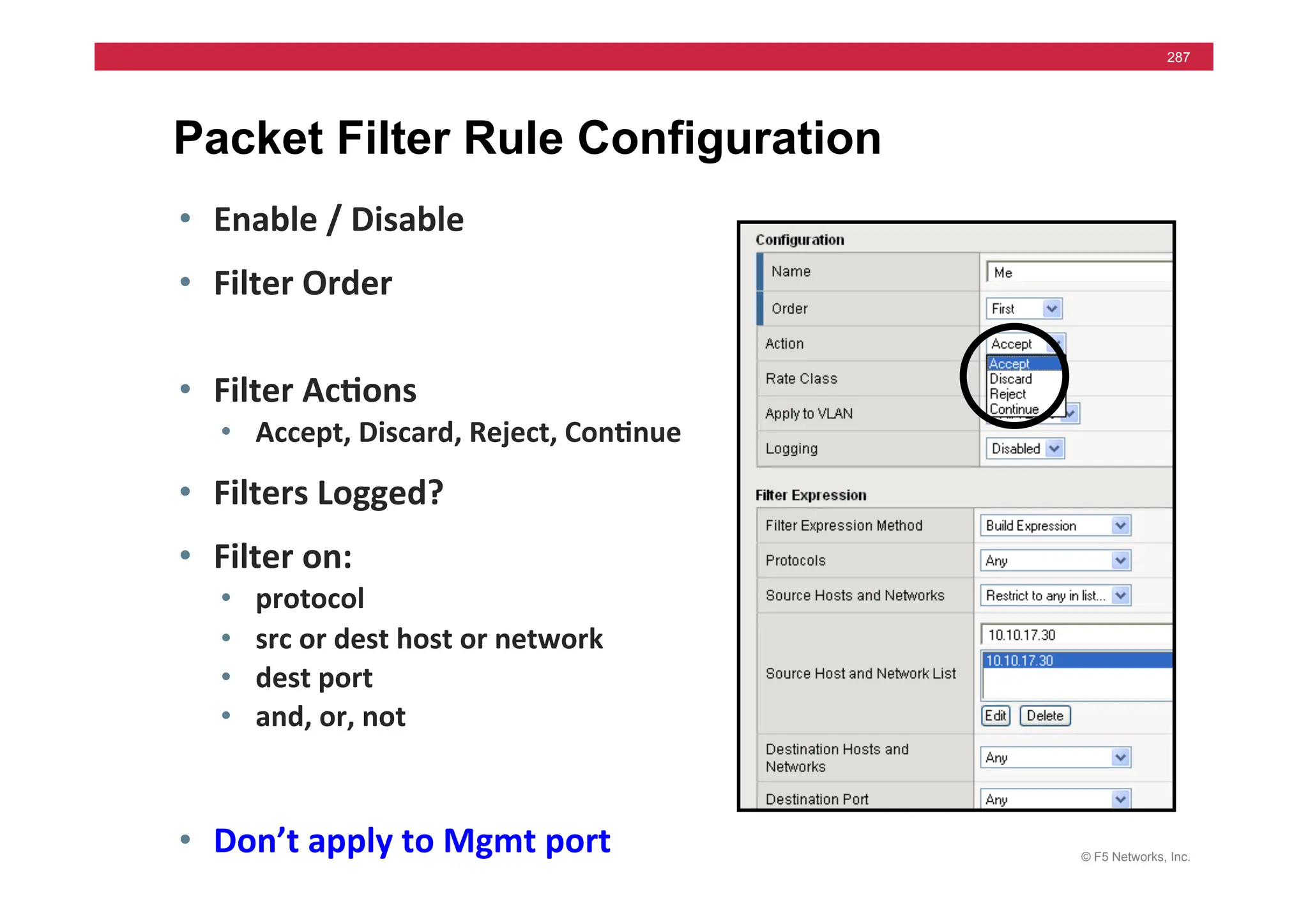
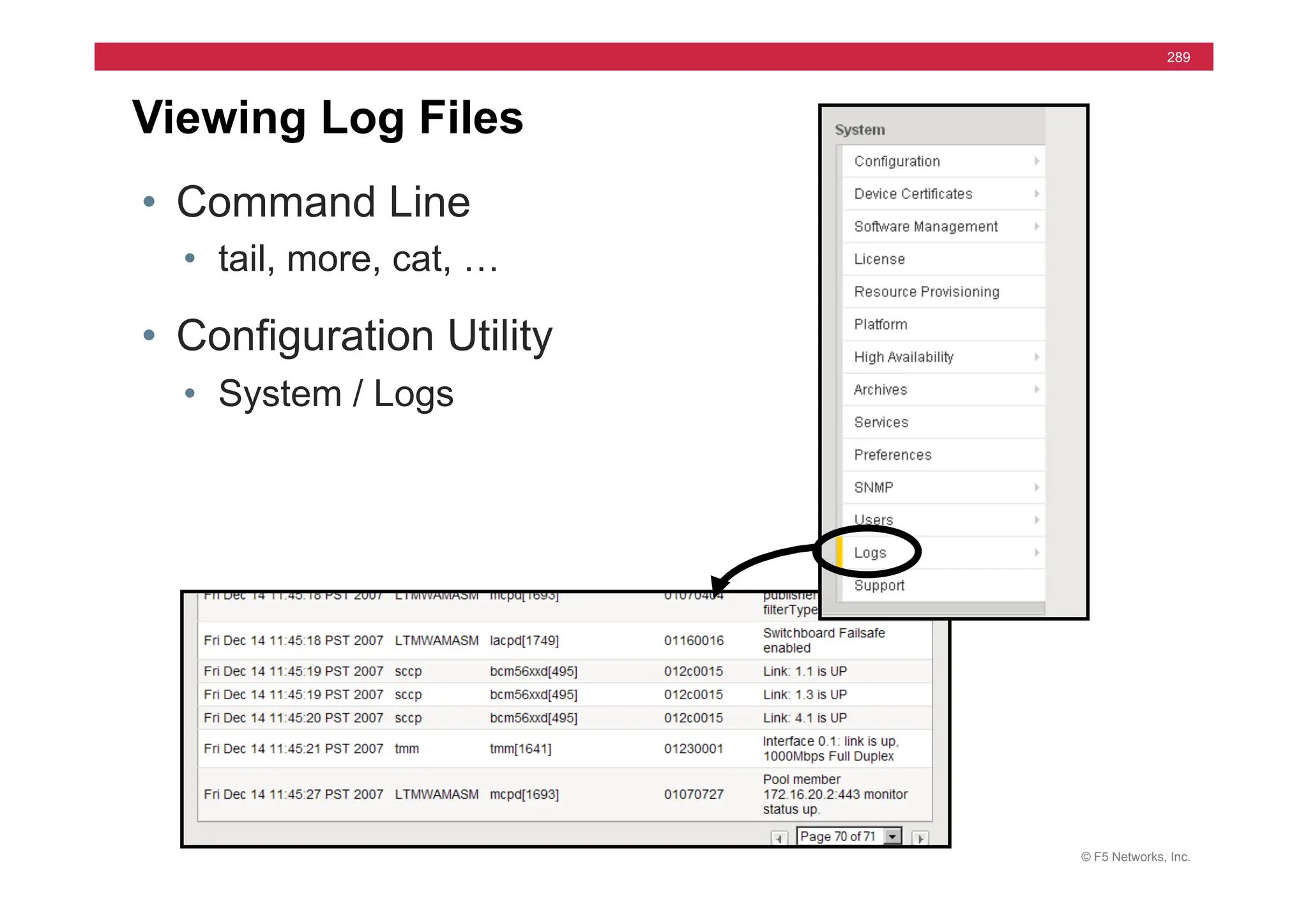
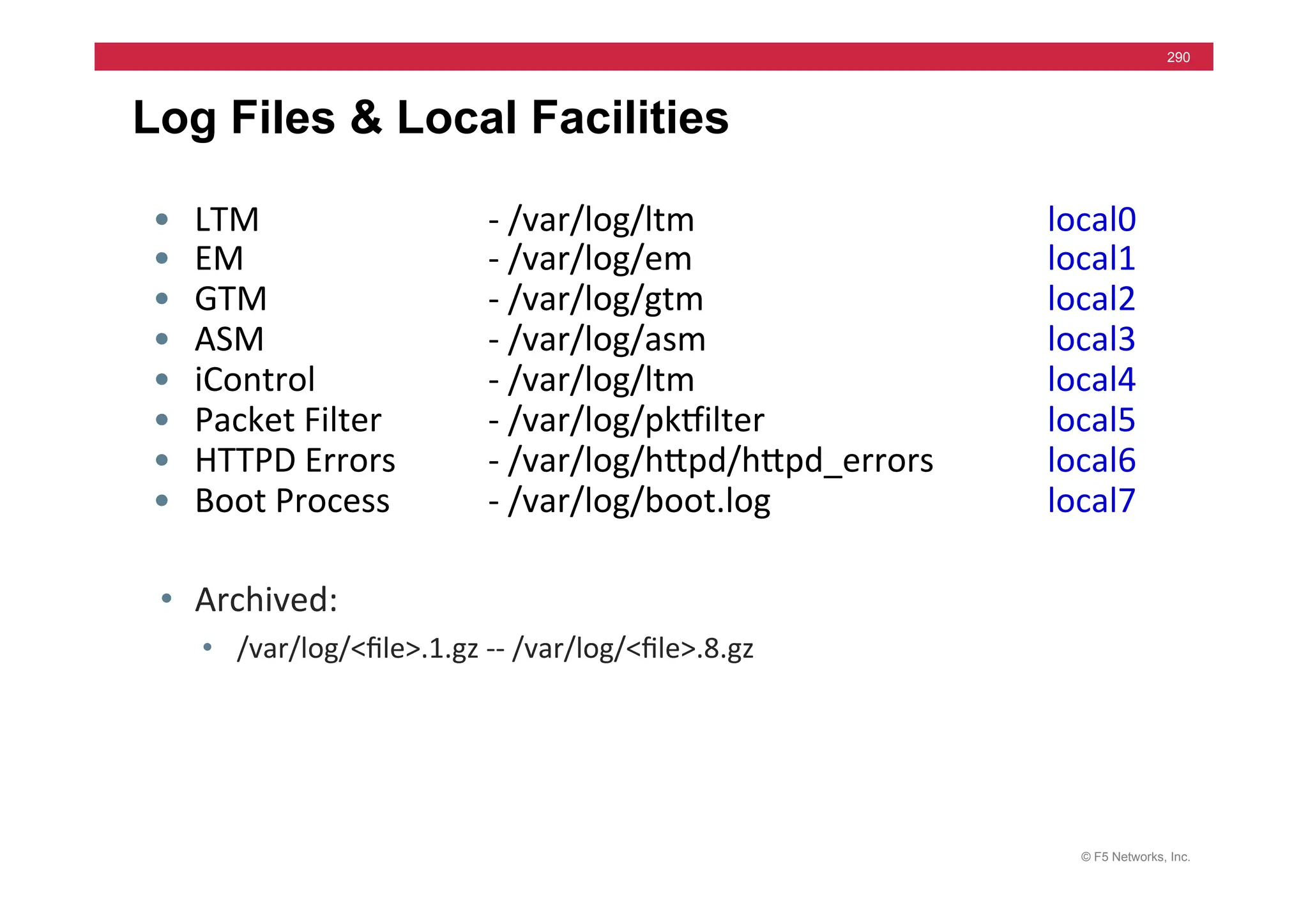
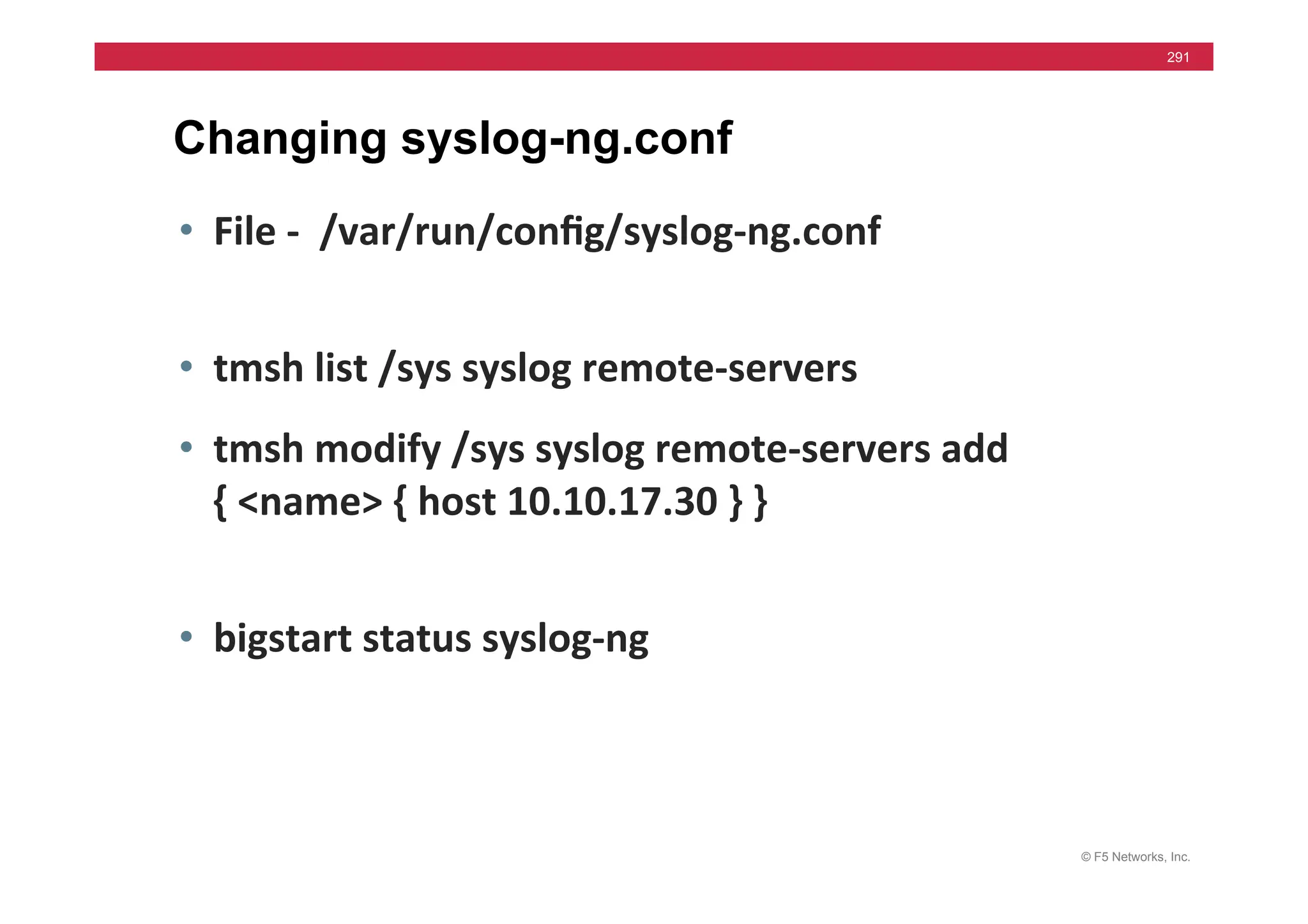
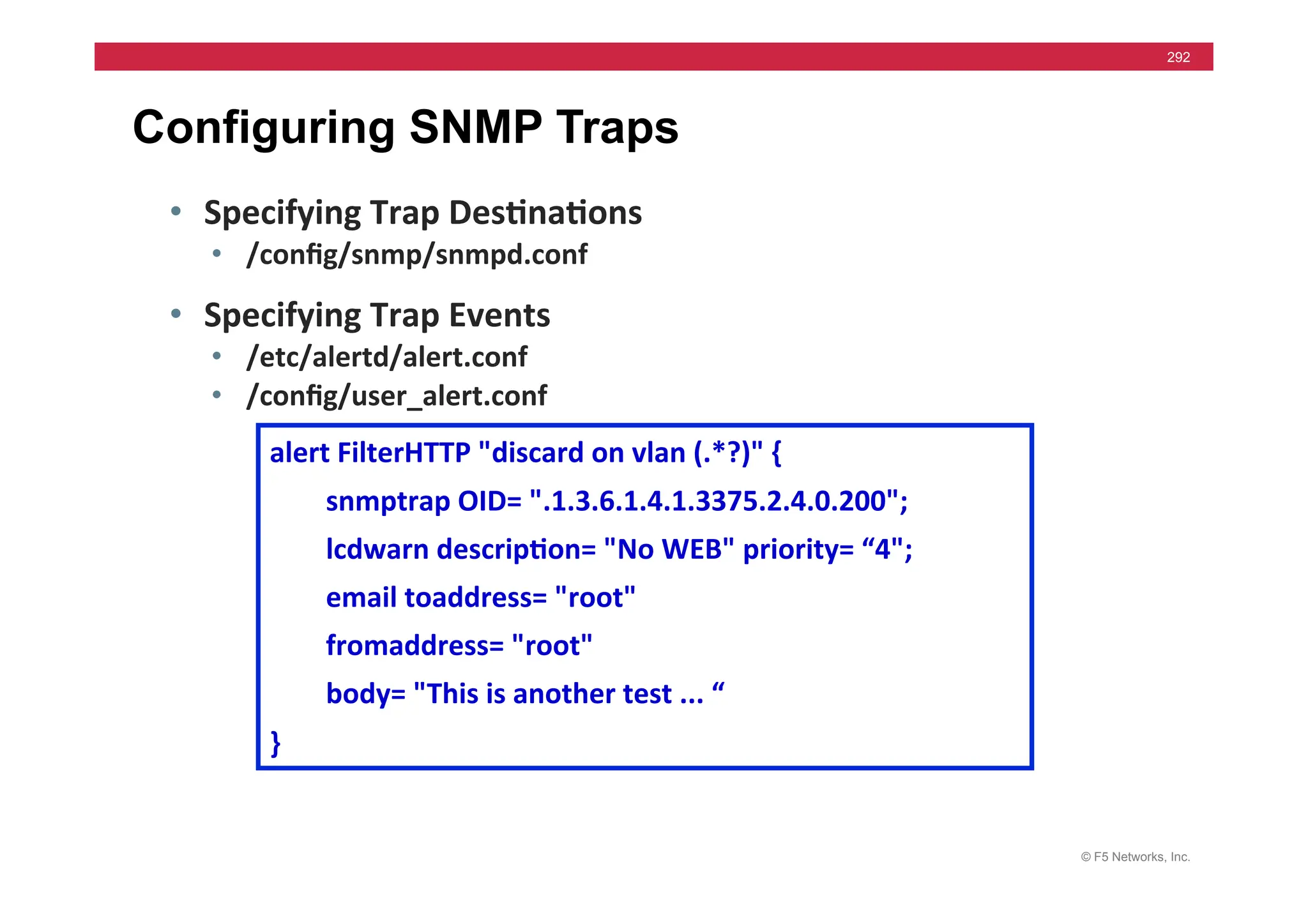
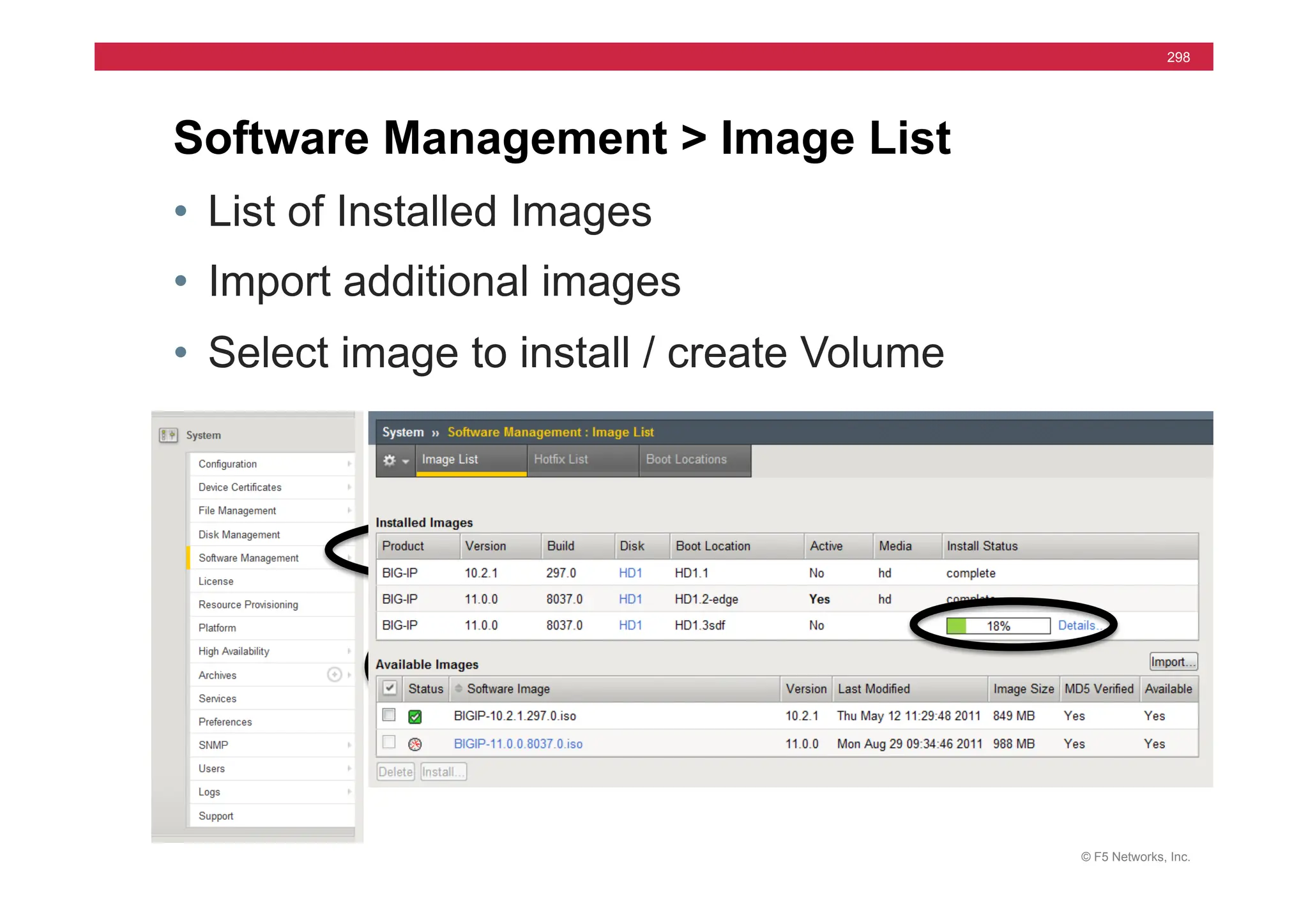
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
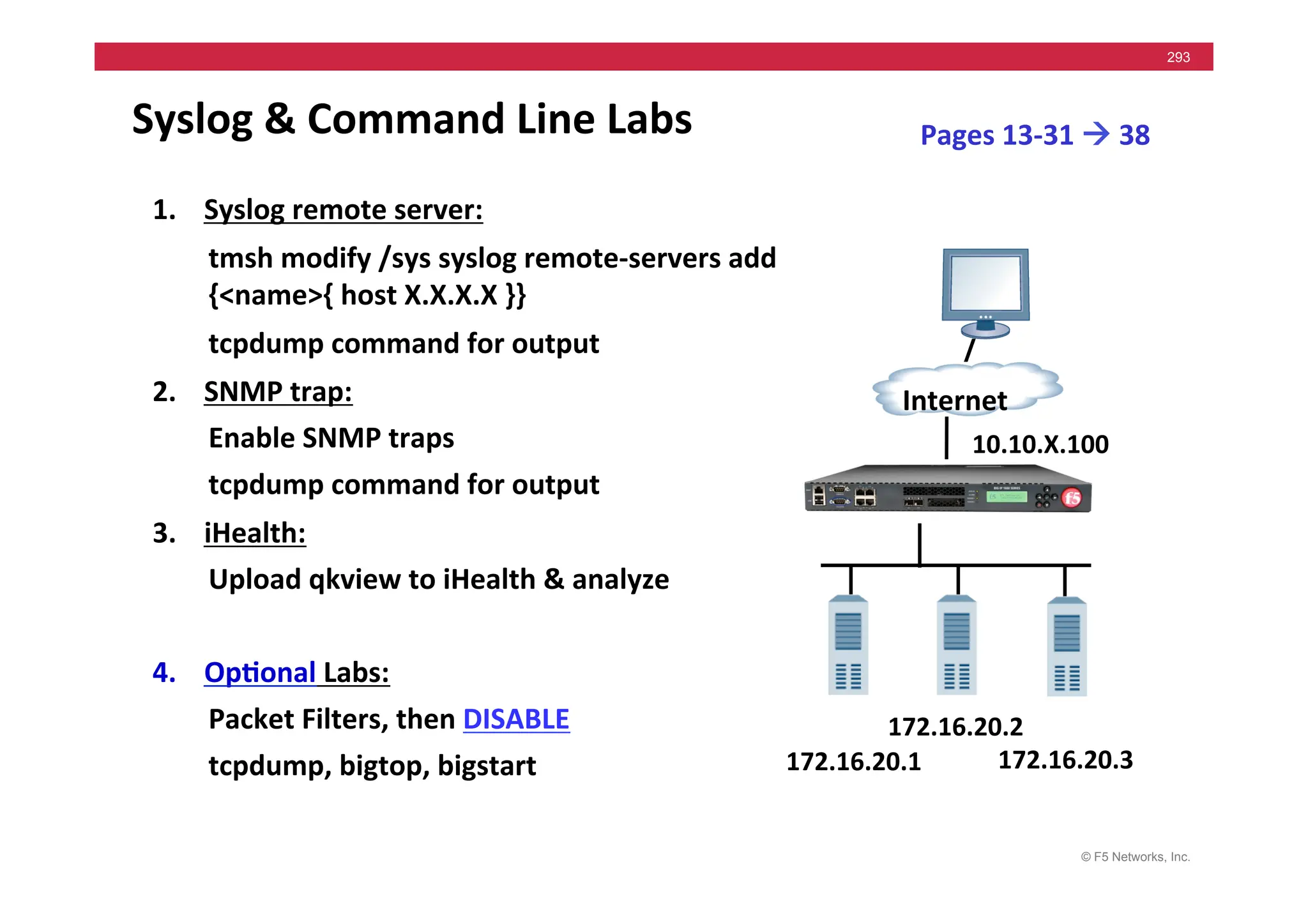
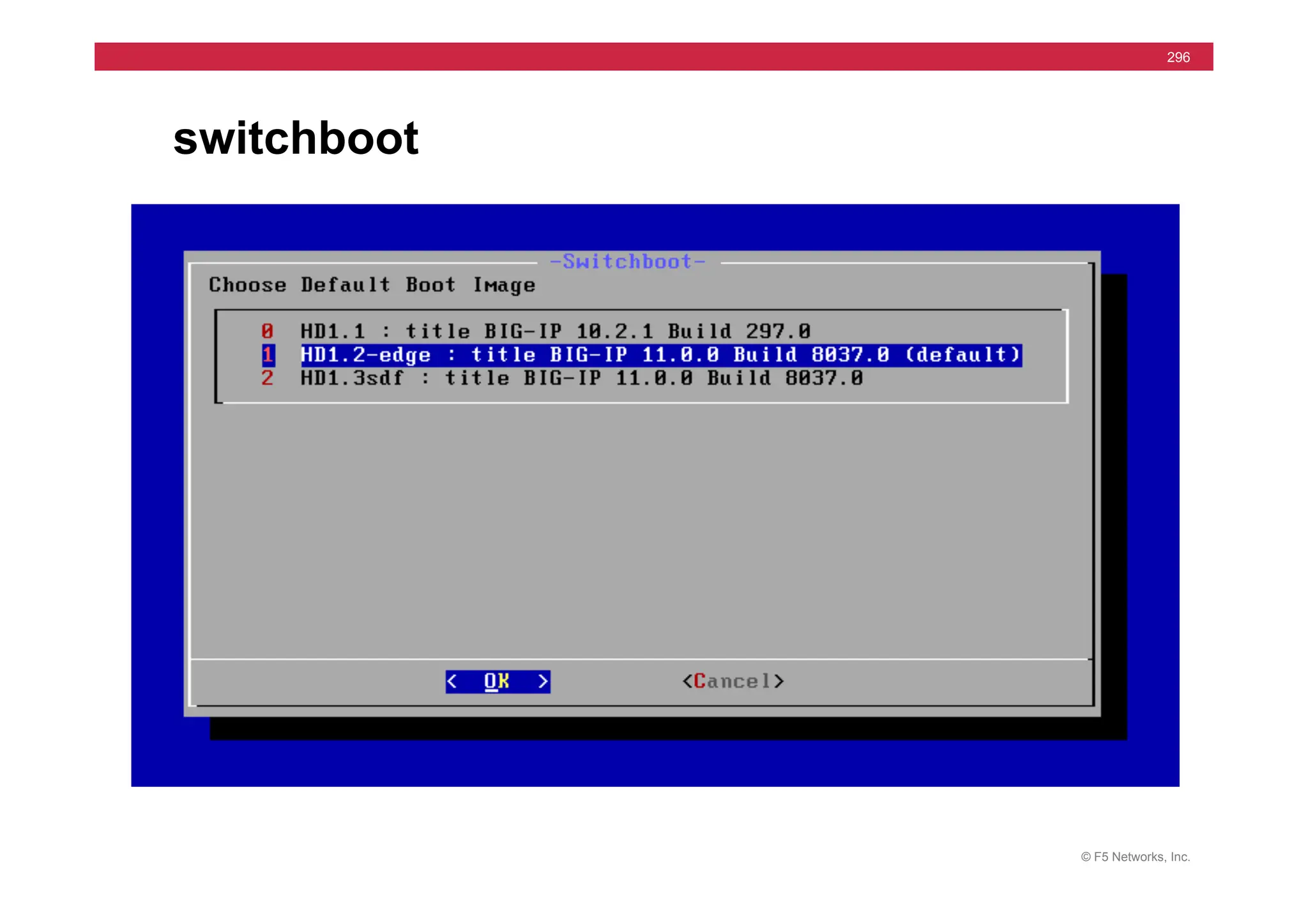
295
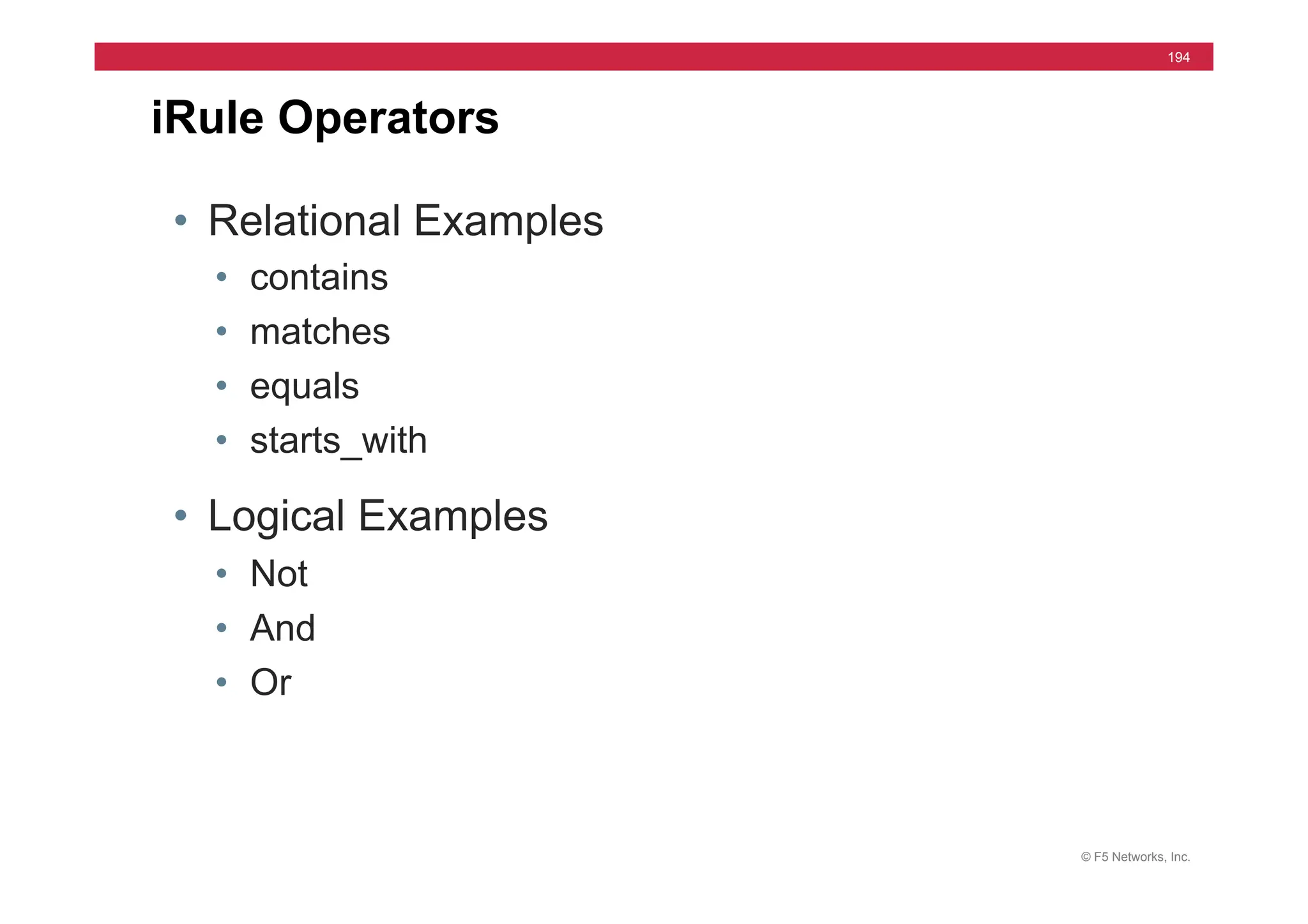
• Syntax
• install /sys software image [image.iso] volume [HD1.#]
• Used for Hotfix also
• install /sys software hotfix [hotfix.iso] volume [HD1.#]
• Install to Inactive Volume
• Set default boot
• run /util bash –c “switchboot”
• switchboot from linux
• list /sys software volume [ [default-boot-location]
install from tmsh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-295-2048.jpg)
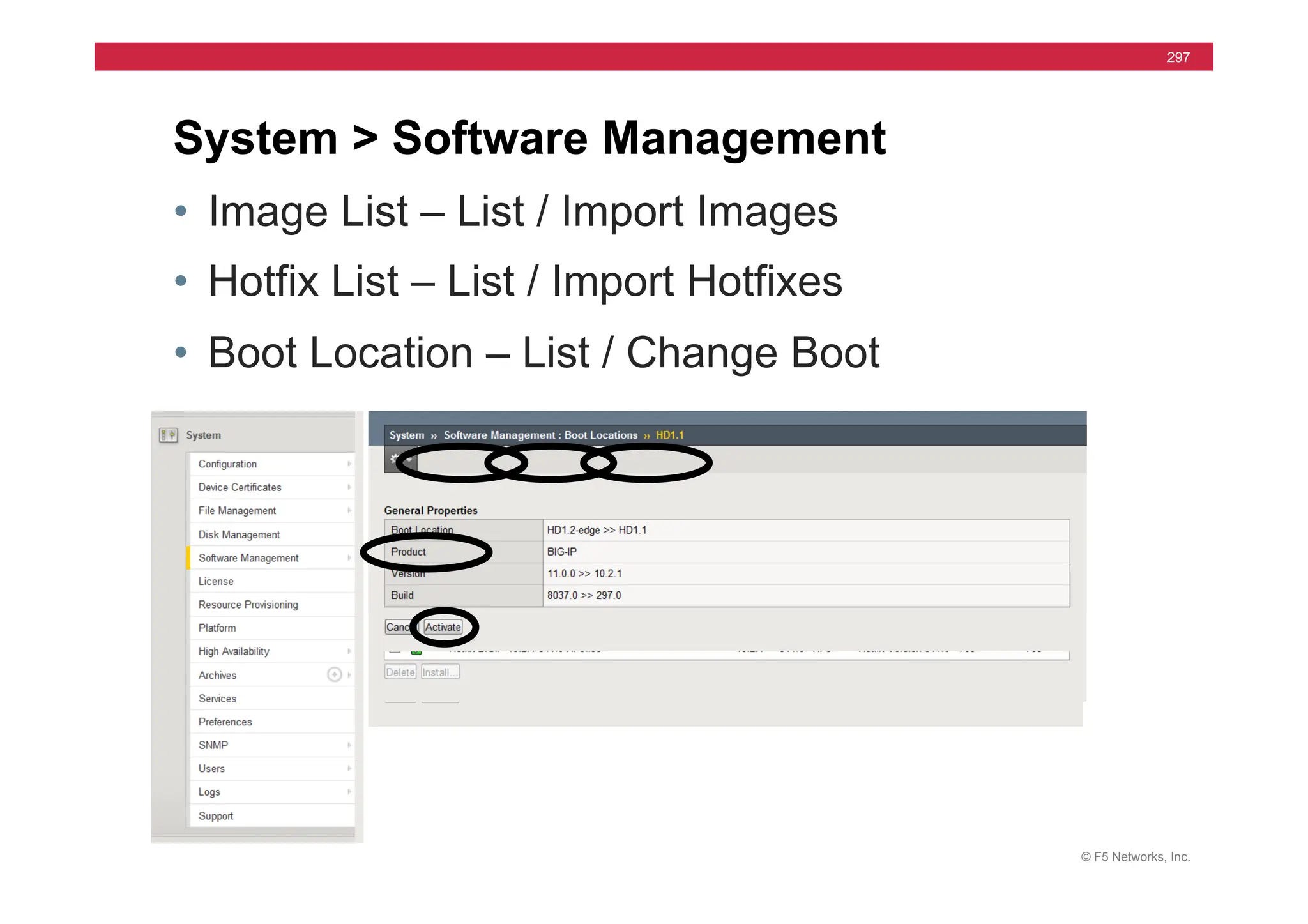

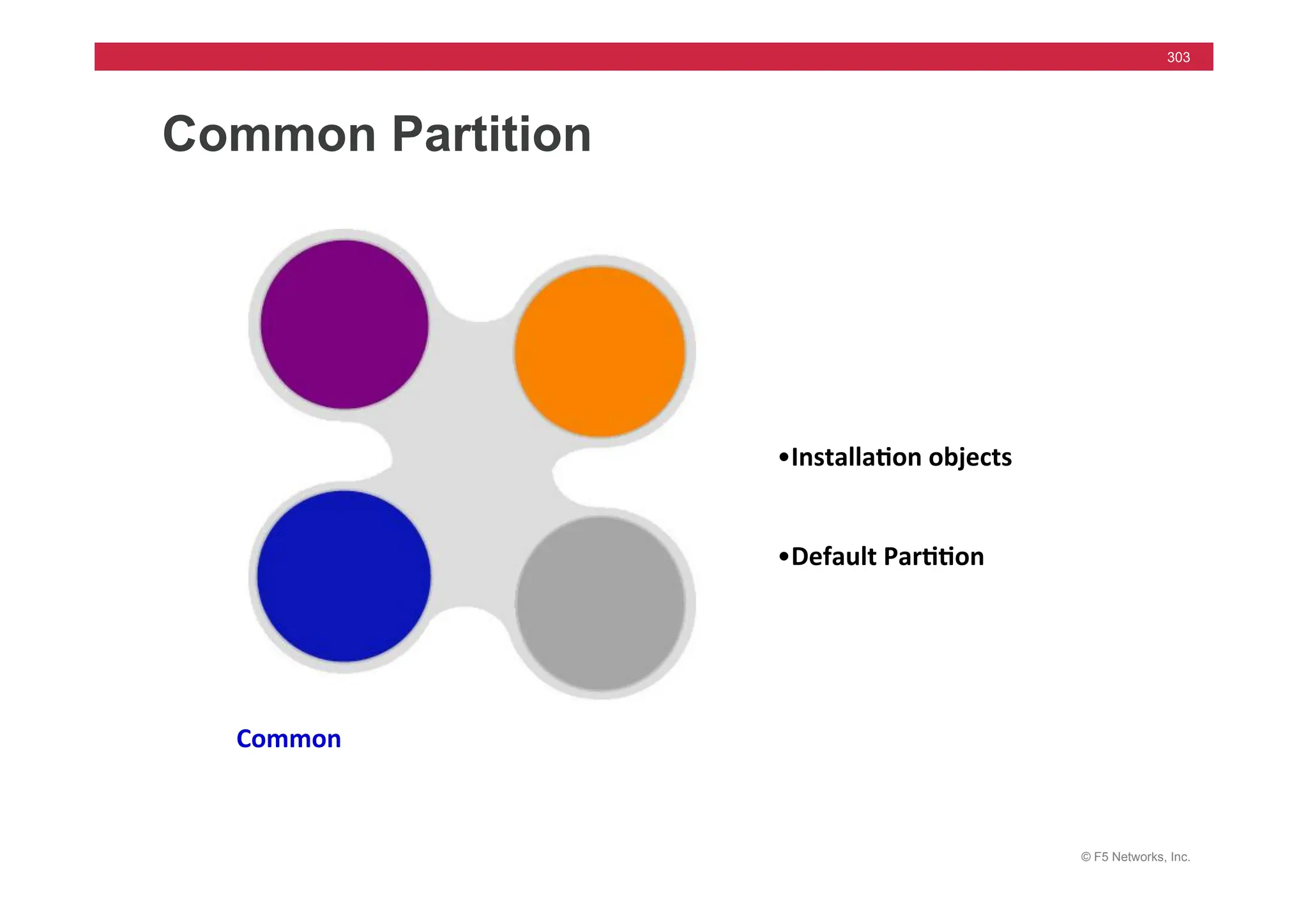
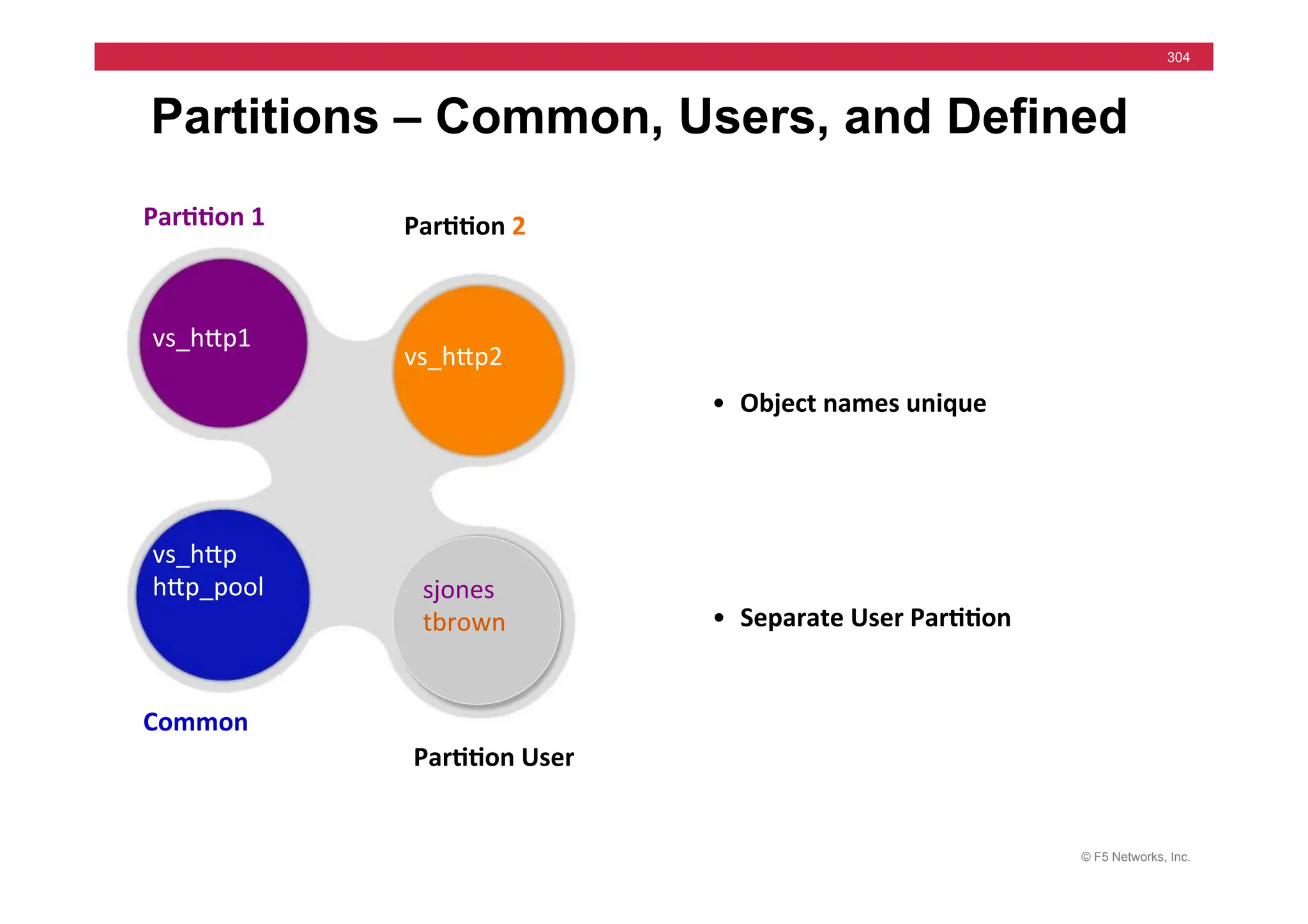
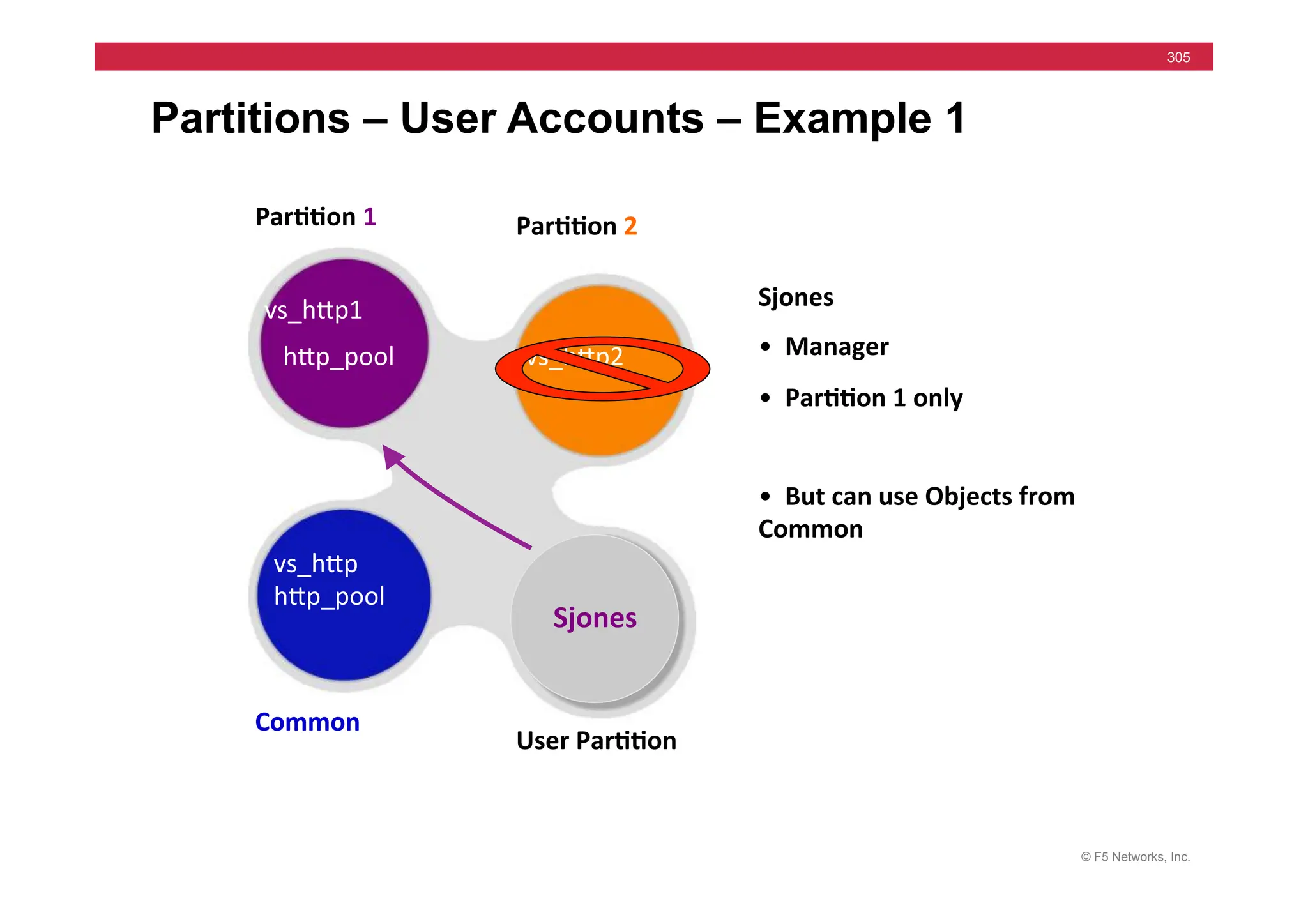
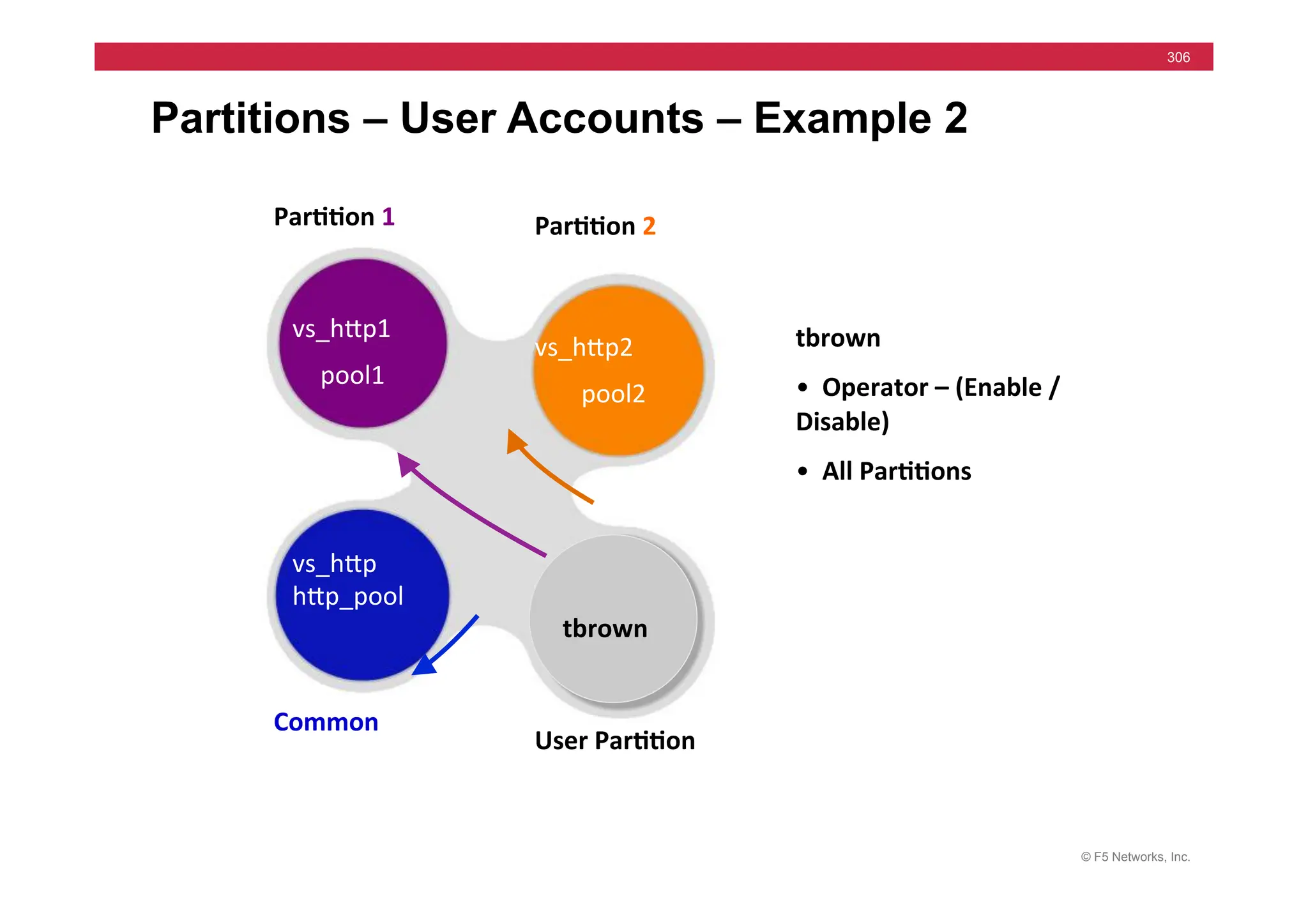


