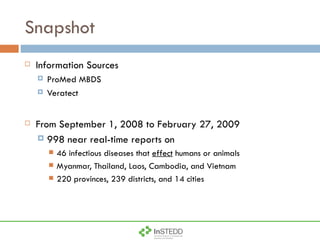
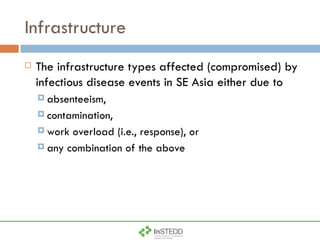
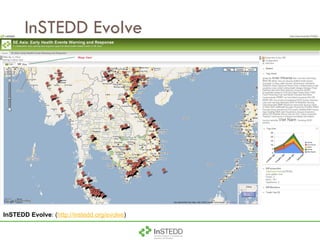
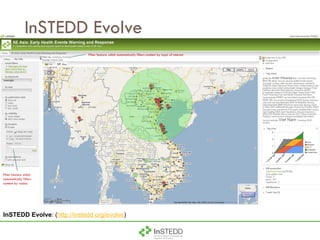
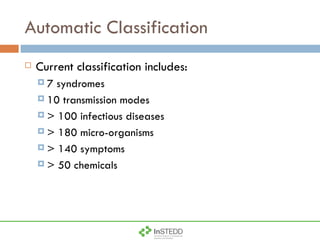
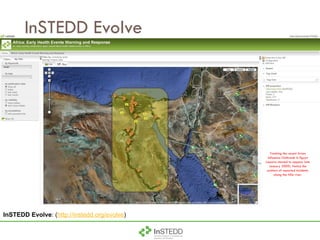
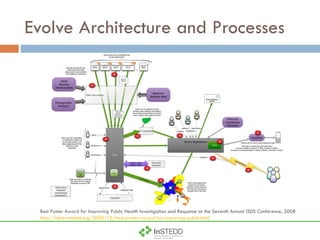
The document summarizes an information and communication technology forum on disease surveillance in the Mekong Basin held in Thailand in April 2009. It discusses efforts to create an early warning system for infectious disease events using various information sources. Key topics included estimating epidemiological patterns, analyzing social and infrastructure impacts, and classifying over 100 diseases and organisms using an online tool called InSTEDD Evolve.














![Thank You! InSTEDD 400 Hamilton Avenue, Suite 120 Palo Alto, CA 94301, USA +1.650.353.4440 +1.877.650.4440 (toll-free in the US) [email_address] Cambodia, Photo taken by Taha Kass-Hout, October 2008 “ this pic says it all- our kids are all the same- they deserve the same ”, Comment by Robert Gregg on Facebook, October 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evolvetahakass-houtmbds2009web-090403190423-phpapp01/85/Evolve-22-320.jpg)