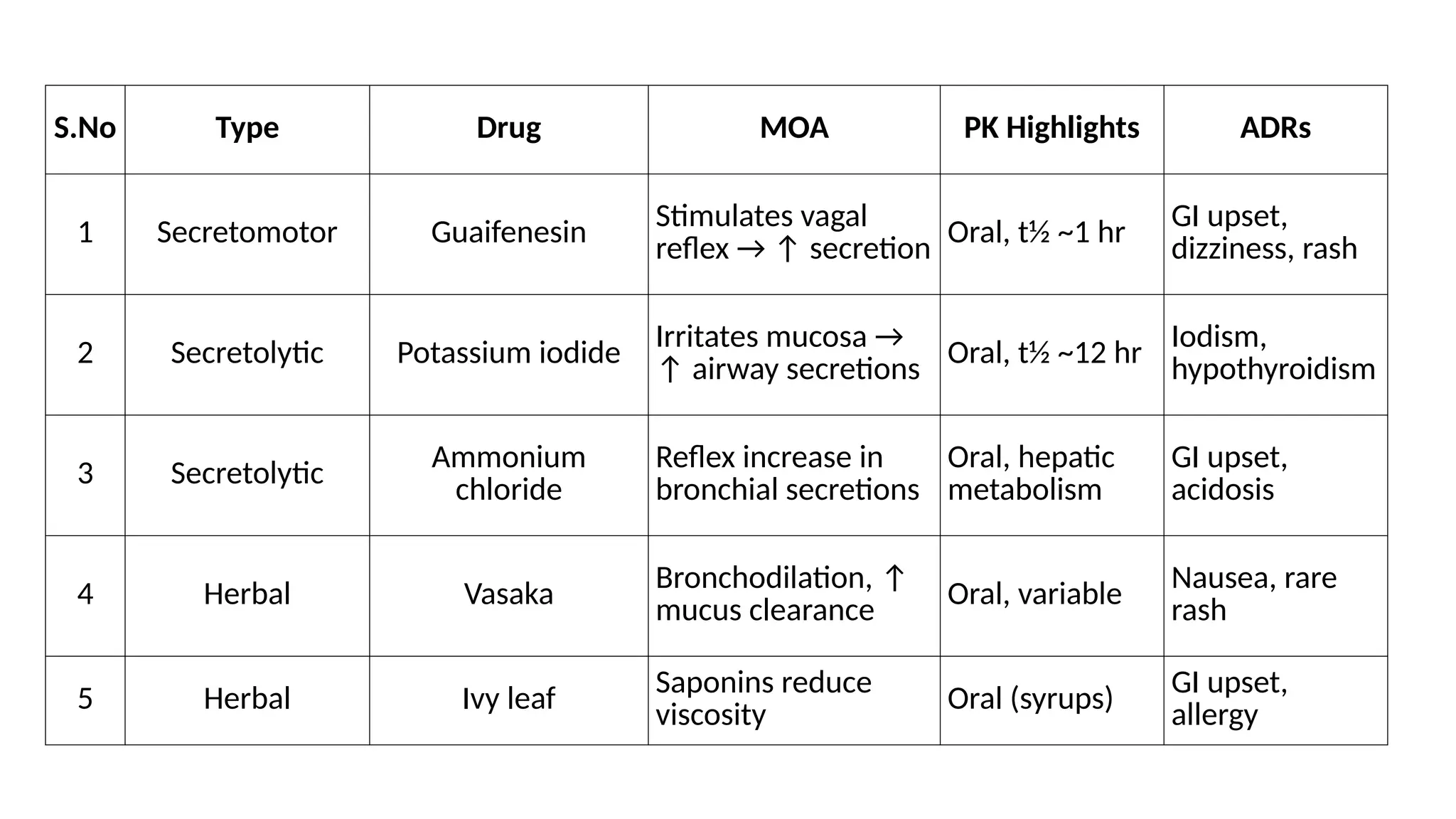
Expectiorants, Classification, MOA, Pk parameters, Therapeutic uses and ADRs
Expectorants are drugs that enhance the expulsion of mucus from the airways by increasing the volume or hydration of respiratory secretions. They are mainly used in productive (wet) coughs where sputum clearance is needed.
1. Secretomotor Expectorants:
Guaifenesin
2. Secretolytic Expectorants:
Potassium iodide, Ammonium chloride
3. Natural Remedies / Herbal:
Vasaka (Adhatoda vasica), Ivy leaf extract, Eucalyptus