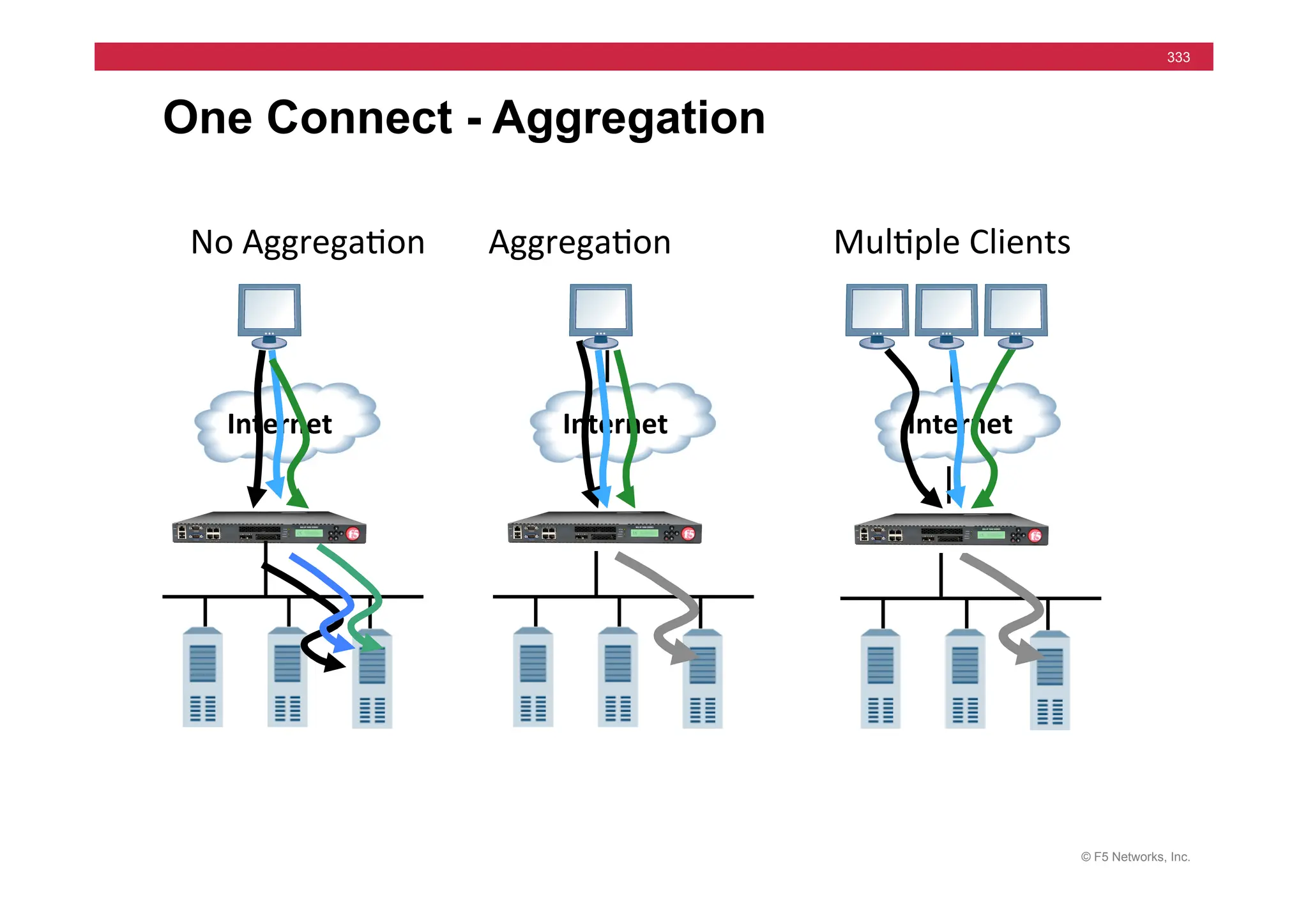
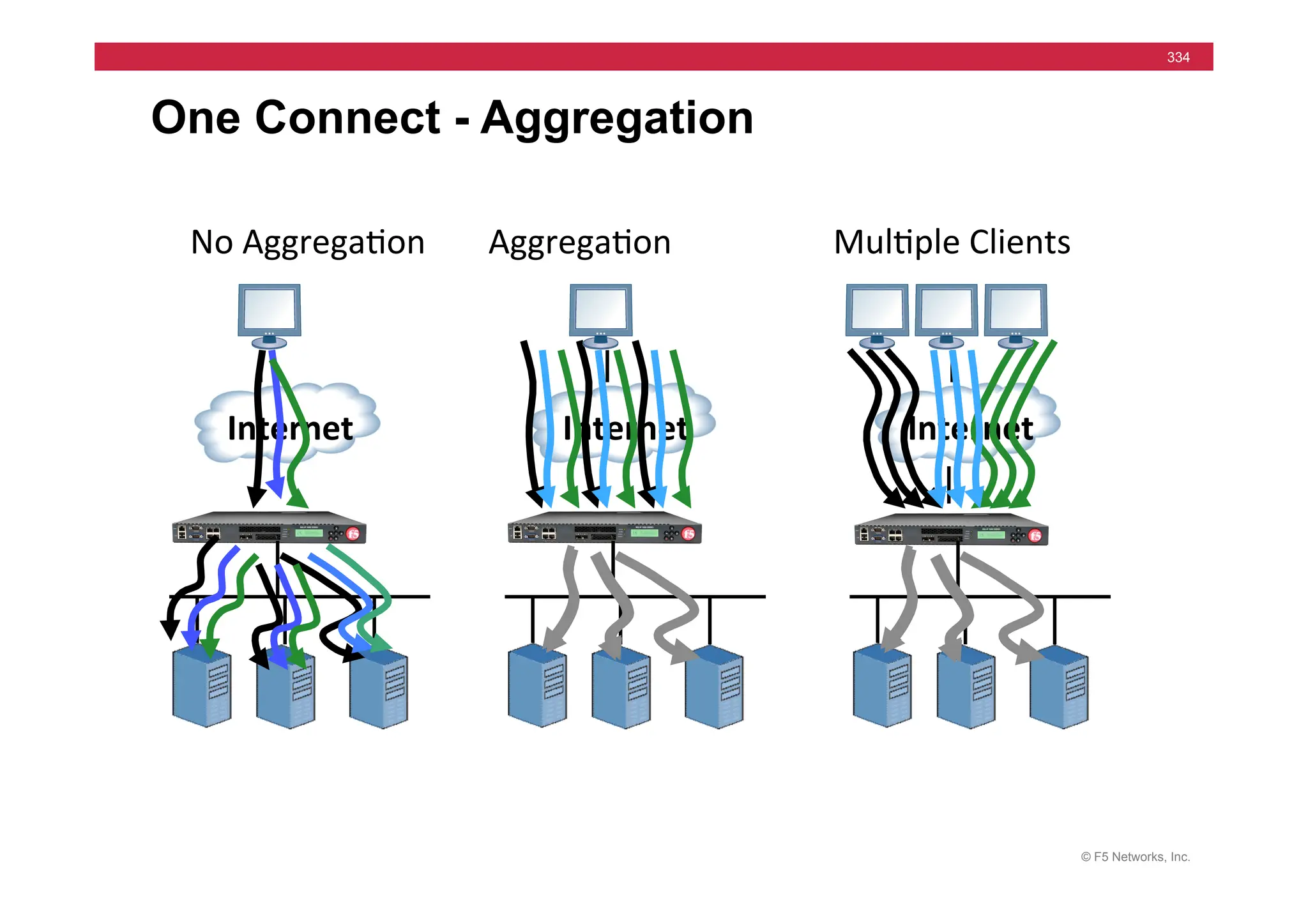
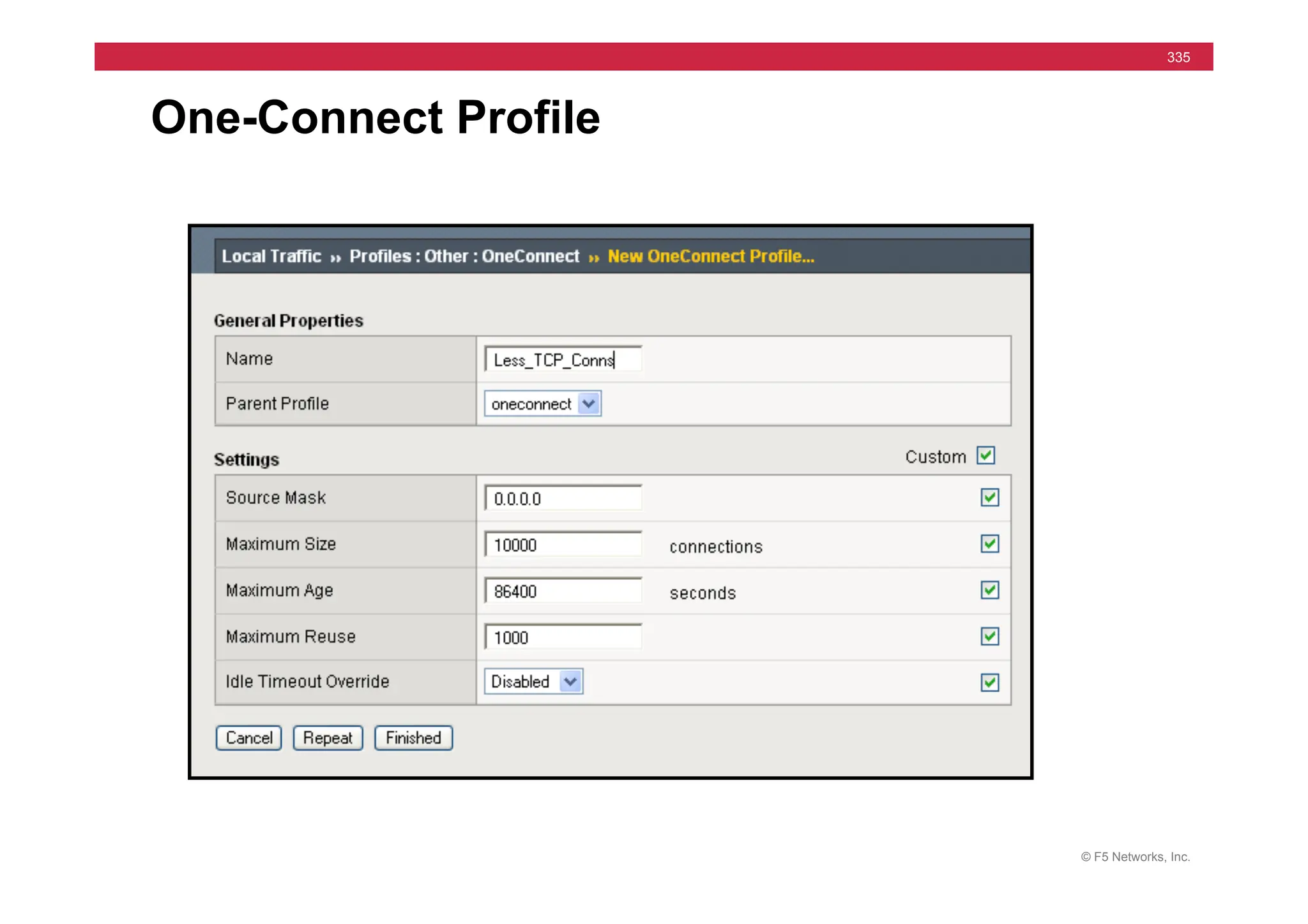
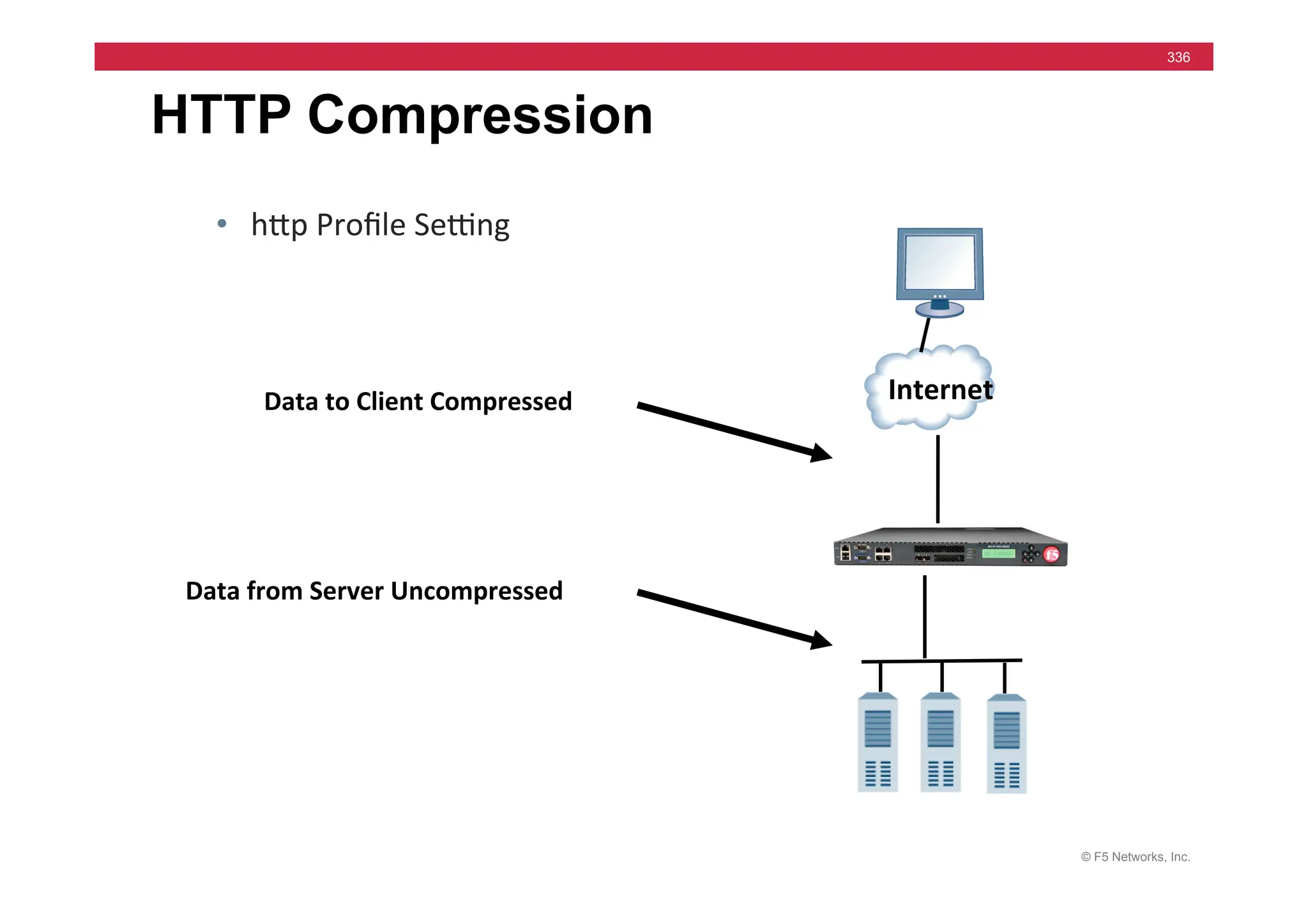

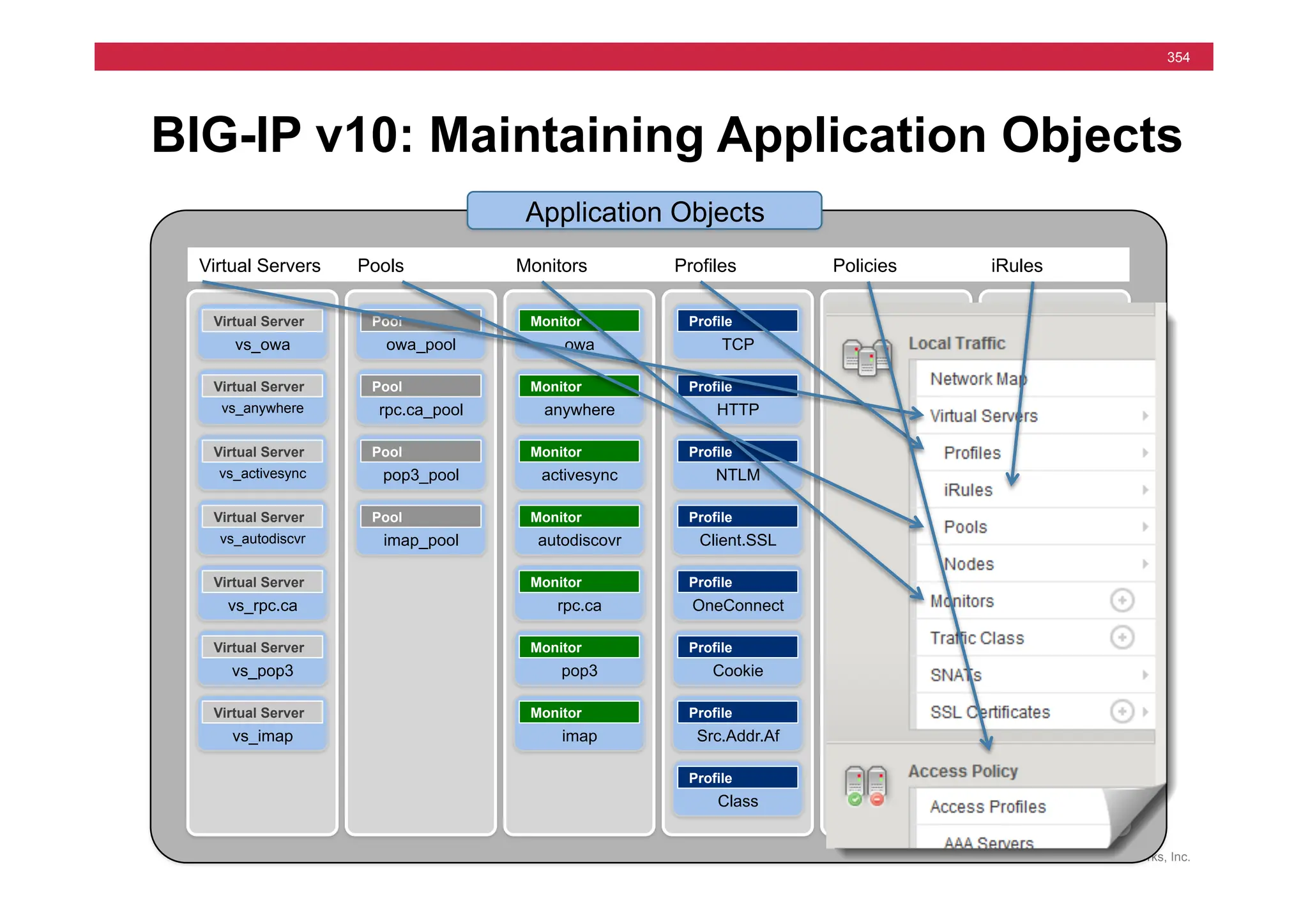
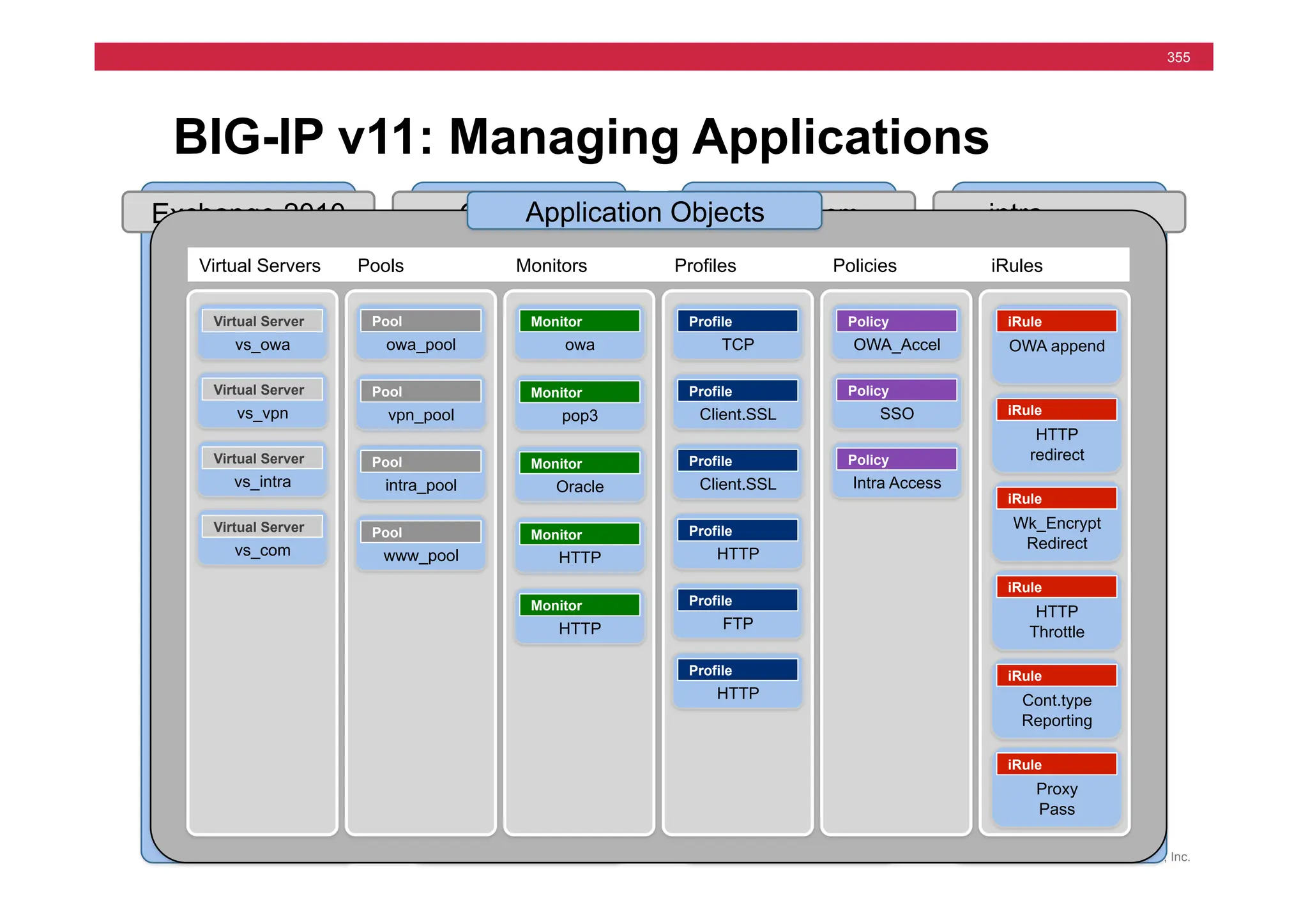
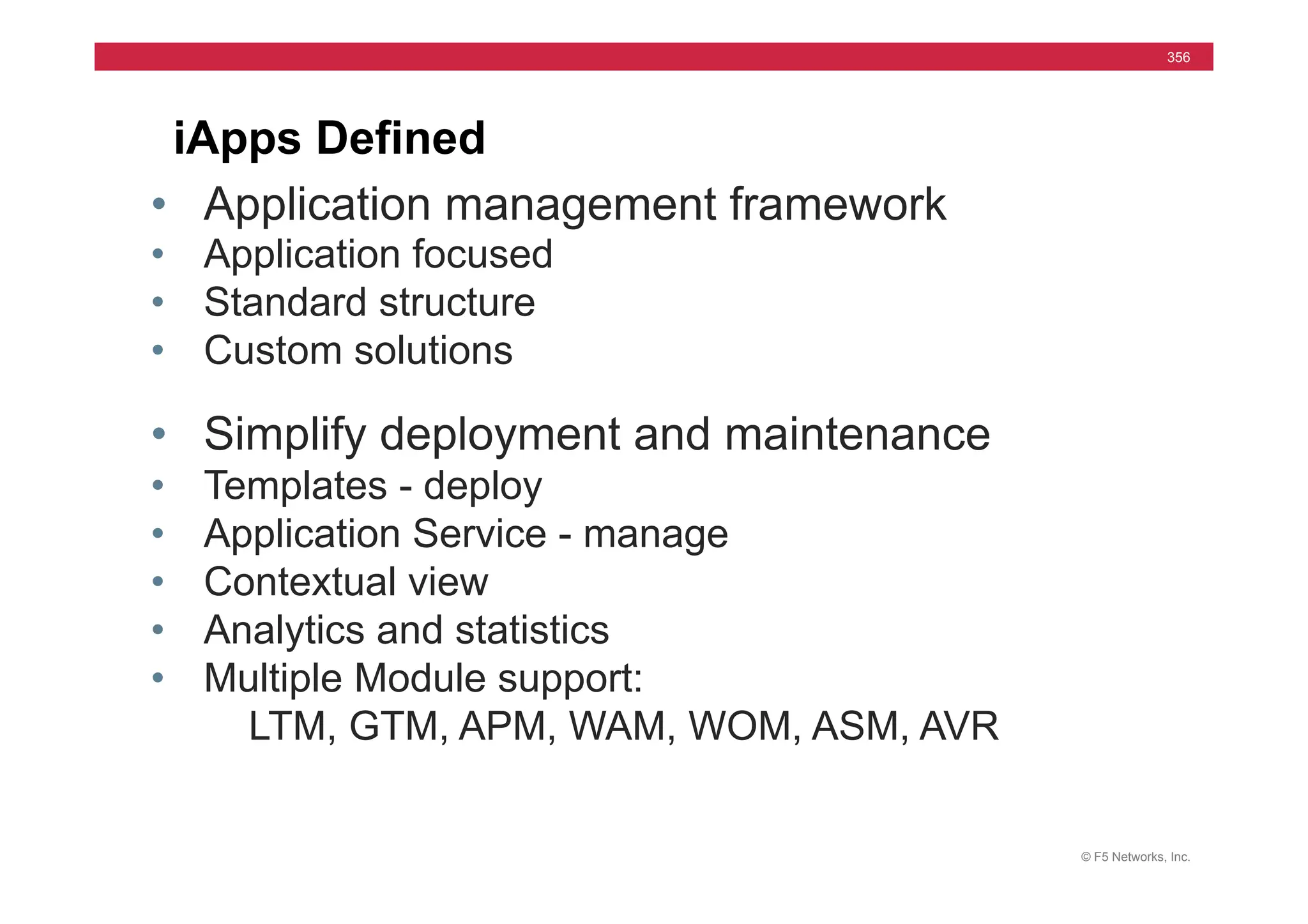

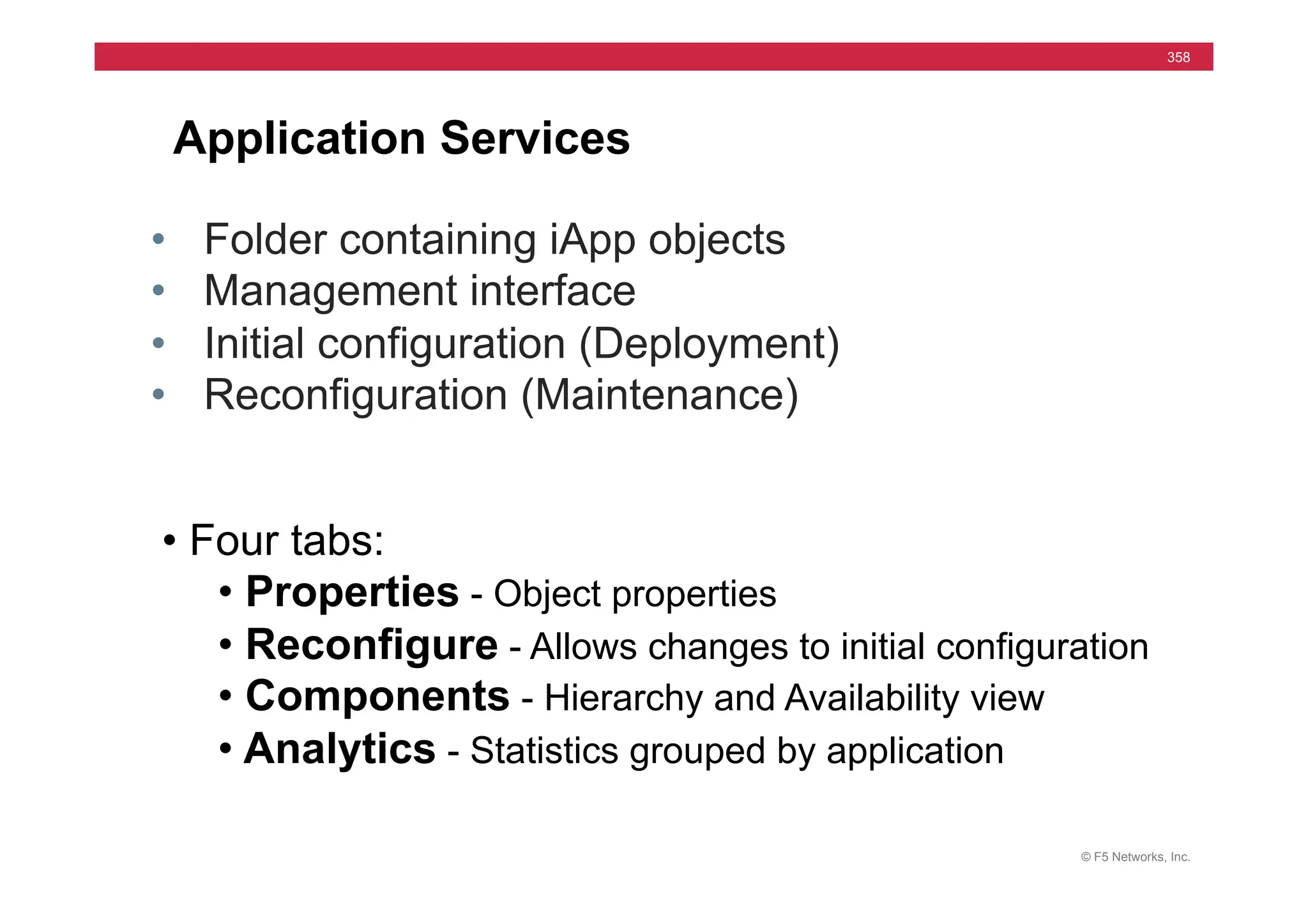



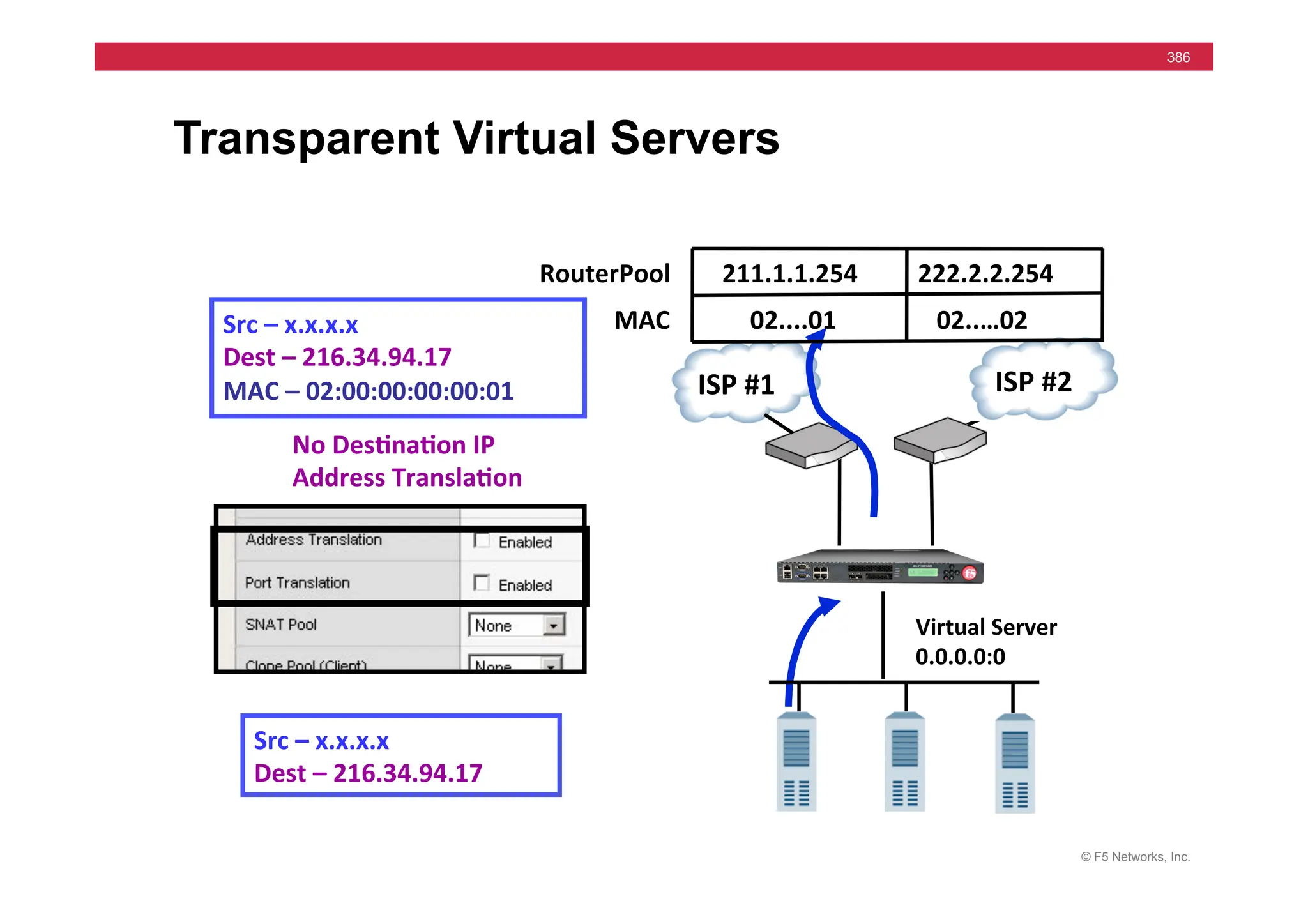
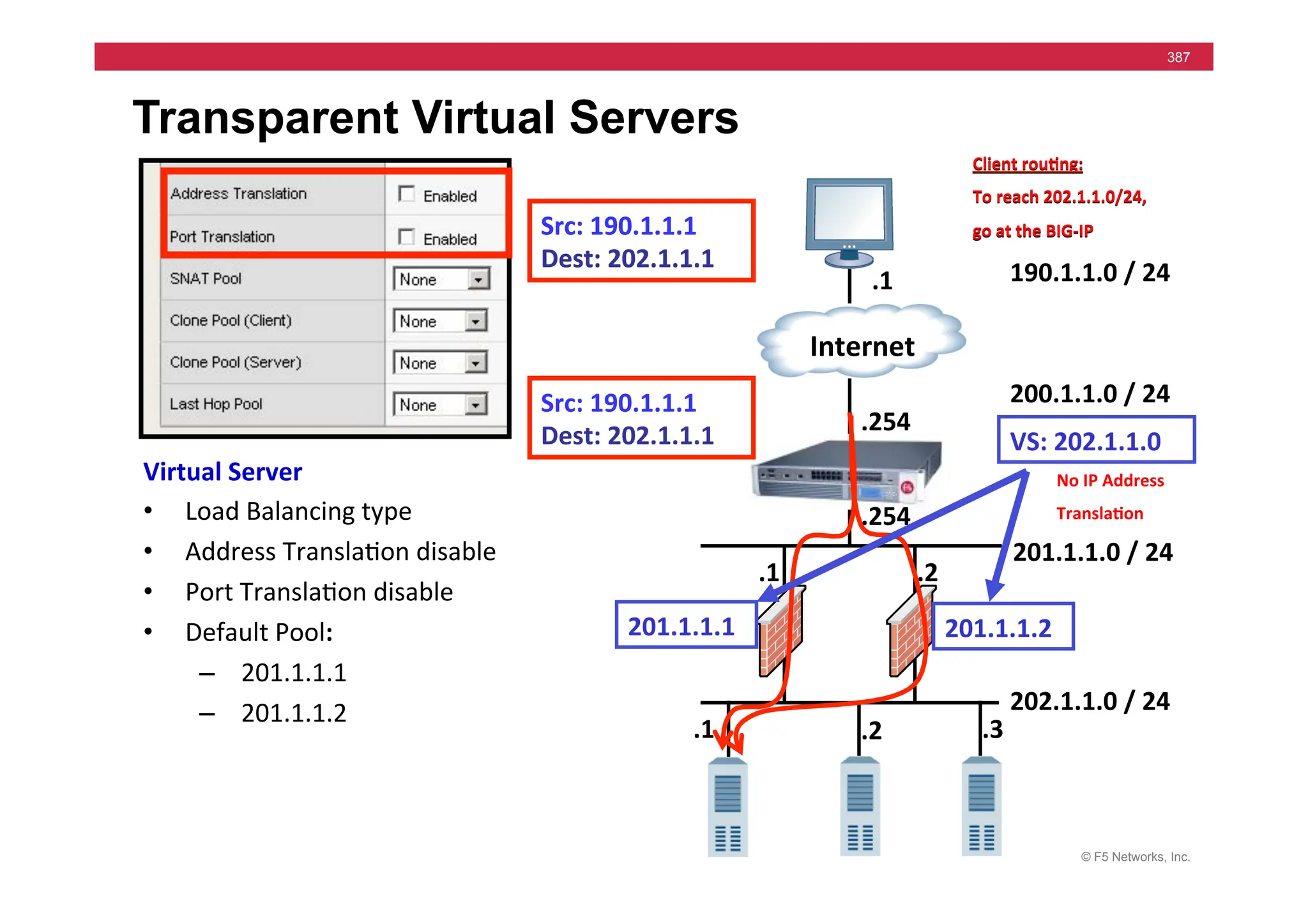
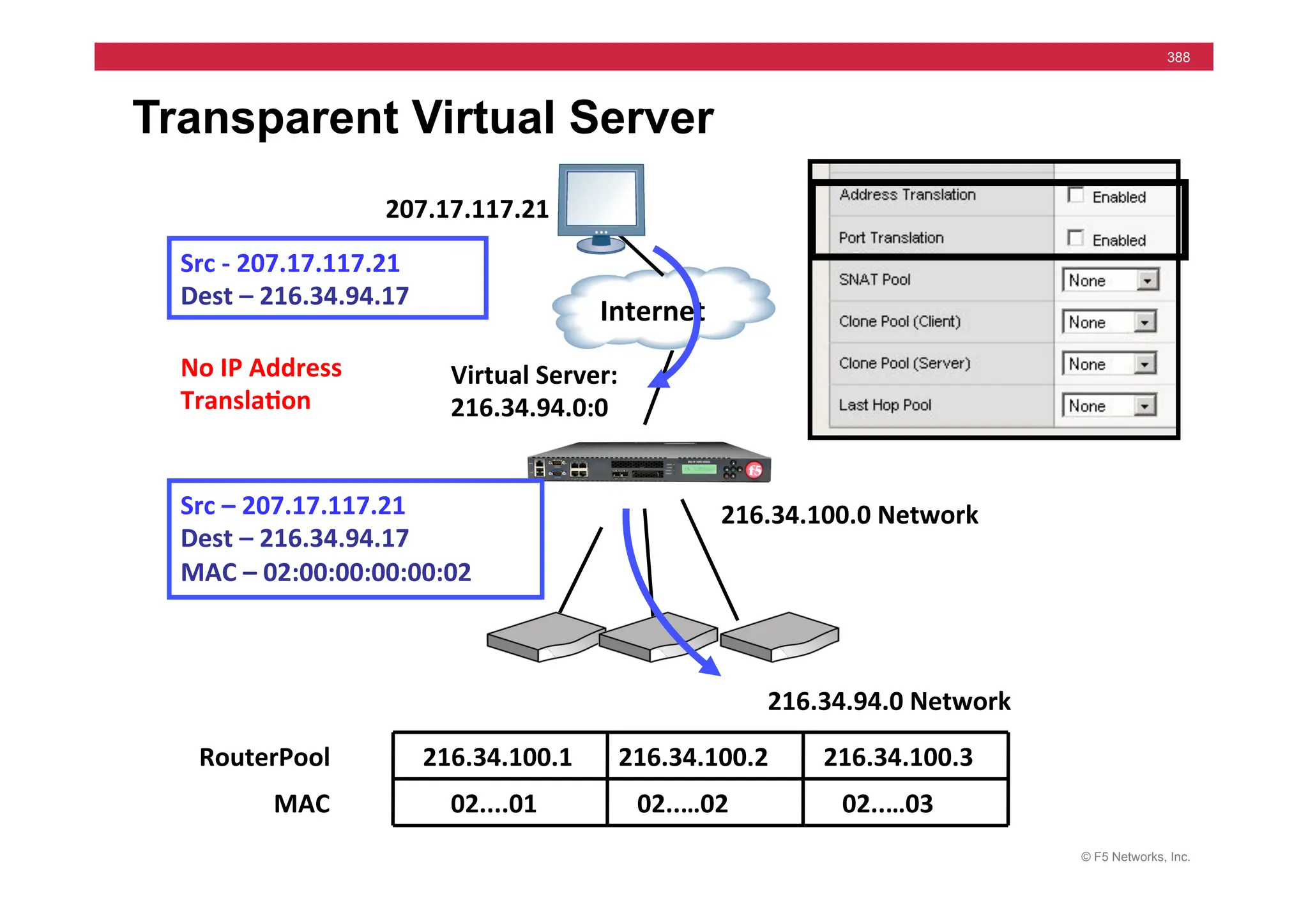
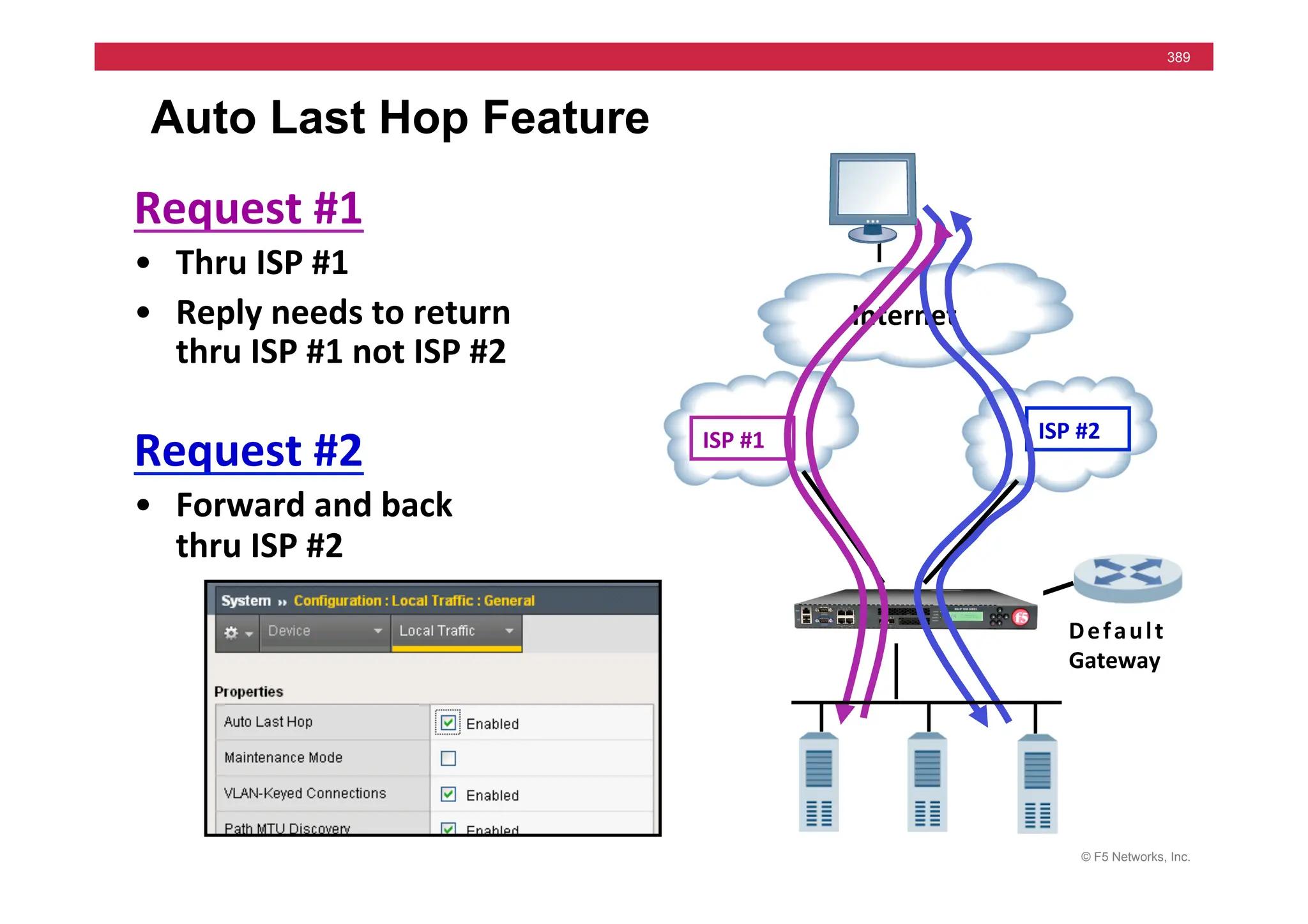
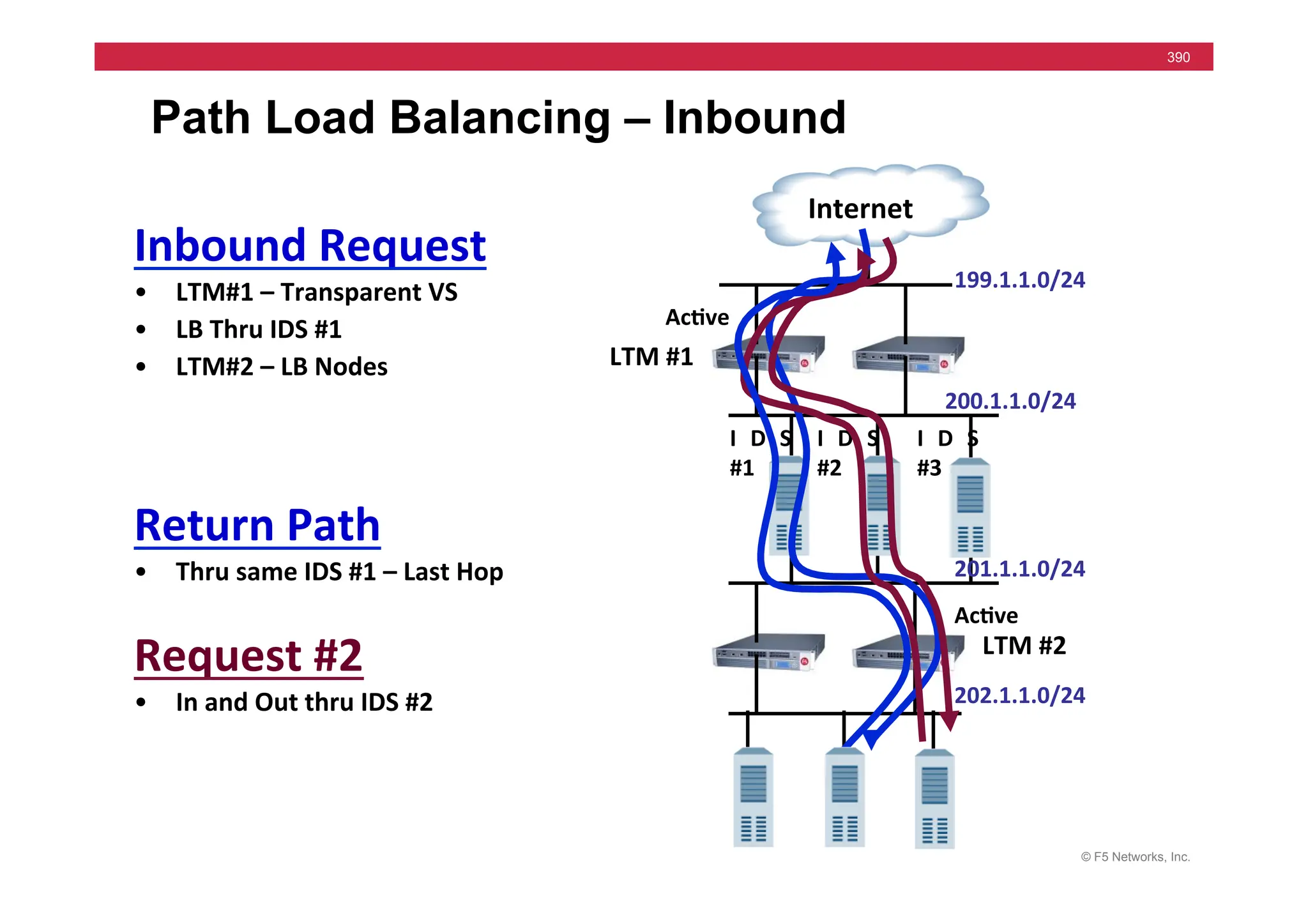
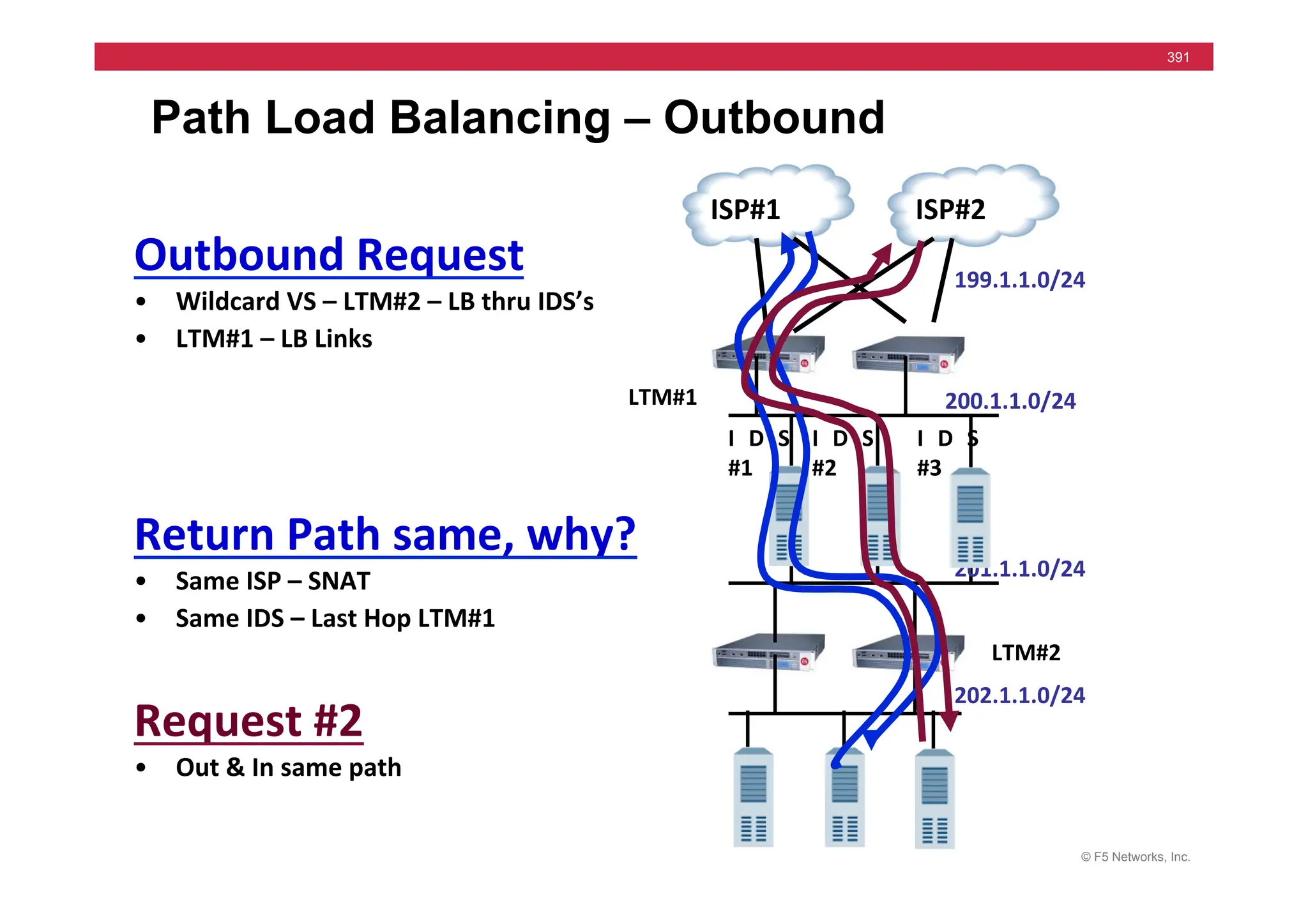
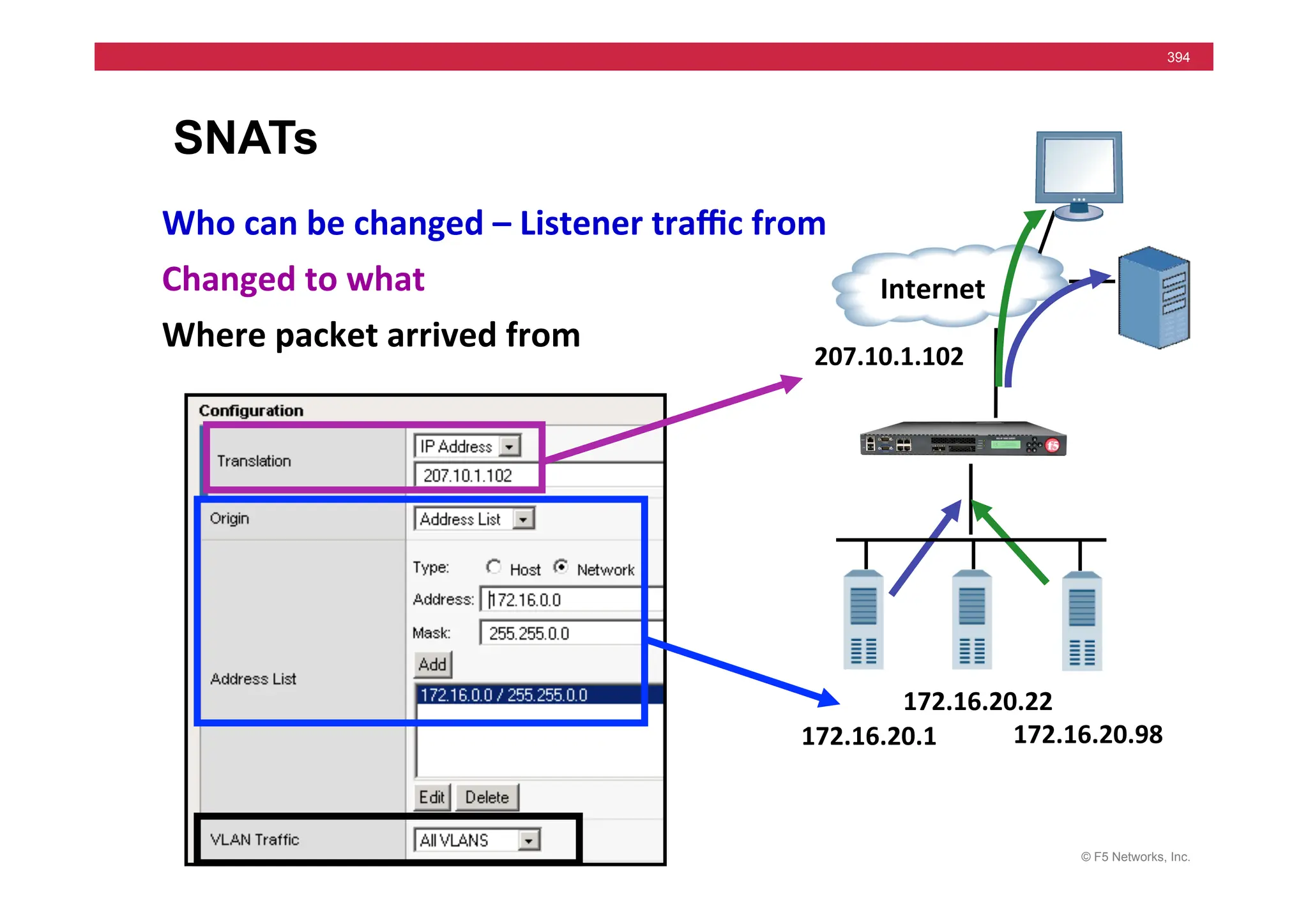
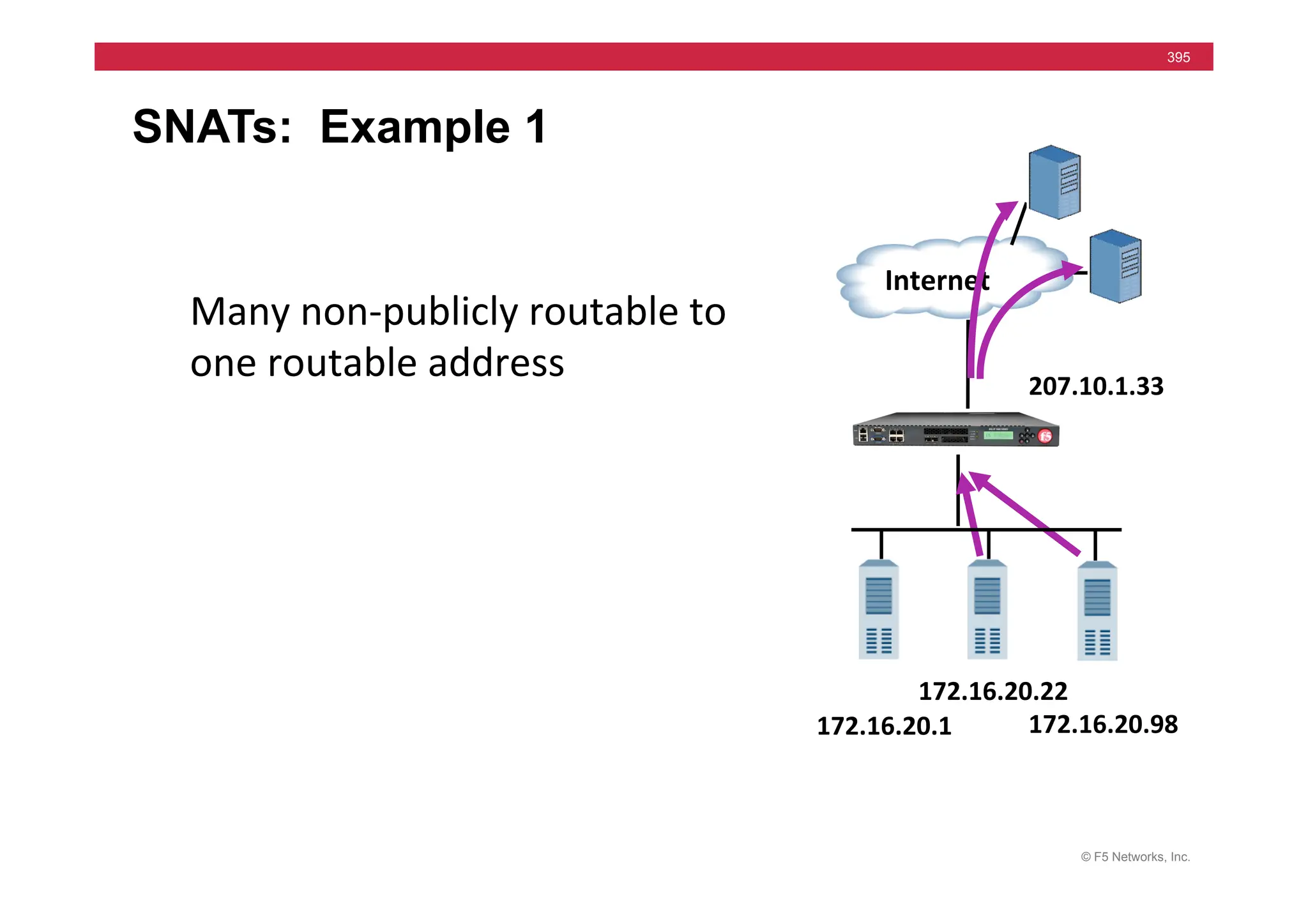
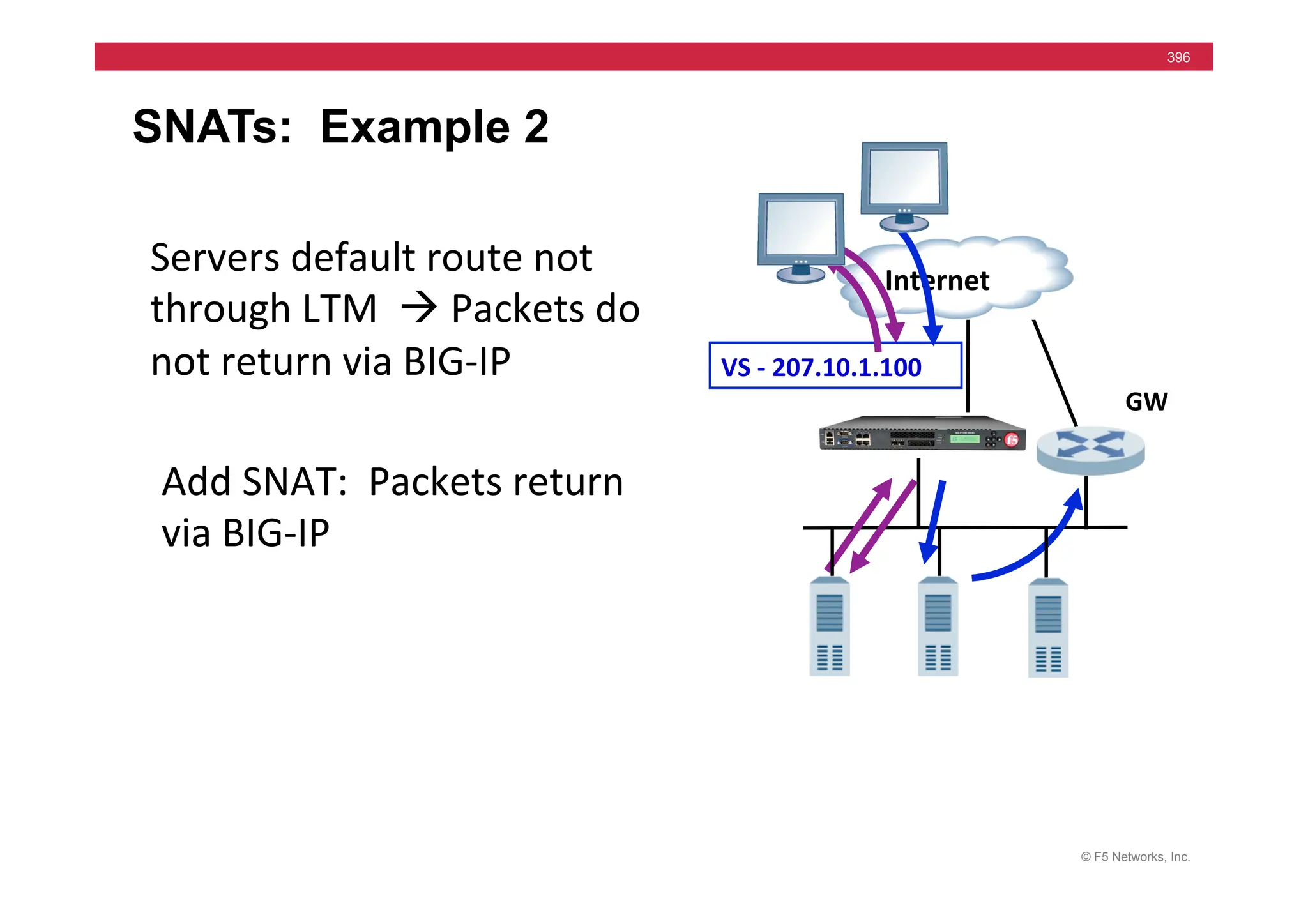
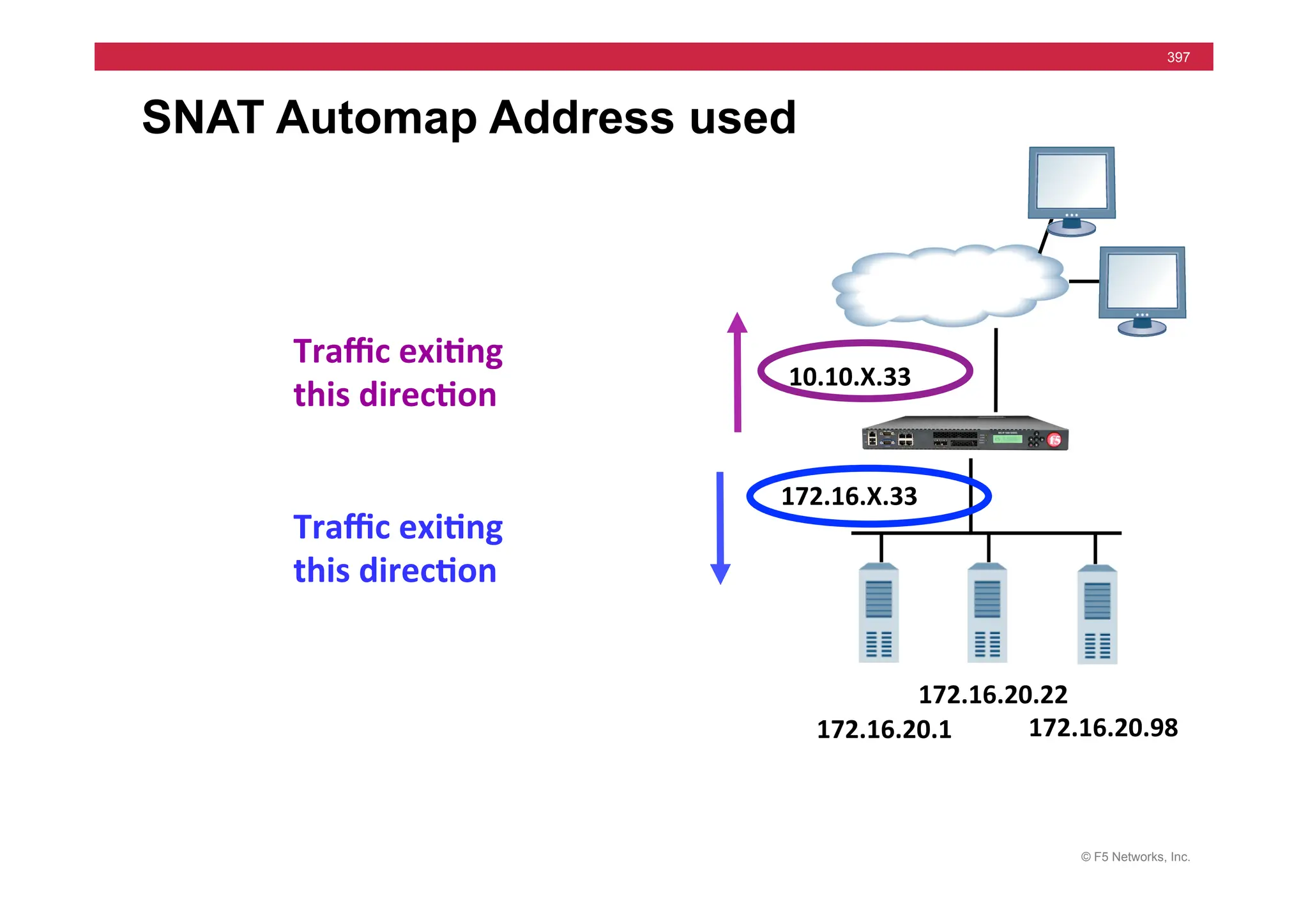
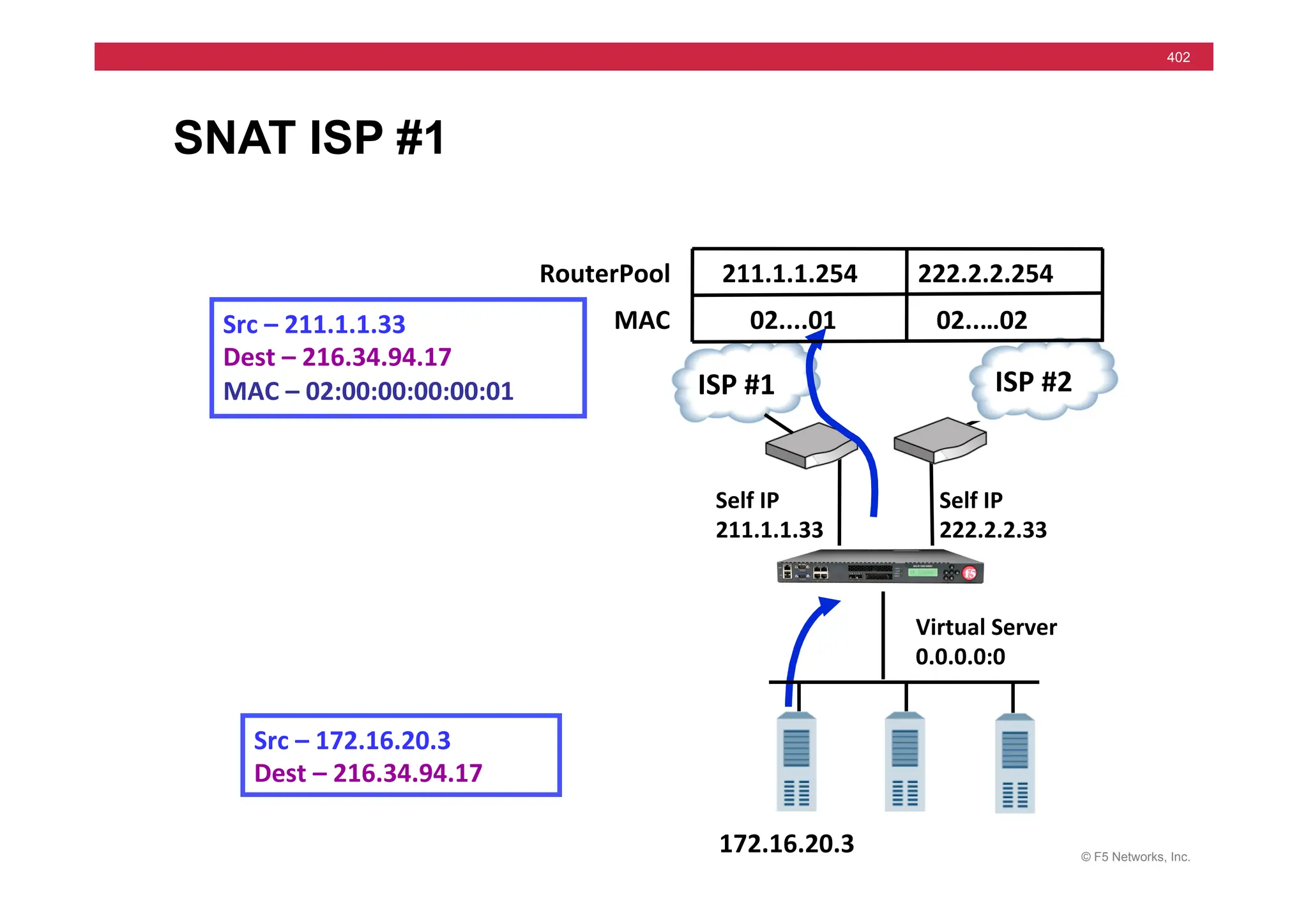
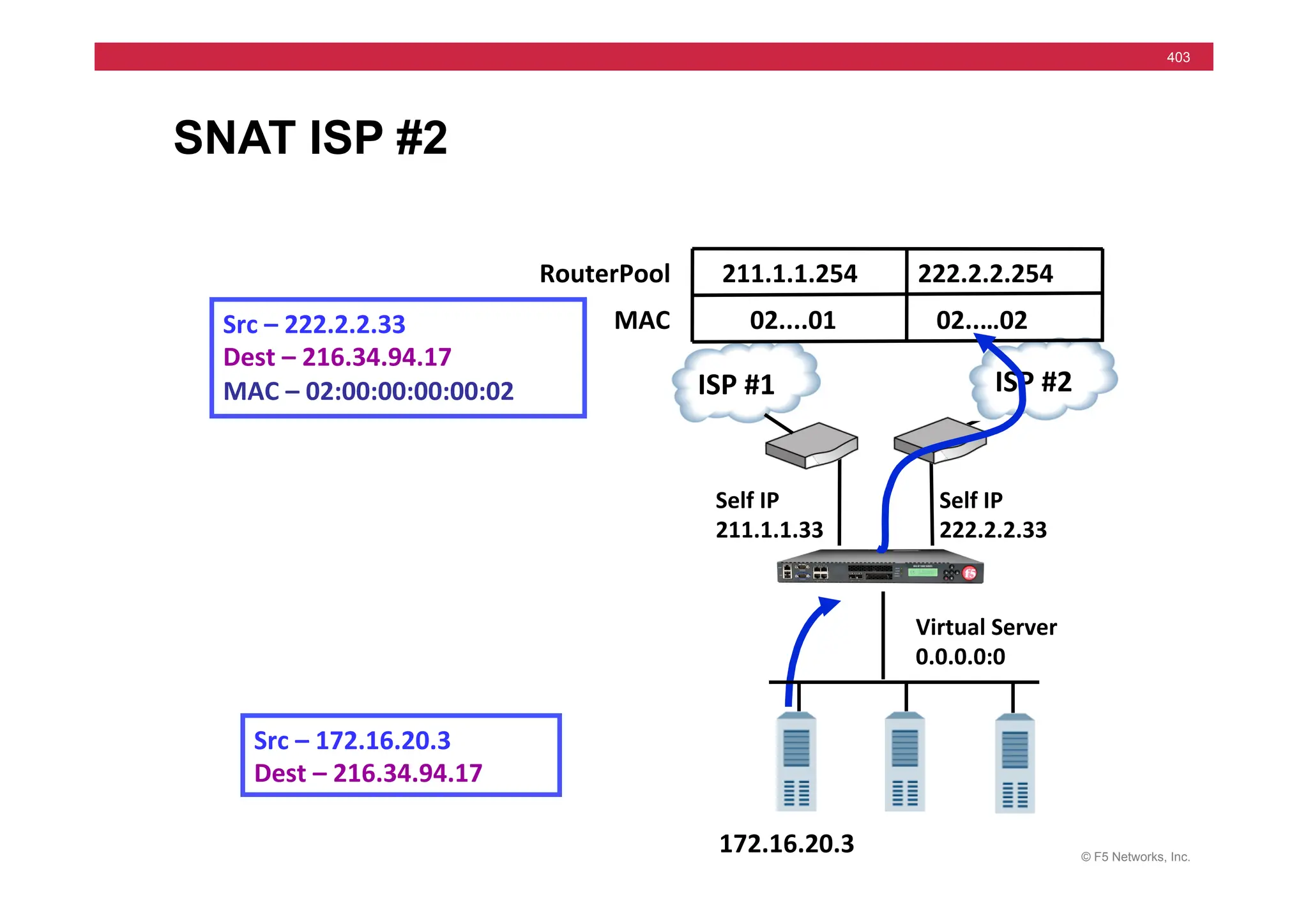
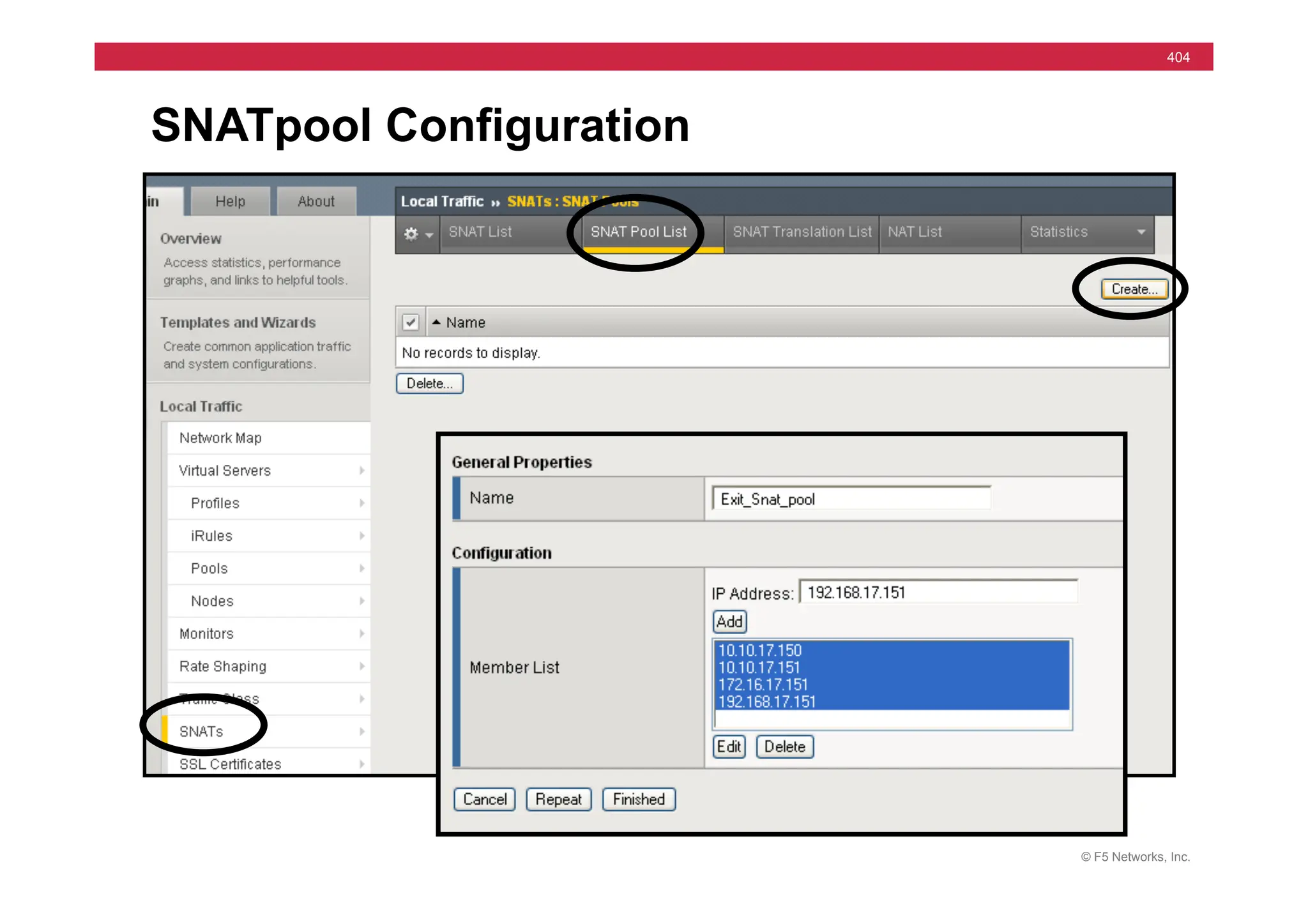
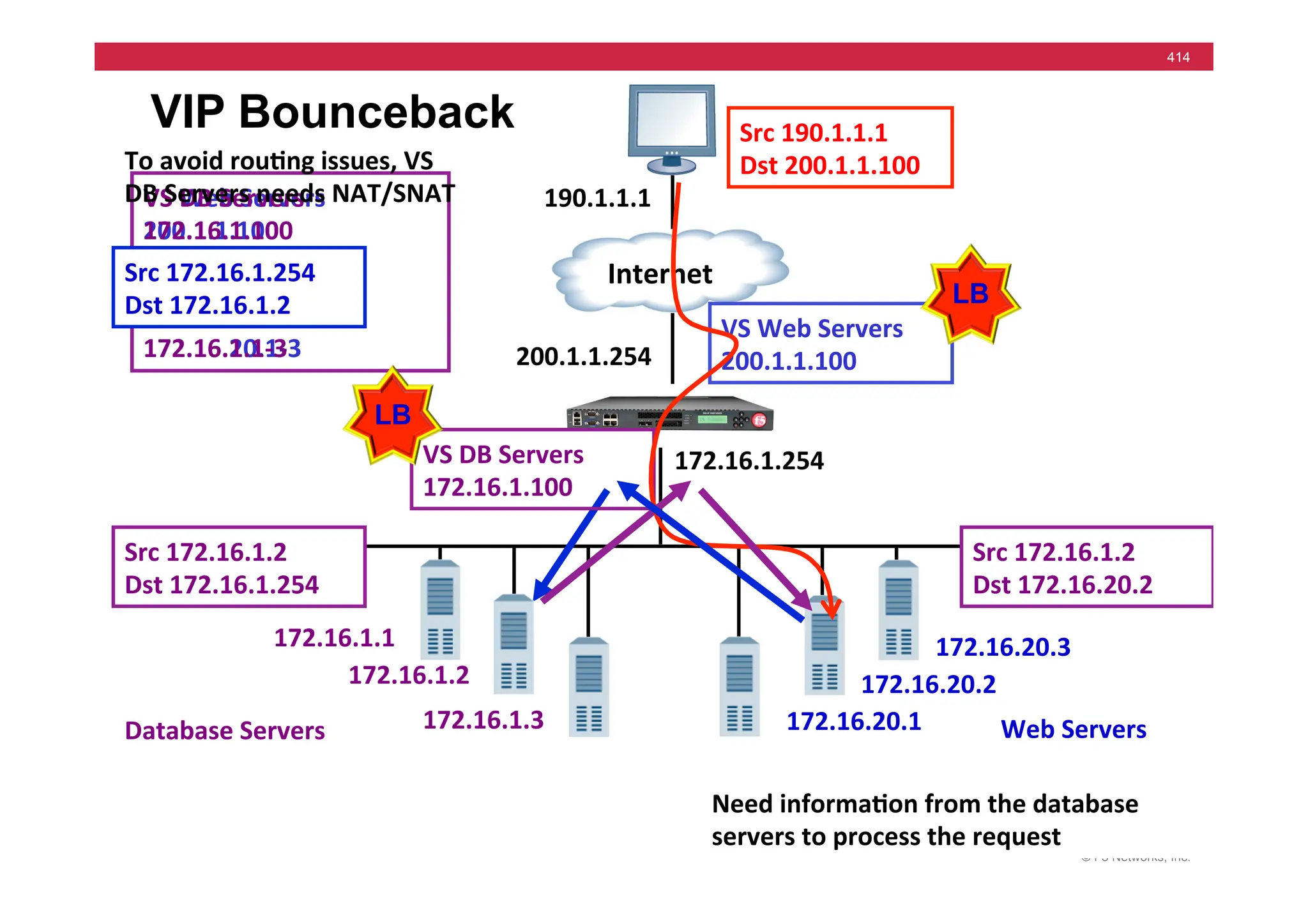
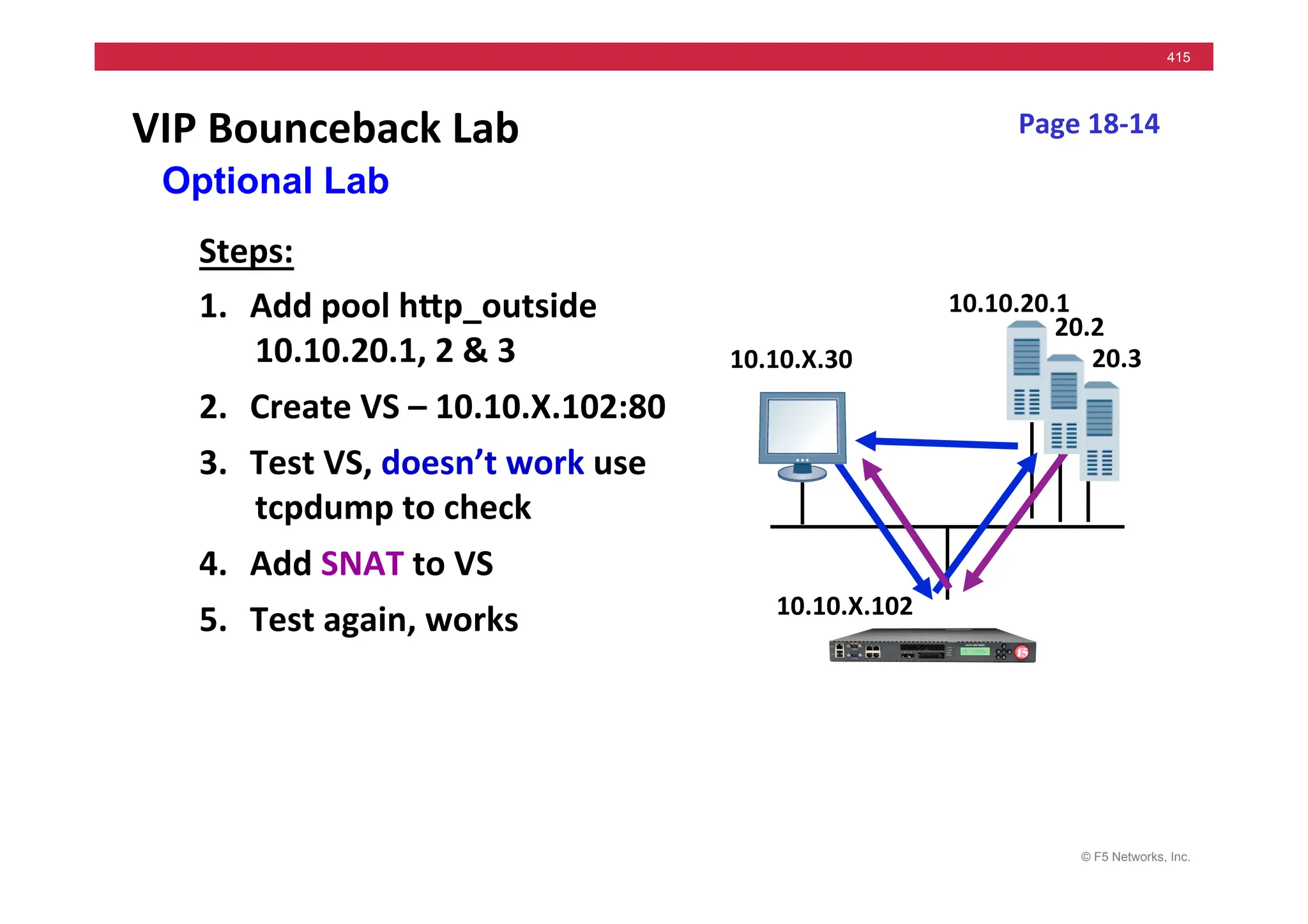
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
417
