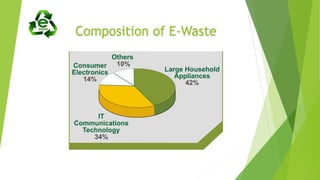
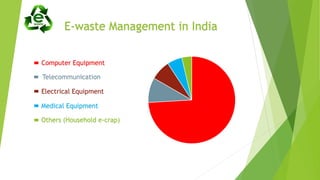
This document discusses e-waste and green computing. It defines e-waste as electronic products that are no longer working or obsolete, containing toxic materials. E-waste is generated from technology advances and short product lifecycles. Green computing aims to reduce hazardous materials and maximize energy efficiency throughout a product's lifecycle, including recycling. Some approaches are green disposal, design, manufacturing and use. Tips for individuals include using sleep/power save modes, LCD monitors, notebooks, and refilling cartridges.