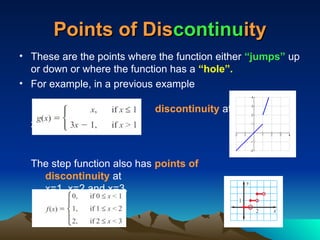
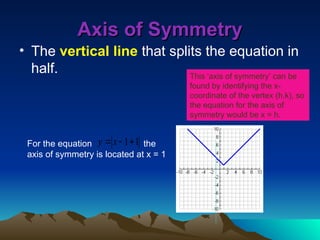
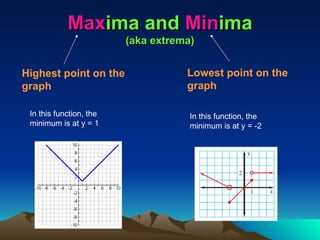
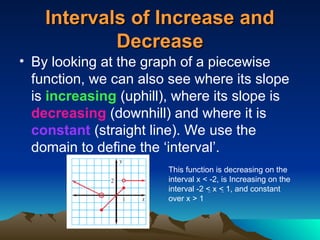
Piecewise functions consist of multiple equations, each applicable to different parts of the domain, requiring specific evaluations based on defined intervals. They can exhibit discontinuities where the function jumps or has holes, and the domain and range must be identified for proper evaluation. Additionally, features like the axis of symmetry and intervals of increase or decrease are crucial for understanding the behavior of these functions.