SNAT Example: Using an iRule
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
if
{
[TCP::local_port]
==
531
}
{
snatpool
chat_snatpool
}
elseif
{
[TCP::local_port]
==
25
}
{
snatpool
smtp_snatpool
}
else
{
snatpool
other_snatpool
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-417-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
418
SNAT Example: Using an iRule
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
set
MYPORT
[TCP::local_port]
switch
$MYPORT
{
80
{
snatpool
SNATPool_80
pool
hMp_pool
}
443
{
snatpool
SNATPool_443
pool
hMps_pool
}
default
{
pool
Pool_Other
}
}
}
Internet
Pool_Other
HTTP
&
HTTPS
GW](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-418-2048.jpg)
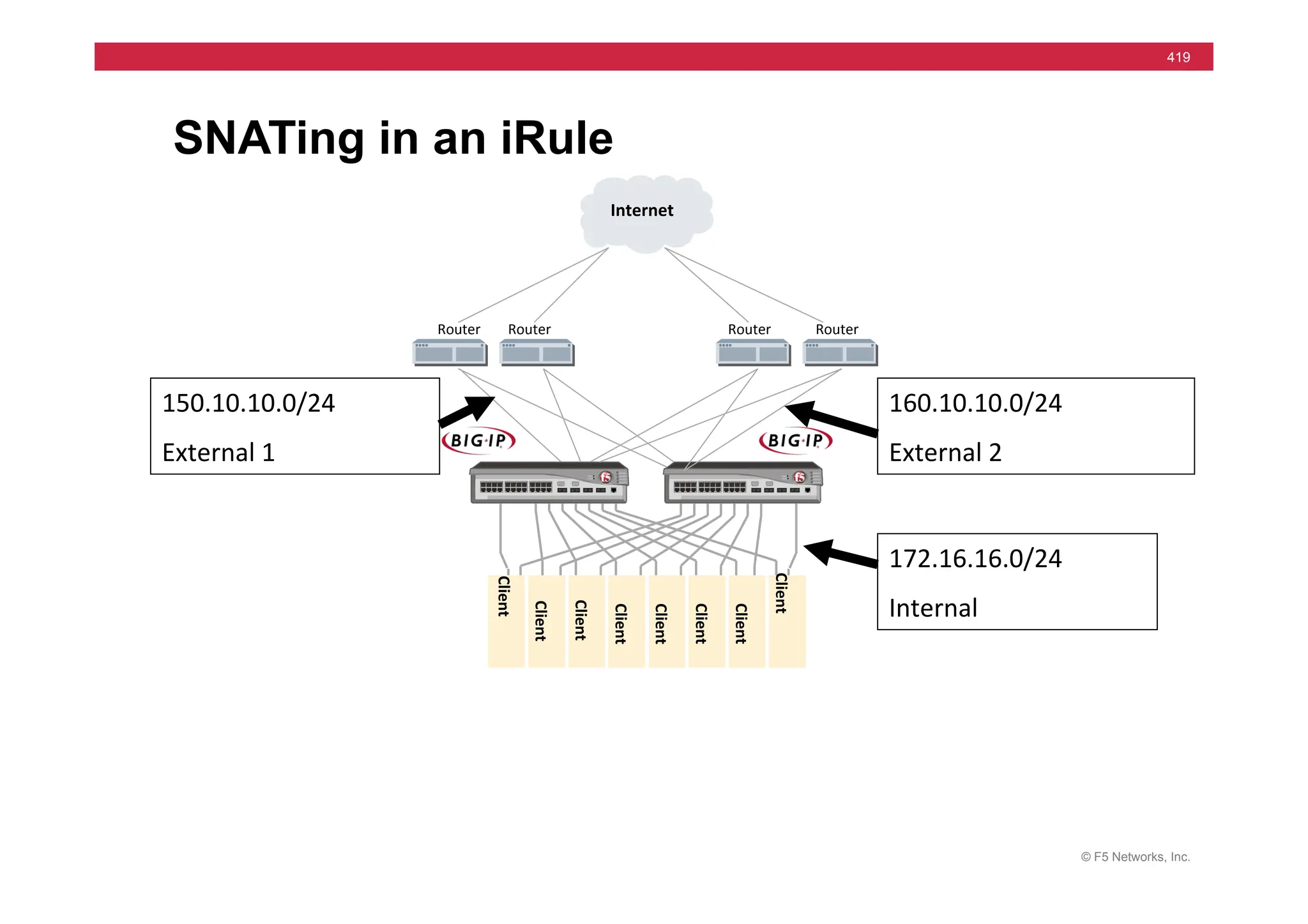
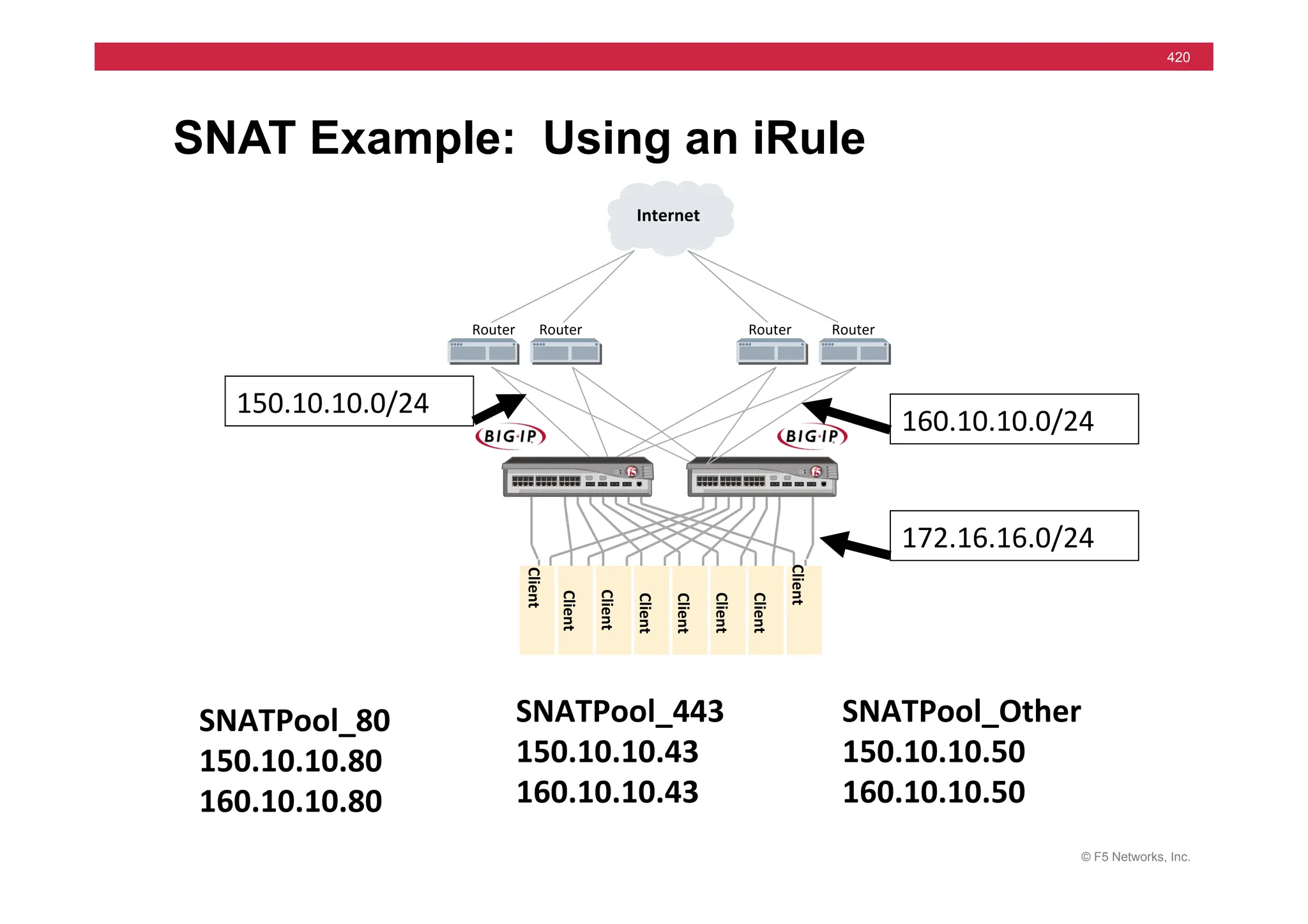
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
421
SNAT Example: Using an iRule
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
if
{
[TCP::local_port]
==
80
}
{
snatpool
SNATPool_80
}
elseif
{
[TCP::local_port]
==
443
}
{
snatpool
