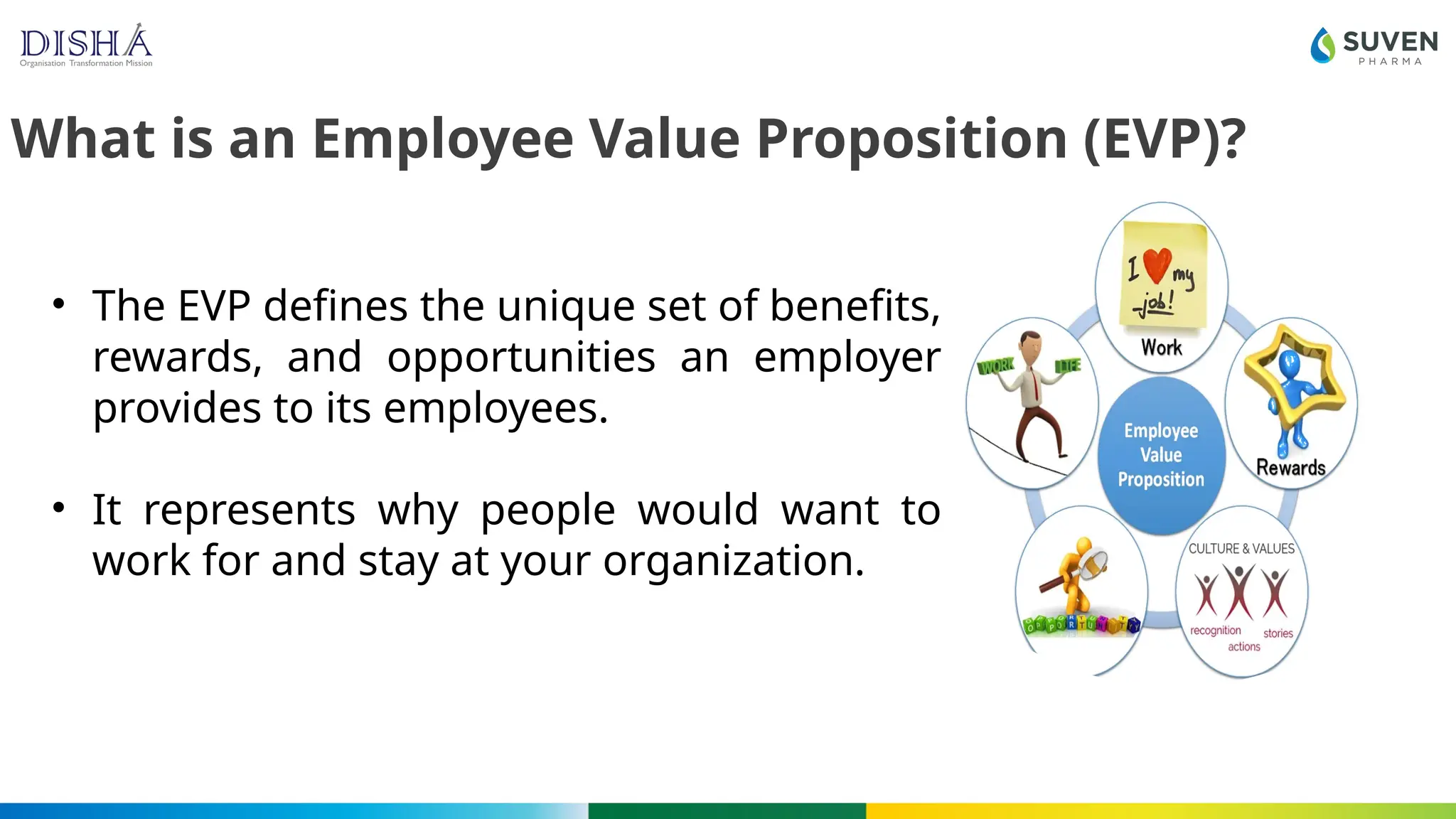
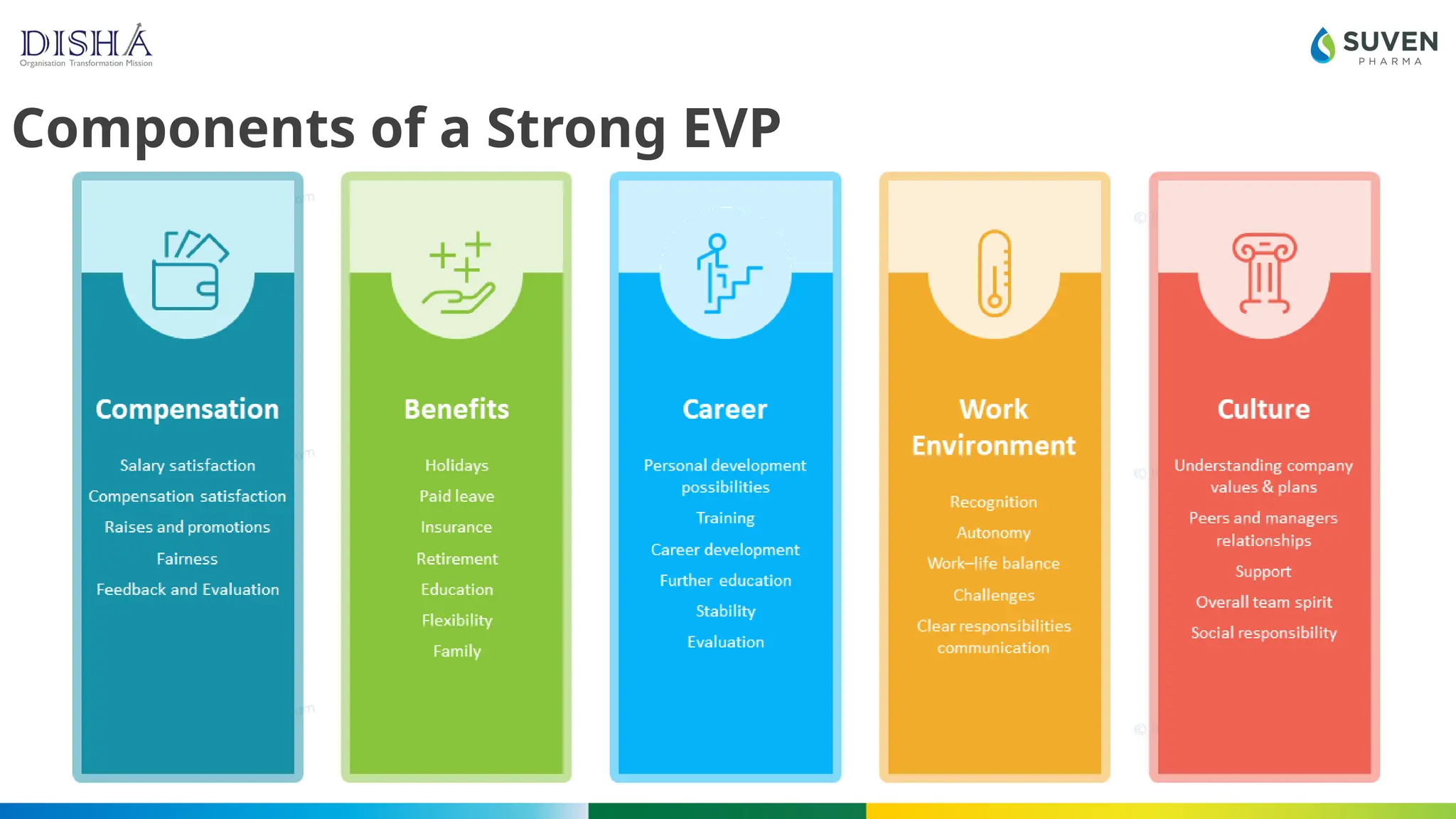
The document discusses the concept and importance of Employee Value Proposition (EVP), highlighting how it attracts talent, enhances retention, and improves engagement. It outlines the components of a strong EVP with examples from companies like Google and Netflix, and offers guidance on creating and measuring an effective EVP. The conclusion emphasizes that EVP is a strategic asset essential for business success in evolving workplaces.