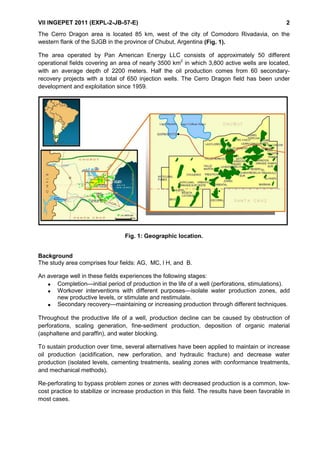
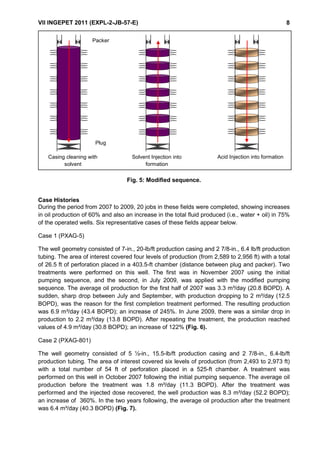
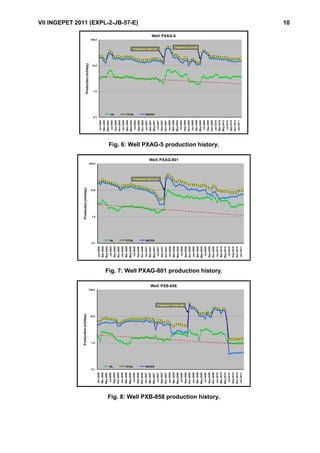
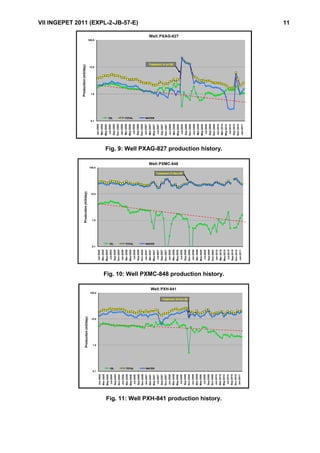
This document summarizes the results of using coiled tubing and a true fluidic oscillator tool to stimulate 20 low production wells in the San Jorge Gulf area of Argentina. Deposits of paraffin, asphaltene, and calcium carbonate were causing damage to the wells. The fluidic oscillator tool generated pressure waves of 300-600 Hz to weaken and remove near-wellbore damage. Treatments of solvent followed by acid were pumped selectively into zones. The approach achieved production increases in oil rates of 30-365% and total fluid rates in 75% of wells. It provides a more cost-effective alternative to conventional well interventions.