SNATPool_443
}
else
{
snatpool
SNATPool_Other
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-421-2048.jpg)

![© F5 Networks, Inc.
430
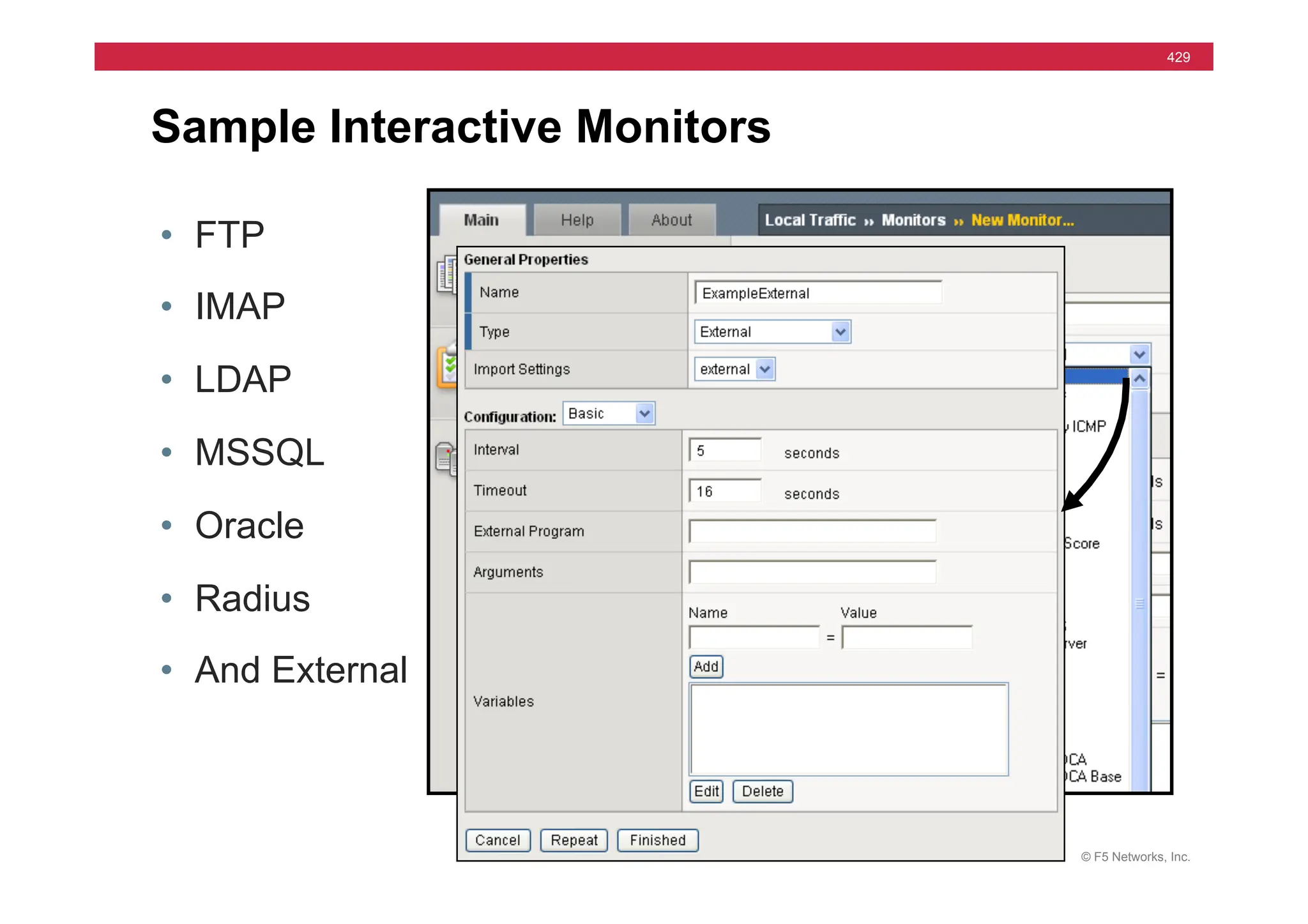
• EAV – Extended Application Verification
• External Program
• Independent Action
• Positive Results à “up” to standard out
status=$?
if
[
$status
–eq
0
]
then
echo
“up”
fi
Portion of an External Monitor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-430-2048.jpg)
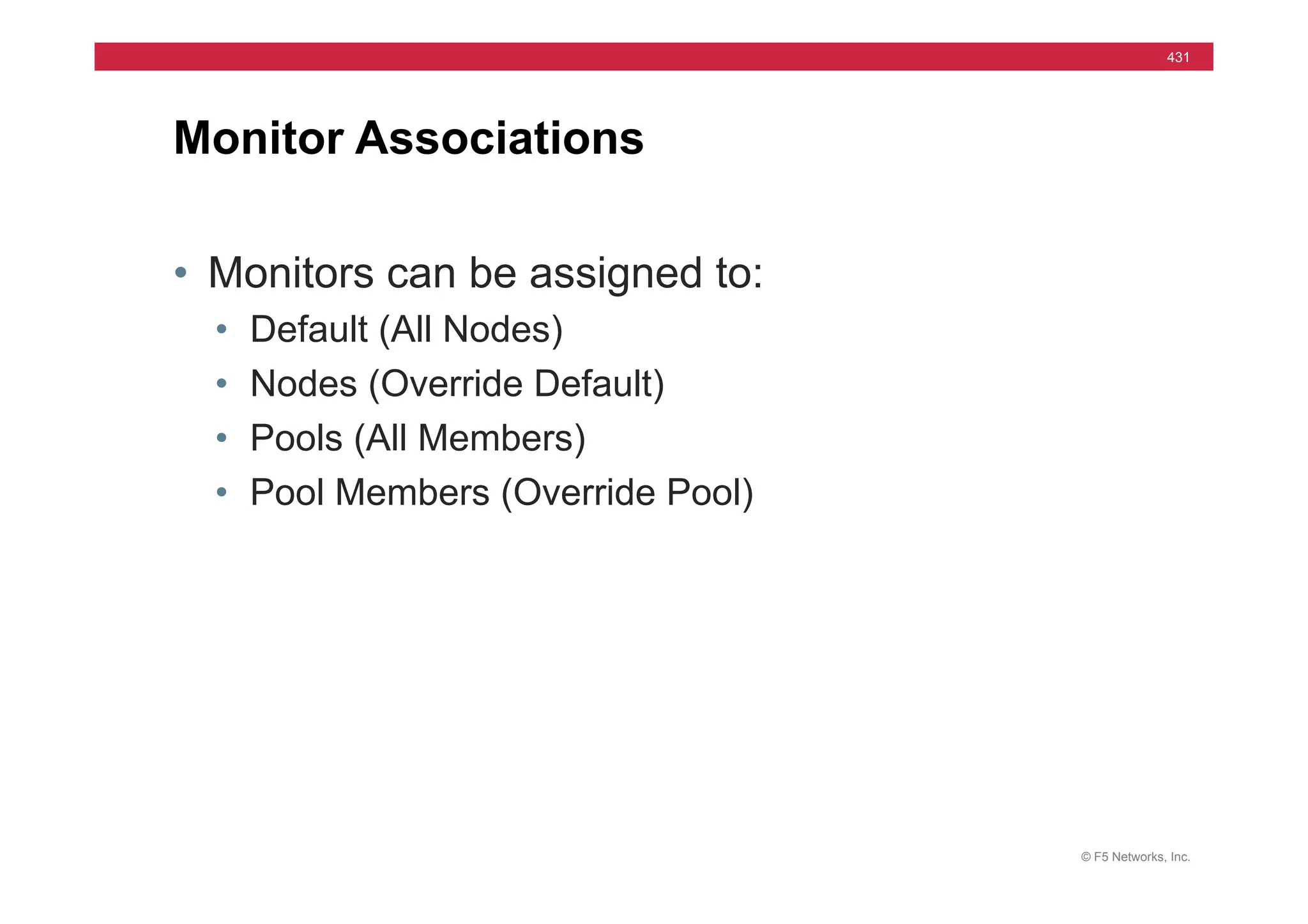
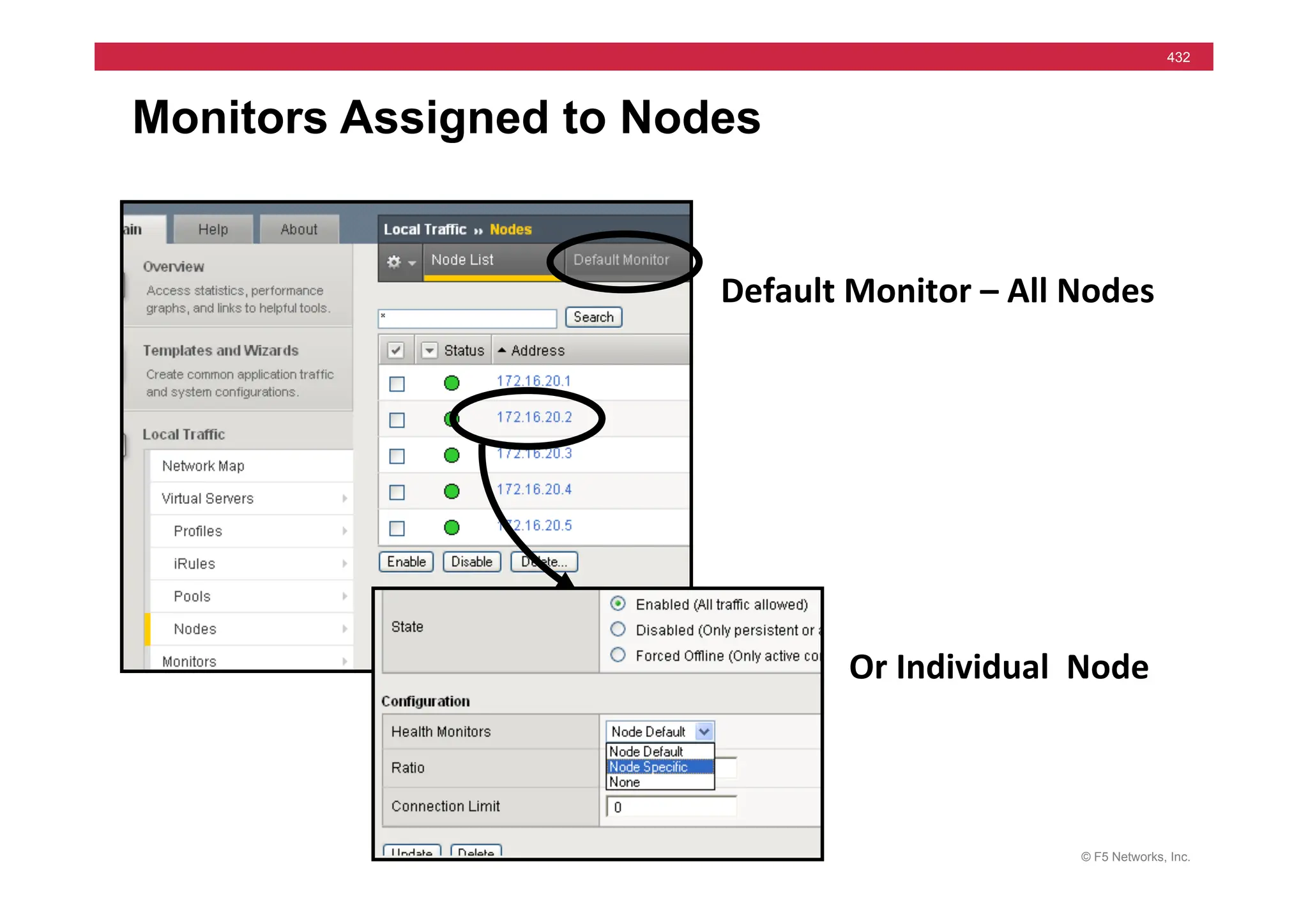
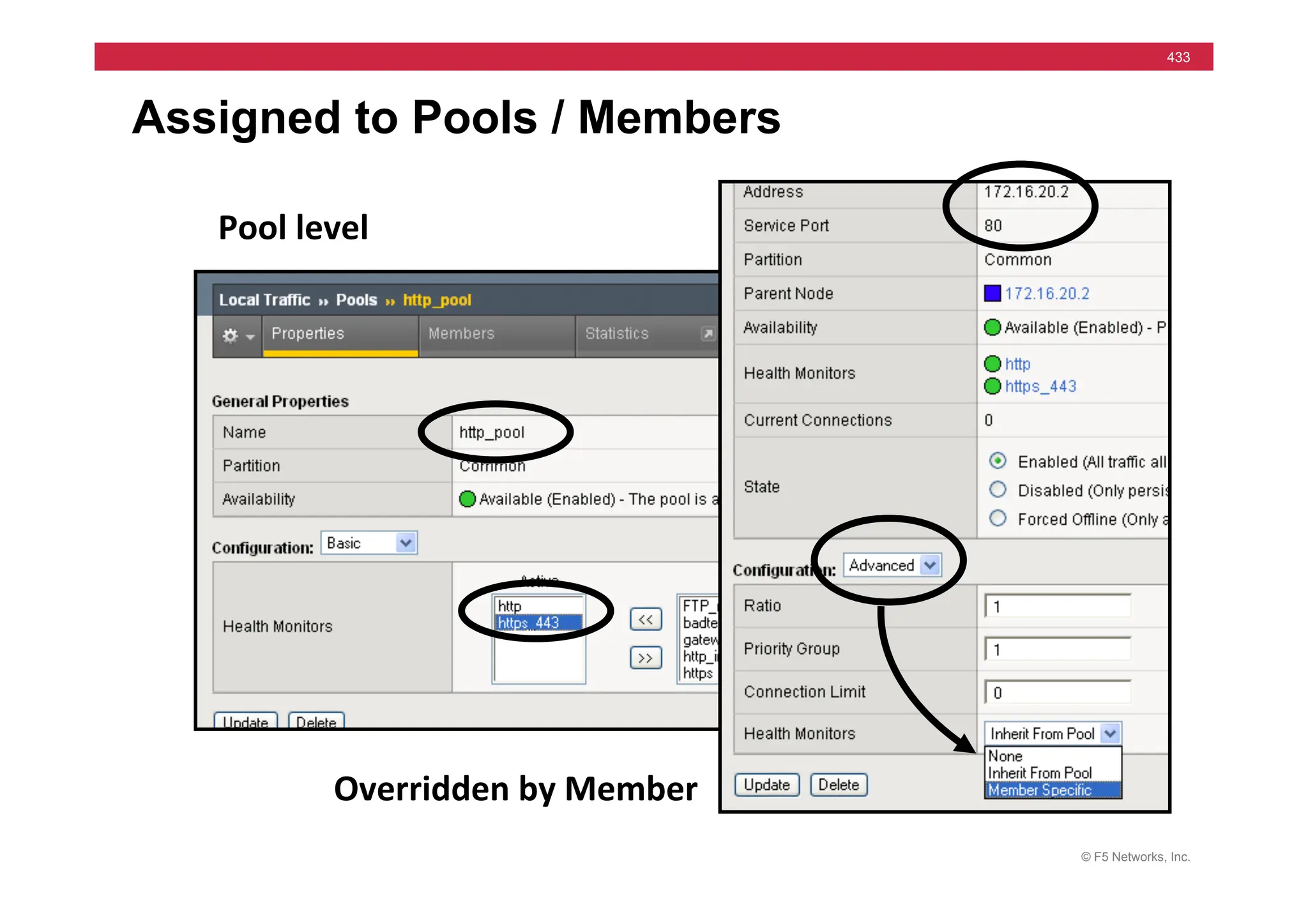
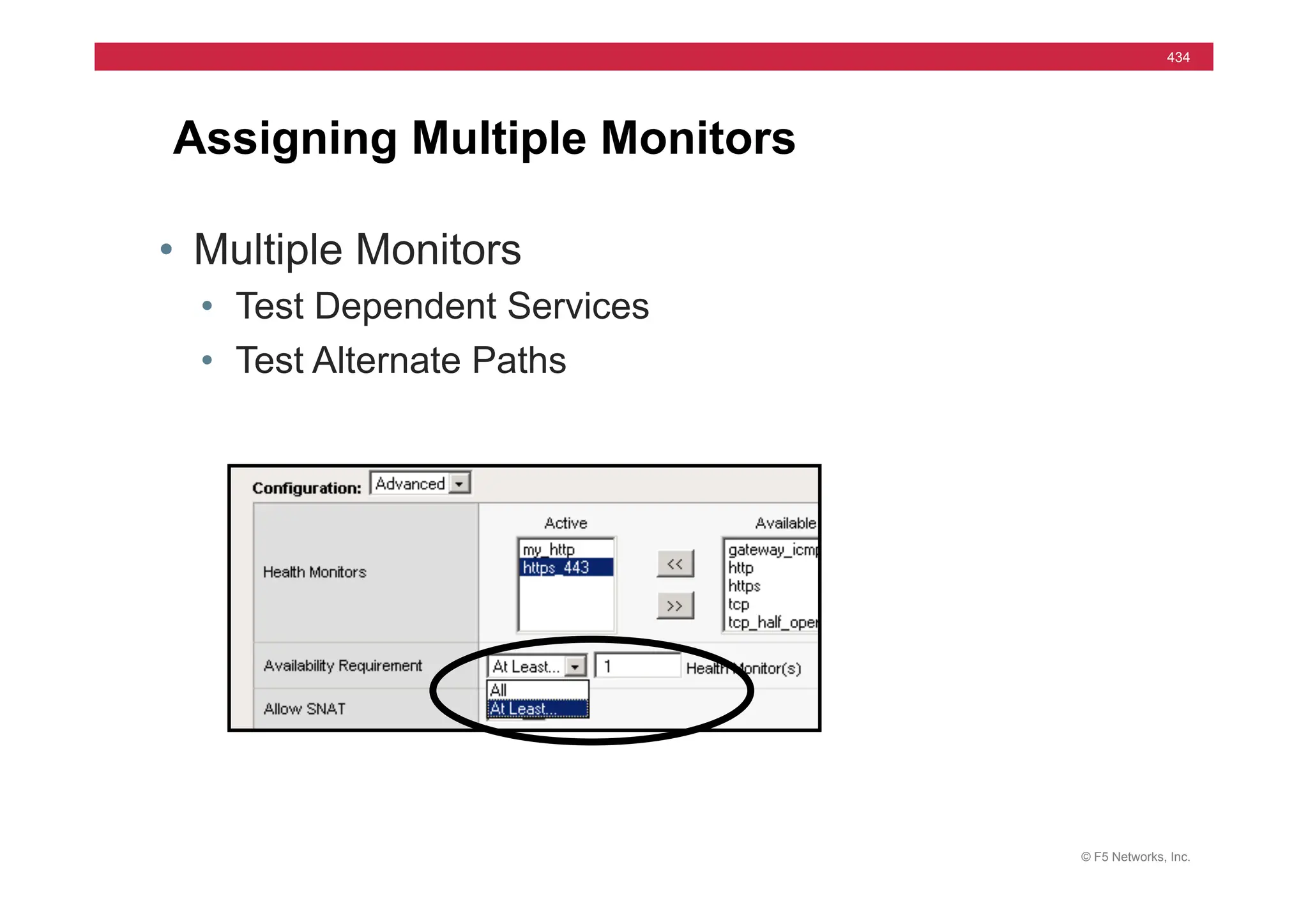

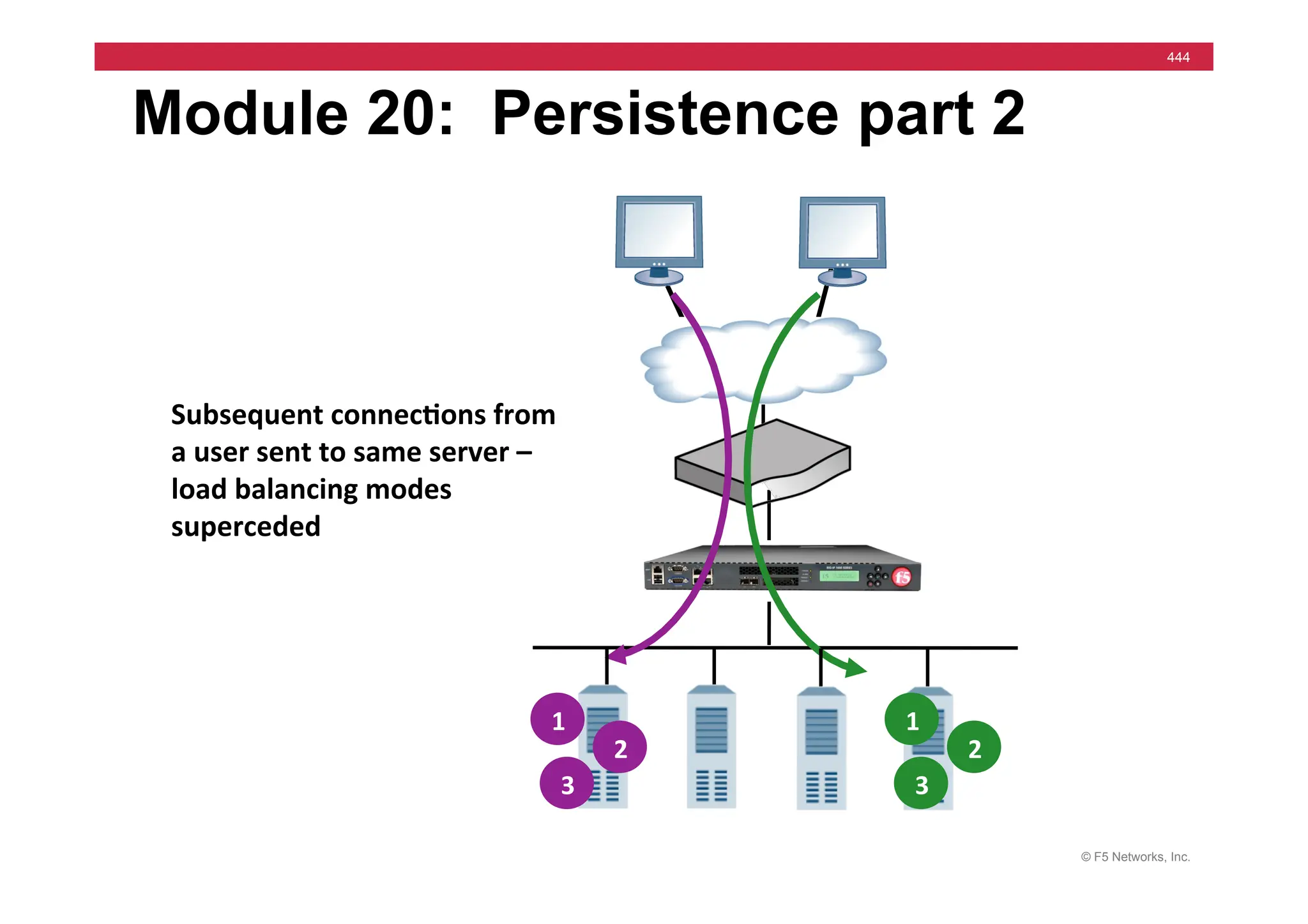

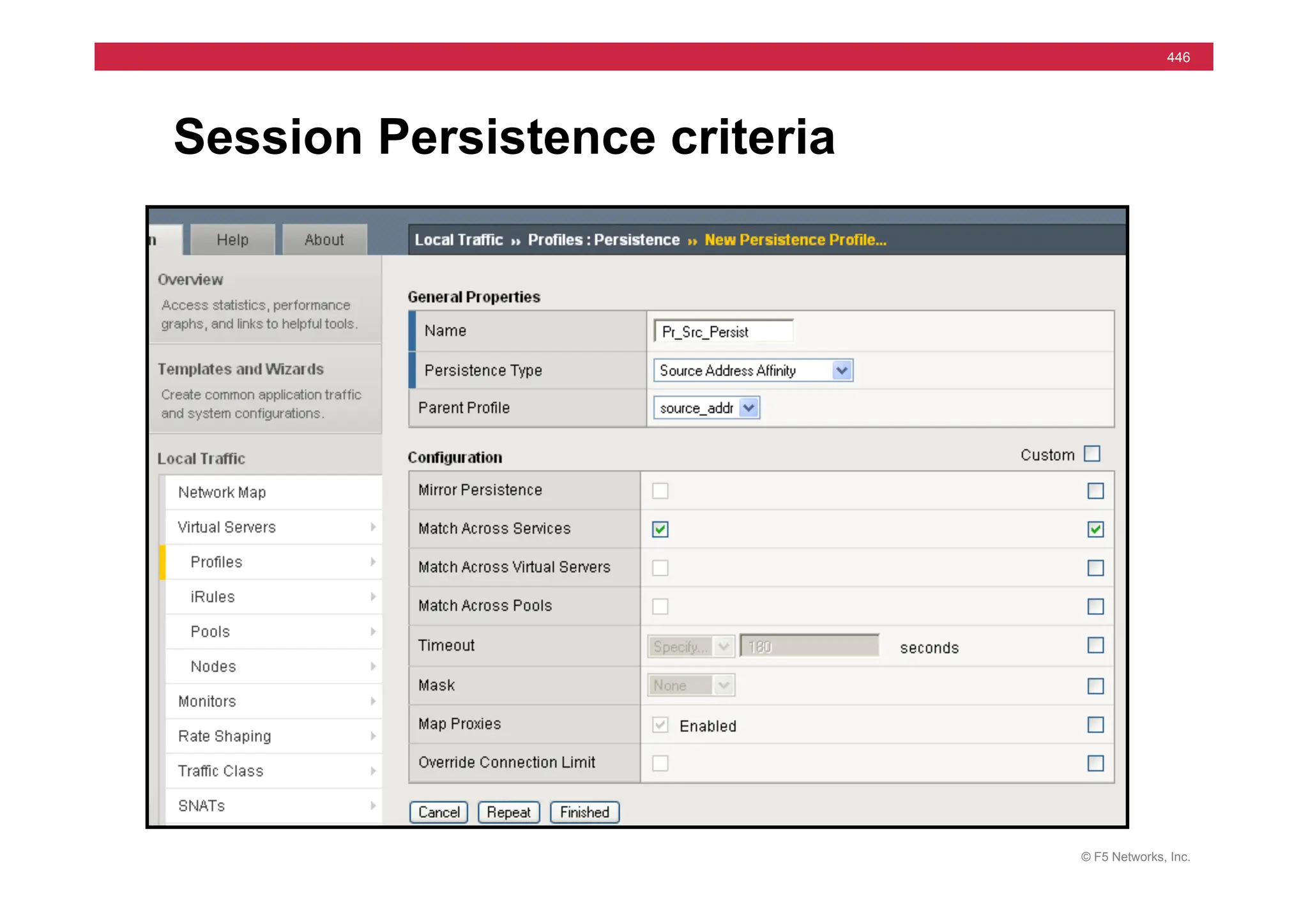


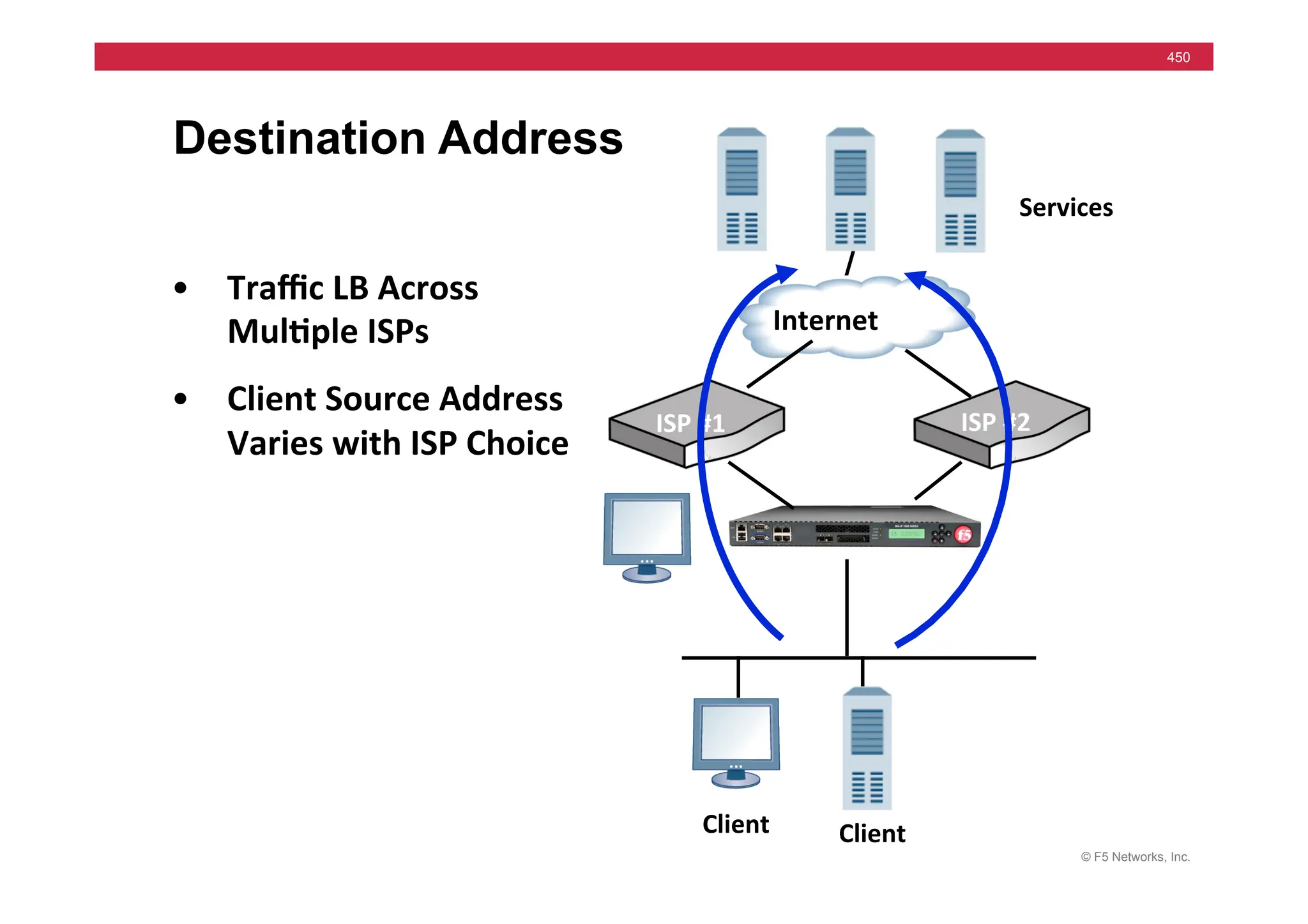
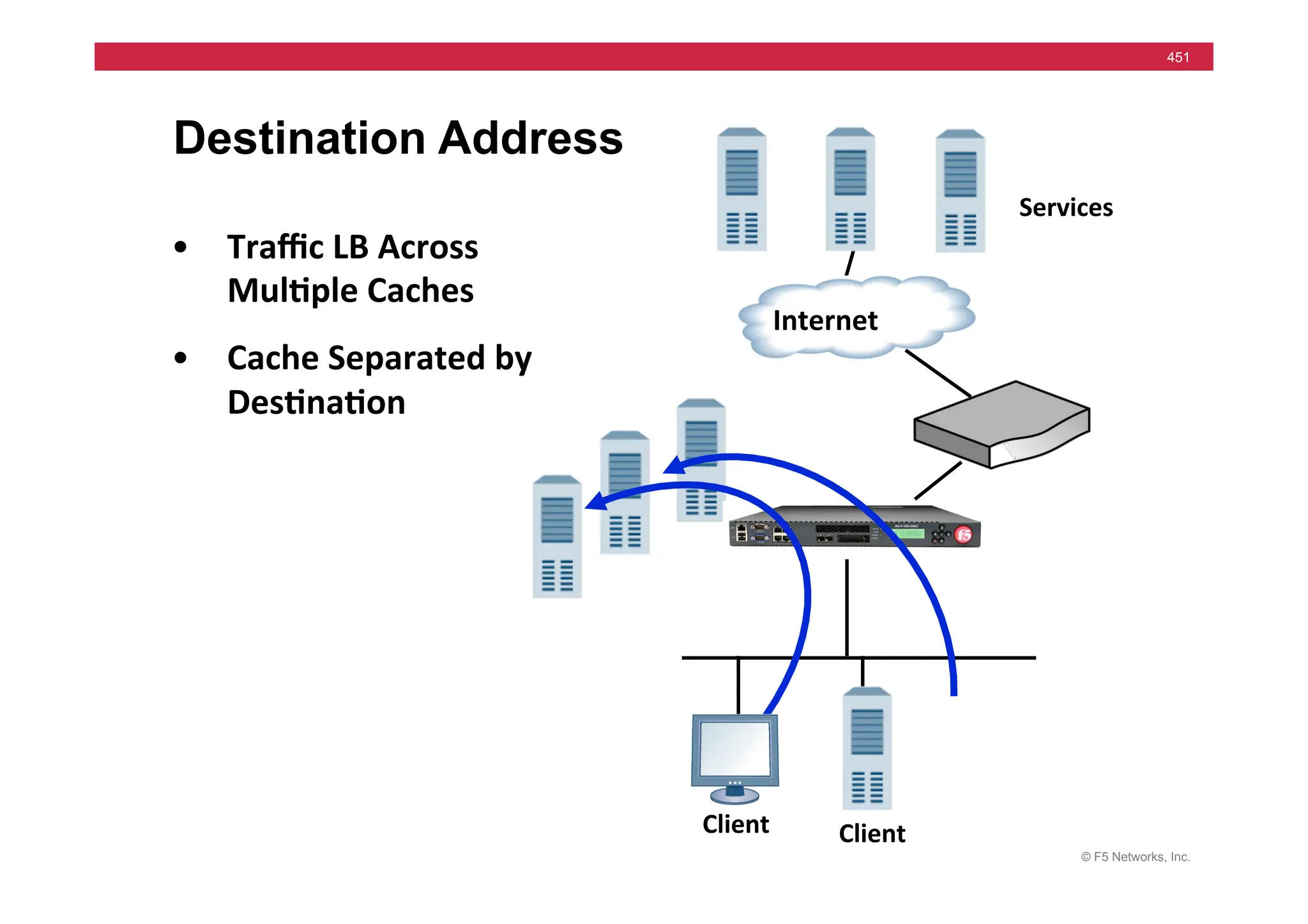
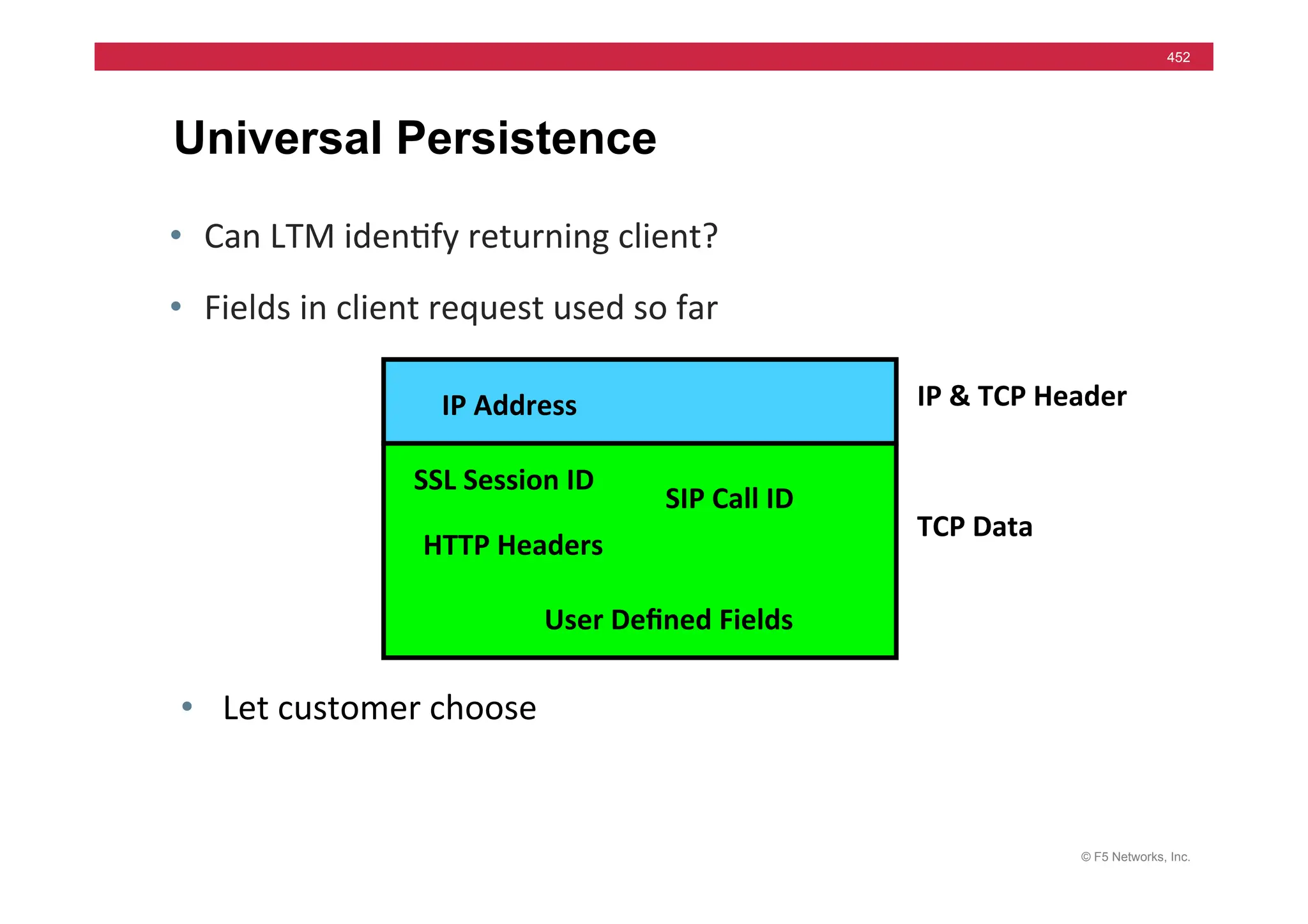
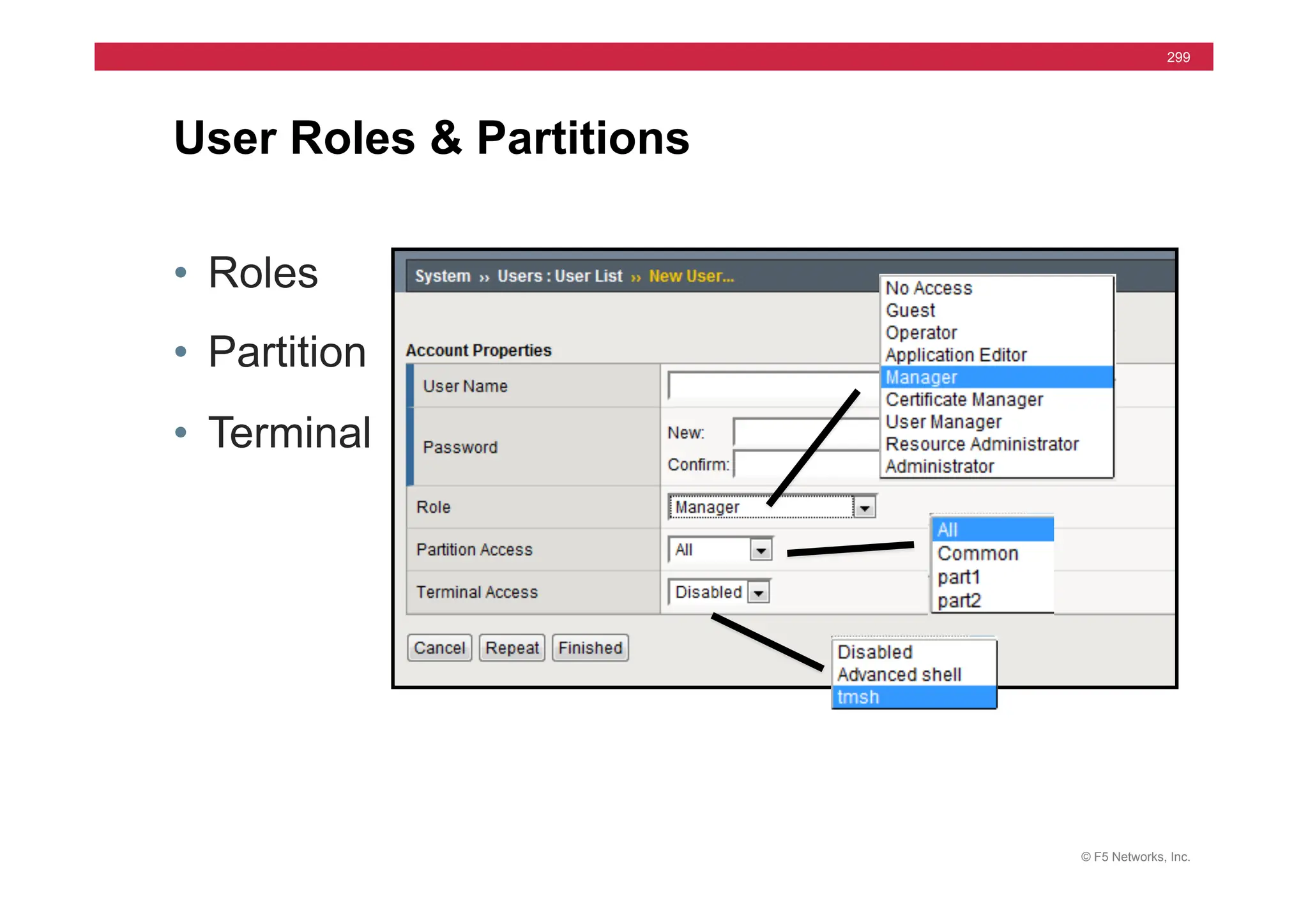
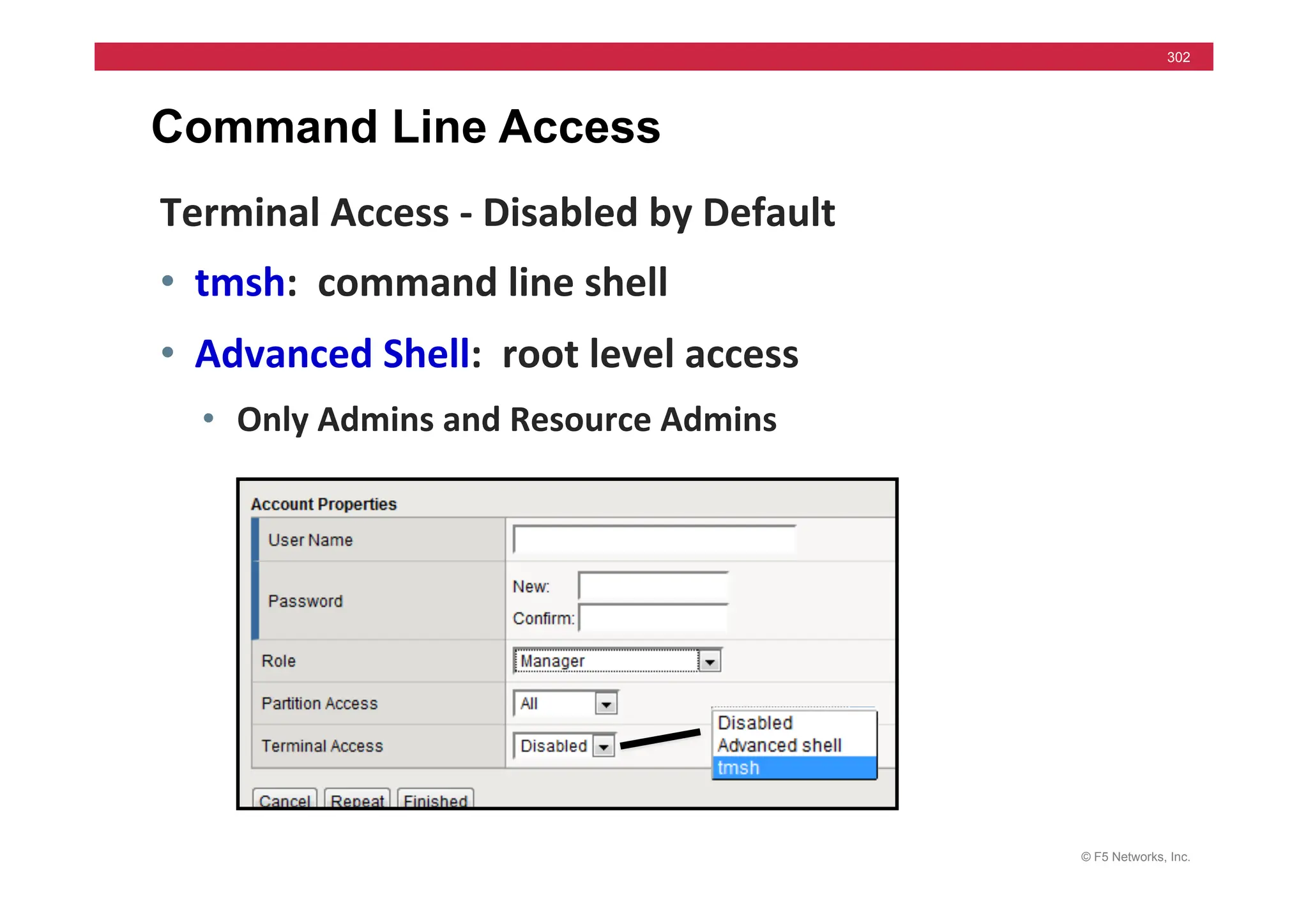
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
453
Universal Persistence
• Persist
on
any
part
of
packet
