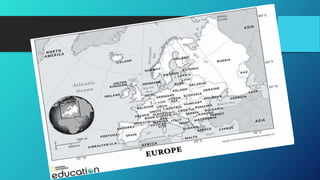
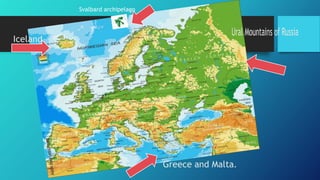
1) Europe is the second smallest continent located between the Arctic and North Atlantic oceans, extending from Iceland in the west to Russia in the east.
2) Europe is characterized by several peninsulas including the Iberian, Italian, Balkan, Scandinavian, and Jutland peninsulas which have made Europe an important economic and cultural force.
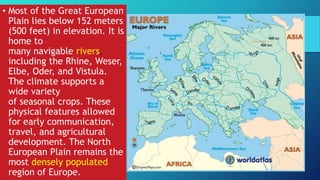
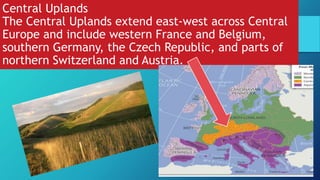
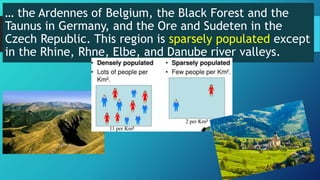
3) The continent can be divided into four main physical regions from north to south - the Western Uplands along its western edge including mountainous Scandinavia and the British Isles, the low-lying North European Plain extending east across northern Europe, the Central Uplands of western-central Europe, and the highest Alpine Mountains of southern Europe including