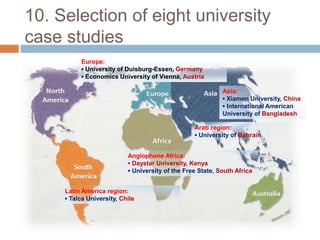
The document discusses a research project by IIEP that explores innovative methods for internal quality assurance (IQA) in higher education, highlighting the challenges and the need for sustainable improvement. It outlines a case study approach involving eight universities across various regions, aiming to understand effective IQA systems and their impact on academic quality and management. The methodology includes qualitative and quantitative data collection, while acknowledging limitations in generalizability and focus areas.