• Syntax
based
on
iRules
when
HTTP_REQUEST
{
persist
uie
[findstr
[HTTP::uri]
“user=“
5
“&”
]
}
hMp://www.test.com/?env.cgi&user=abc&pw=456
More
detail
on
findstr
command
–
iRules
Part
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-453-2048.jpg)
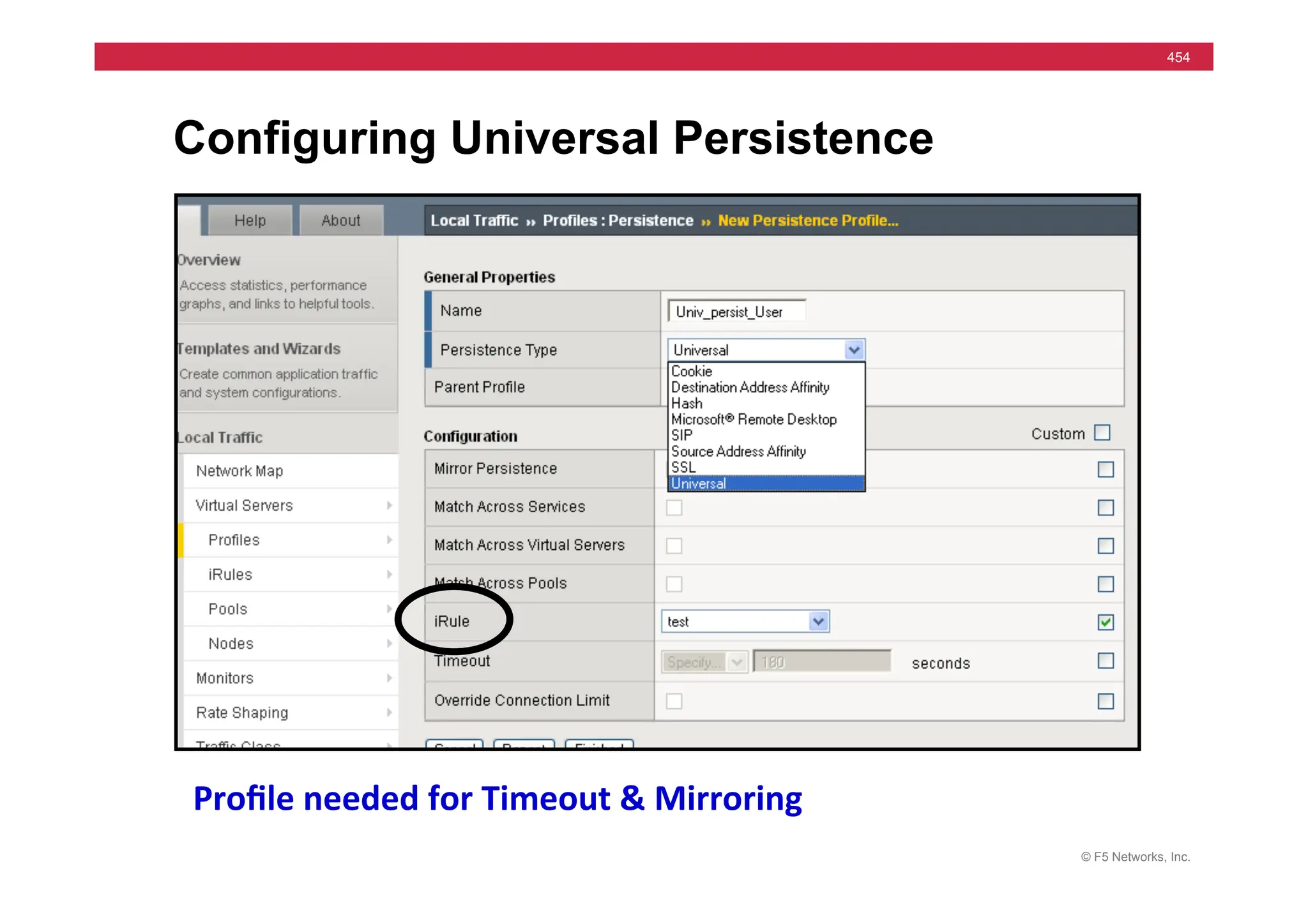
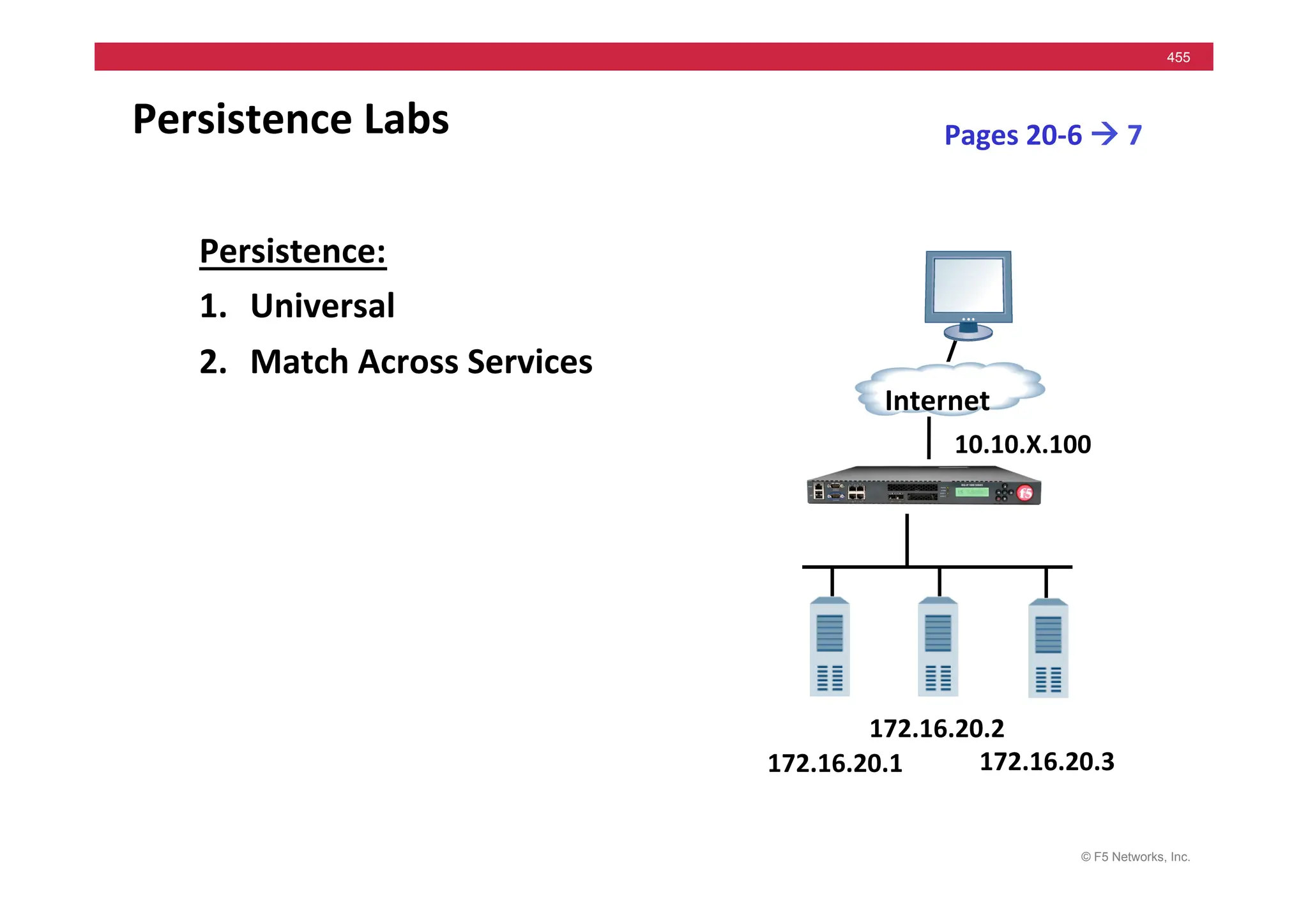
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
456
Module 21 – iRules part 2
Internet
when
CLIENTSSL_HANDSHAKE
{
if
{
[[IP::remote_addr]
equals
10.10.10.10
]}
{
pool
my_pool
}
}
my_pool
Default](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-456-2048.jpg)

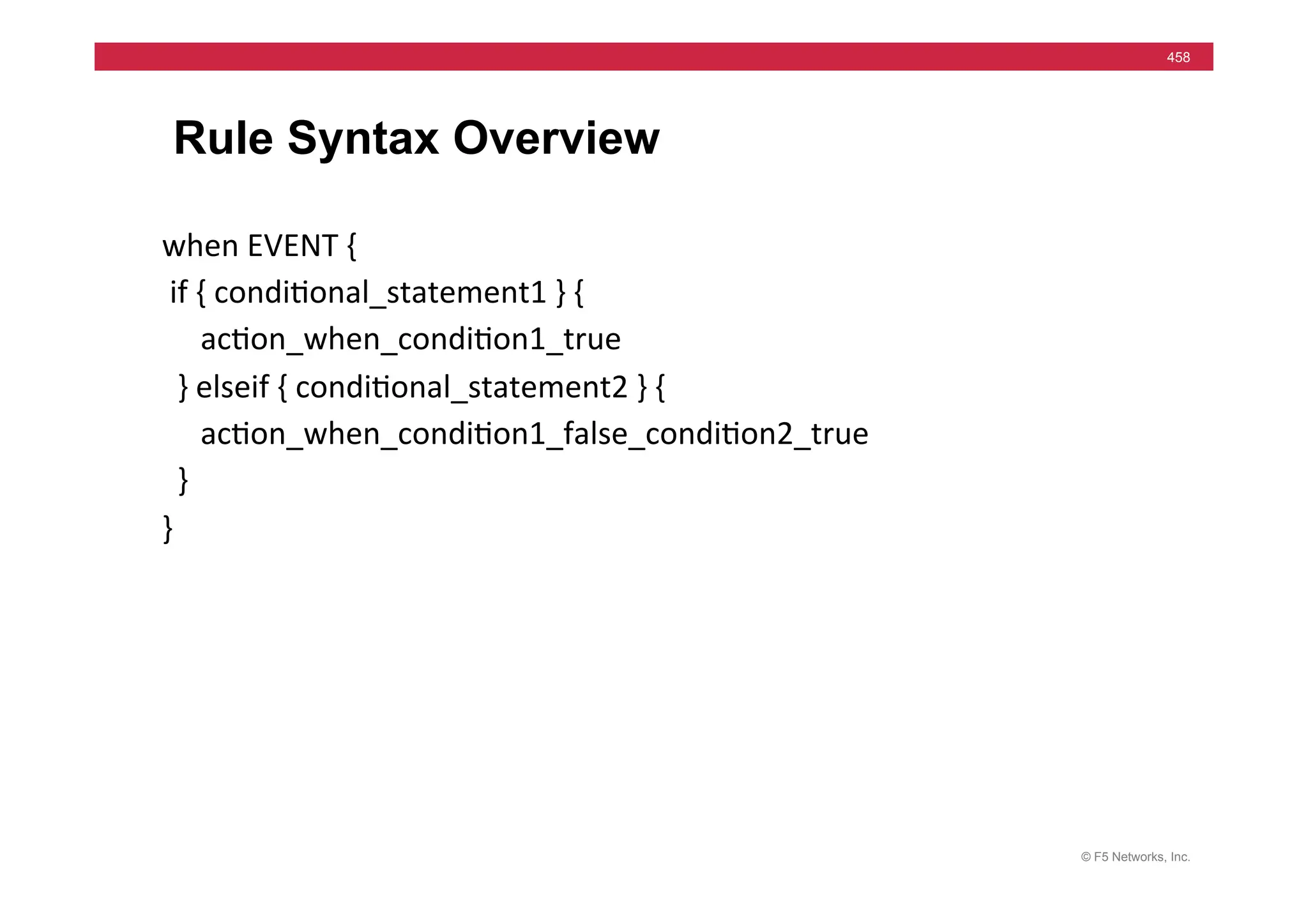
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
459
TCL Syntax Example
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
set
MYPORT
[TCP::local_port]
#log
local0.
"Port
is
$MYPORT"
switch
$MYPORT
{
80
{
snatpool
SNATPool_80
pool
hMp_pool
}
443
{
snatpool
SNATPool_443
pool
hMps_pool
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-459-2048.jpg)
