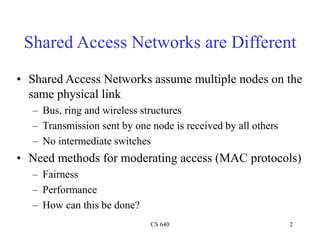
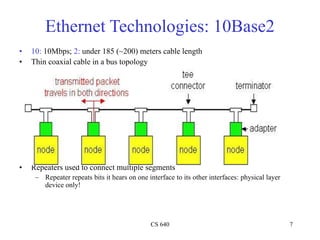
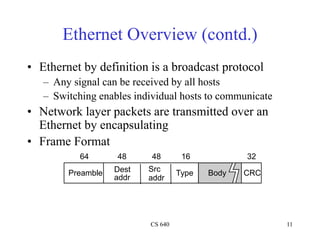
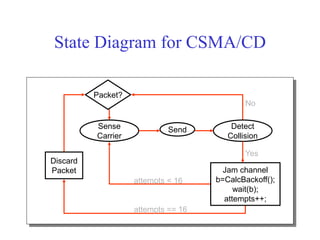
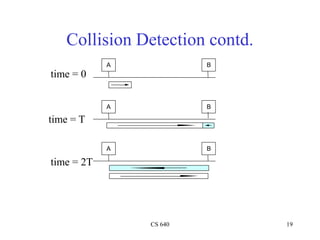
Ethernet is a widely used shared access network technology where multiple nodes share the same physical link. It uses CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) as its media access control protocol. When a node has a packet to transmit, it first listens to ensure the link is idle before transmitting. If a collision is detected during transmission, the node stops transmitting and performs exponential backoff before retransmitting. This helps ensure fair access among nodes. Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet were later developed to provide higher bandwidths up to 1Gbps while maintaining compatibility with Ethernet's CSMA/CD protocol.