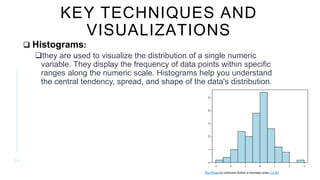
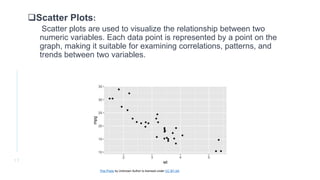
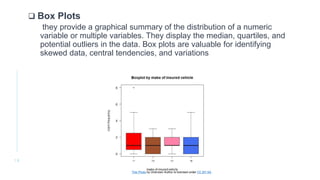
Exploratory data analysis (EDA) is an approach to analyze data using visual techniques to discover trends and patterns. EDA involves understanding the data, detecting issues, discovering patterns, and visualizing relationships. The key steps in EDA are data collection, cleaning, visualization, transformation, summarization, and feature selection. EDA plays a foundational role by assessing data quality, understanding characteristics, and testing assumptions to build accurate statistical models. Common EDA techniques include histograms, scatter plots, box plots, and heatmaps to visualize univariate and bivariate relationships in the data.