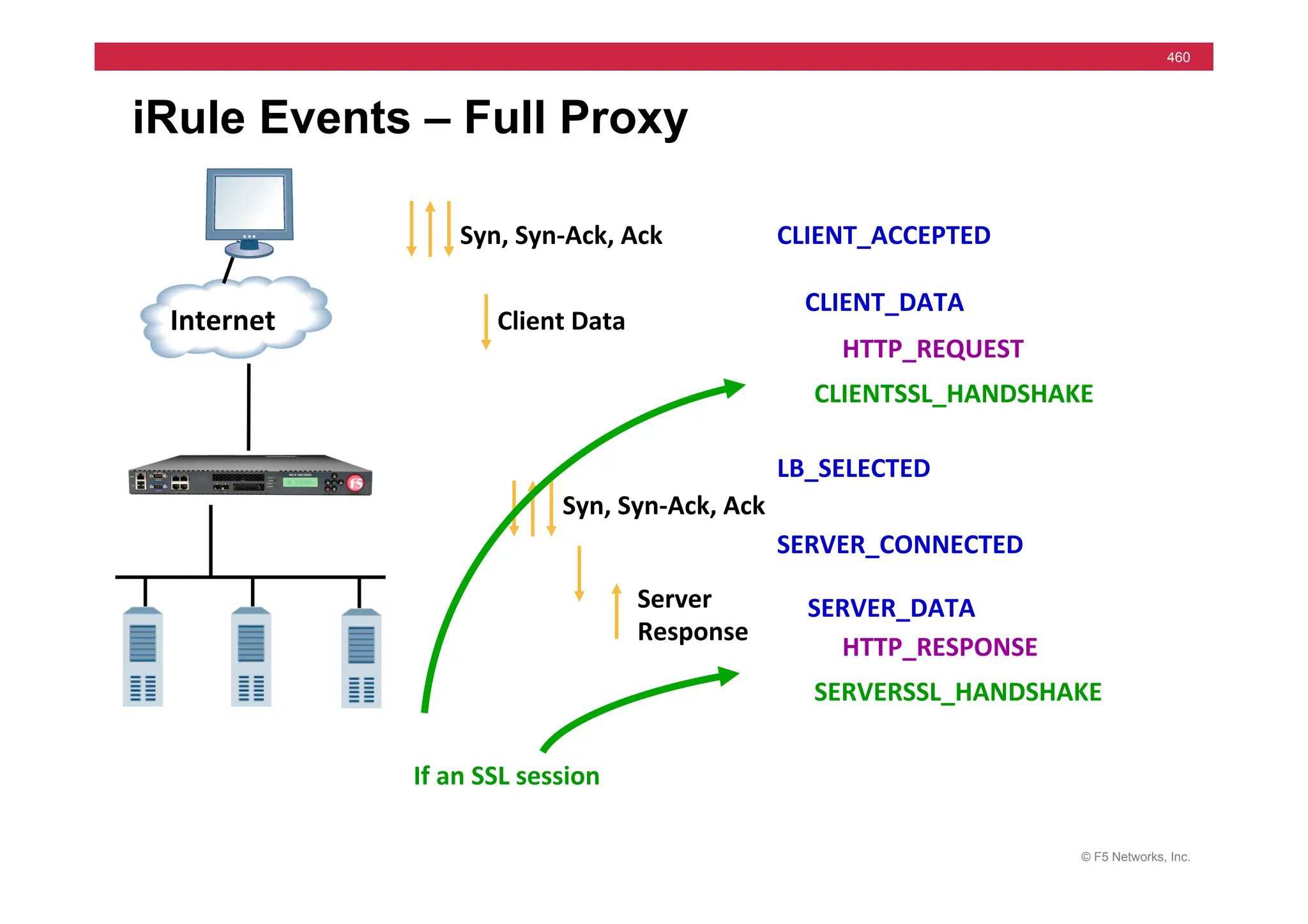
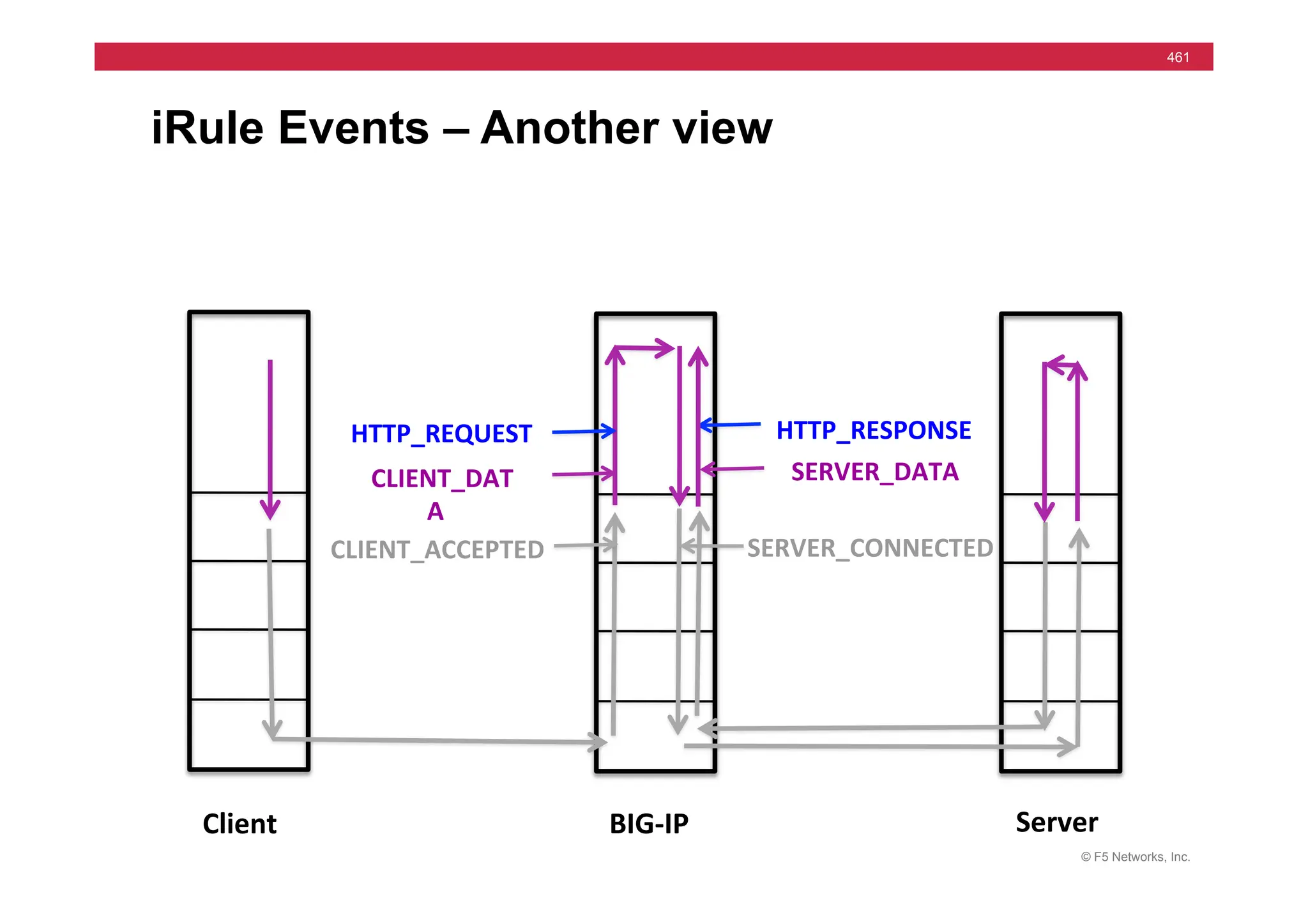
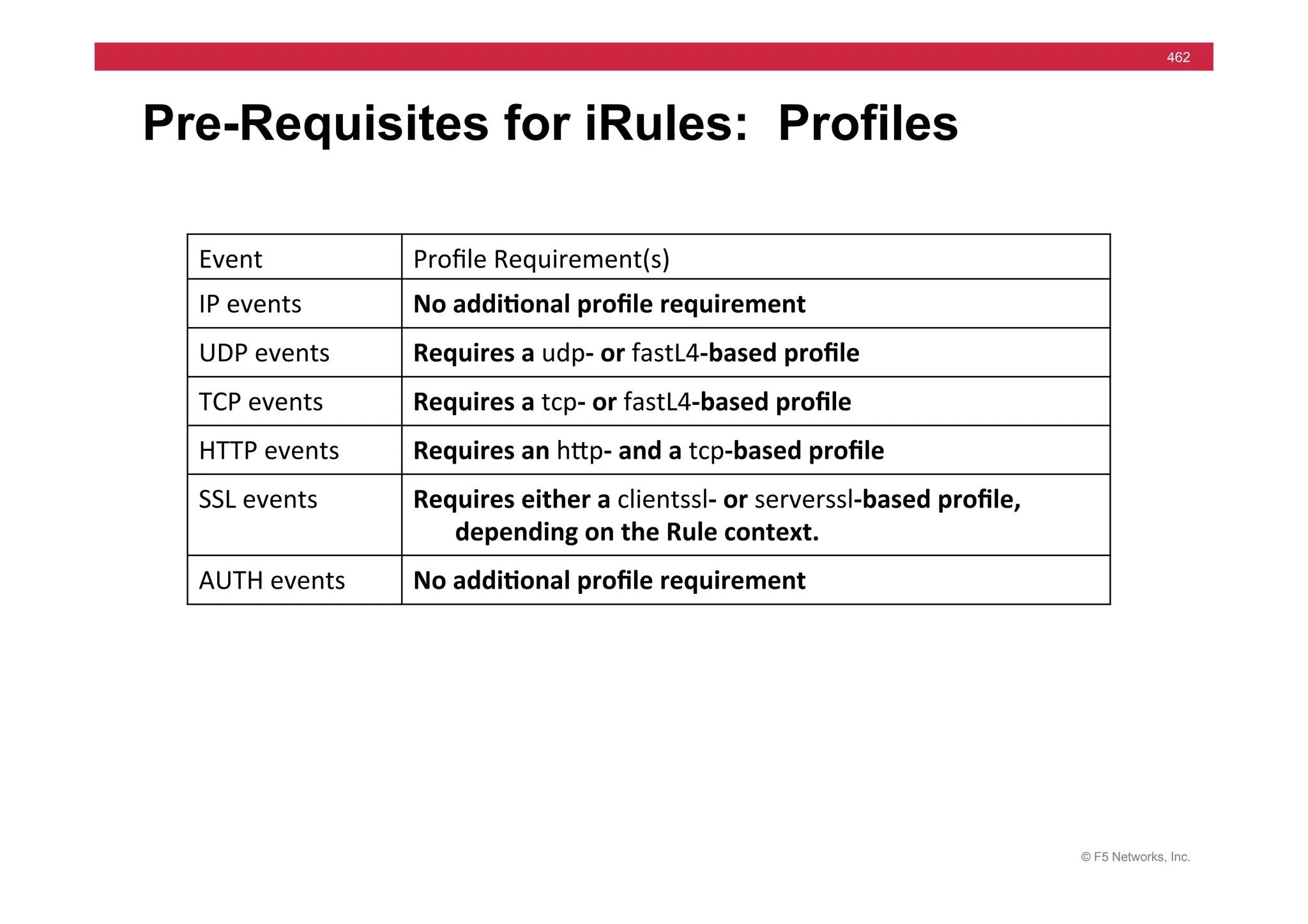



![© F5 Networks, Inc.
469
Example HTTP Commands
iRule Command Result
HTTP::header
[value] <name>
Returns value of the http header named <name>.
The “value” keyword can be omitted if the
<name> does not collide with any of the header
subcommands.
HTTP::header count Returns the number of http headers present on
the request or response.
HTTP::method Returns the type of HTTP request method.
HTTP::status Returns the response status code.
HTTP::uri
[<string>]
Set/Get the complete uri of the request.
HTTP::is_redirect Returns true if the response is a 3XX redirect.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-469-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
470
Example TCP Commands
iRule Command Result
TCP::remote_port Returns the current context’s remote TCP
port/service number.
TCP::local_port Returns the current context’s local TCP port/
service number.
