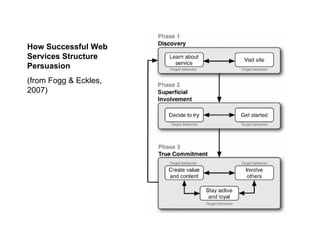
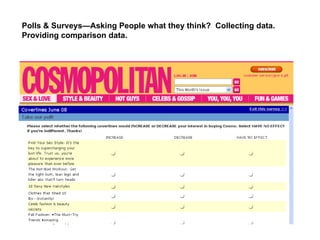
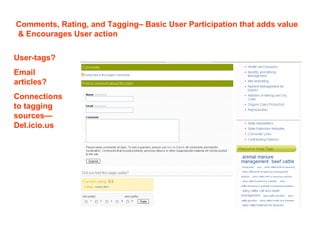
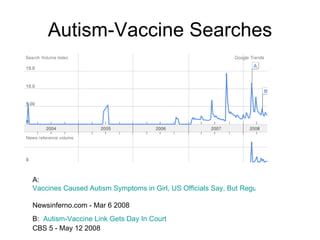
The document discusses the transition from traditional web usage to a Web 2.0 model, emphasizing interaction, participation, and community engagement. It highlights the significance of collaborative learning, user-generated content, and diverse media in fostering active learning environments. The text also explores the motivations behind community participation and the roles individuals play in learning communities.