TCP::payload [<size>] Returns the collected TCP data content.
TCP::payload length Returns the amount of collected TCP data
content in bytes.
TCP::collect <length> Causes TCP to start collecting the specified
amount of payload data and executes the
TCP_DATA rule event when this occurs.
TCP::release Causes TCP to resume processing the
connection and flushes collected data.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-470-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
471
Example UDP Commands
iRule Command Result
UDP::remote_port Returns the current context’s remote UDP
port/service number.
UDP::local_port Returns the current context’s local UDP port/
service number.
UDP::payload [<size>] Returns the current UDP payload content.
UDP::payload length Returns the amount of UDP payload content
in bytes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-471-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
472
iRule Context
With
reference
to
whom?
Internet
Client
Side
Server
Side
when
CLIENT_ACCEPTED
{
if
{
[[IP::remote_addr]
equals
…
when
SERVER_CONNECTED
{
if
{
[[clientside[IP::remote_addr]
equals
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-472-2048.jpg)

![© F5 Networks, Inc.
474
findstr Example
when
HTTP_REQUEST
{
if
{
[
findstr
[HTTP::uri]
"user="
5
"&"
]
starts_with
“A"
}
{
pool
Alogin_pool
}
elseif
{
[
findstr
[HTTP::uri]
"user="
5
"&"
]
starts_with
“B"
}
{
pool
Blogin_pool
}
else
{
pool
other_pool
}
}
hMp://host/path/file.ext?parameters
hMp://host/path/file.ext?comp=F5;user=B23456&...
HTTP::uri](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-474-2048.jpg)
![© F5 Networks, Inc.
475
iRule Logging
• iRules can cause content / status to be logged
• To log into /var/log/ltm:
log local0. “[<strings>]”
• Example:
log local0. “[ findstr [HTTP::uri] "user=" 5 "&" ]”
• Best Practice: log value iRule uses
• High Speed Logging](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/f5-configuringbig-ipltmv11-instructorppt-240802062548-4572a3f1/75/F5-Configuring-BIG-IP-LTM-v11-Instructor-PPT-pdf-475-2048.jpg)