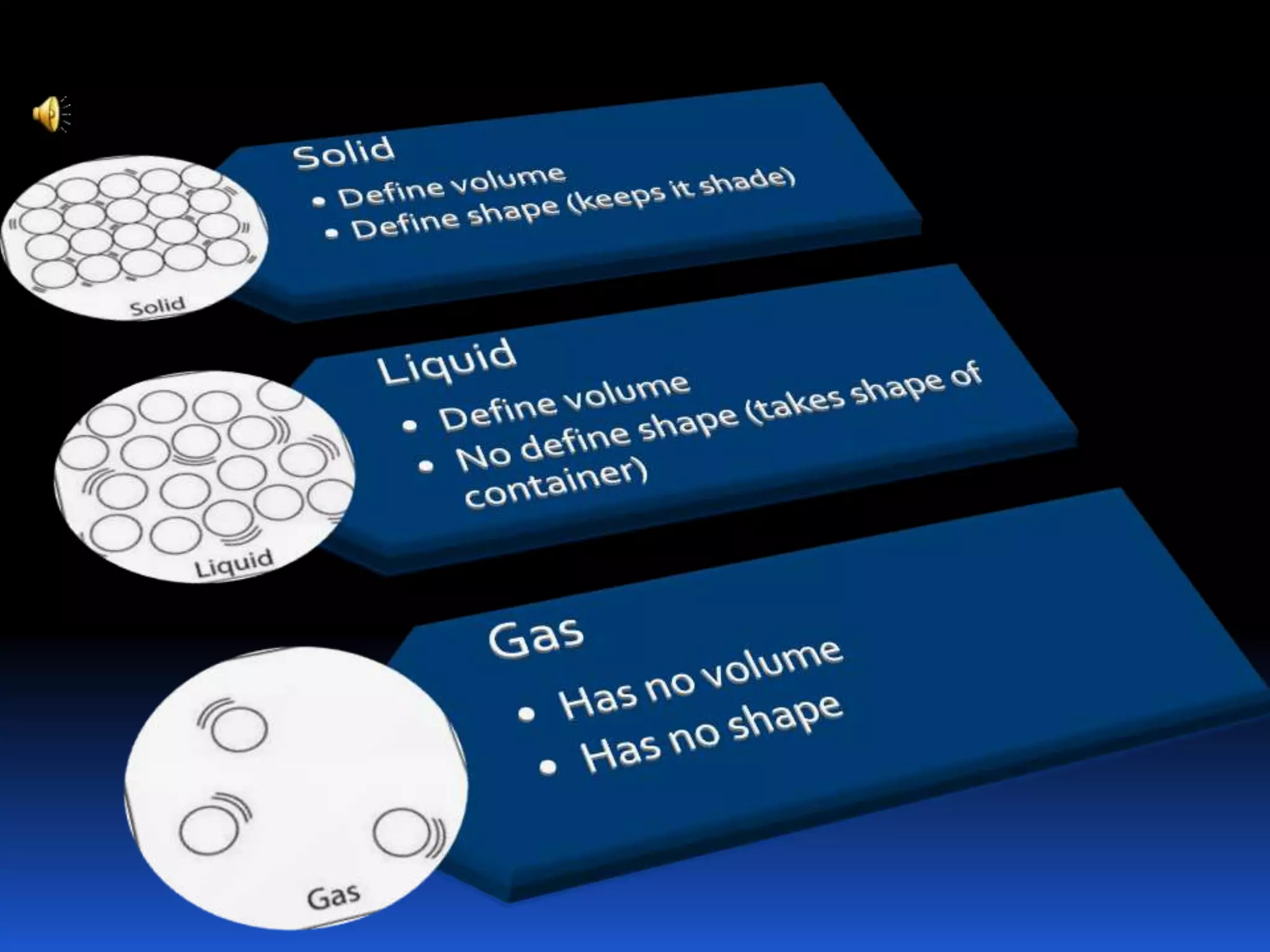
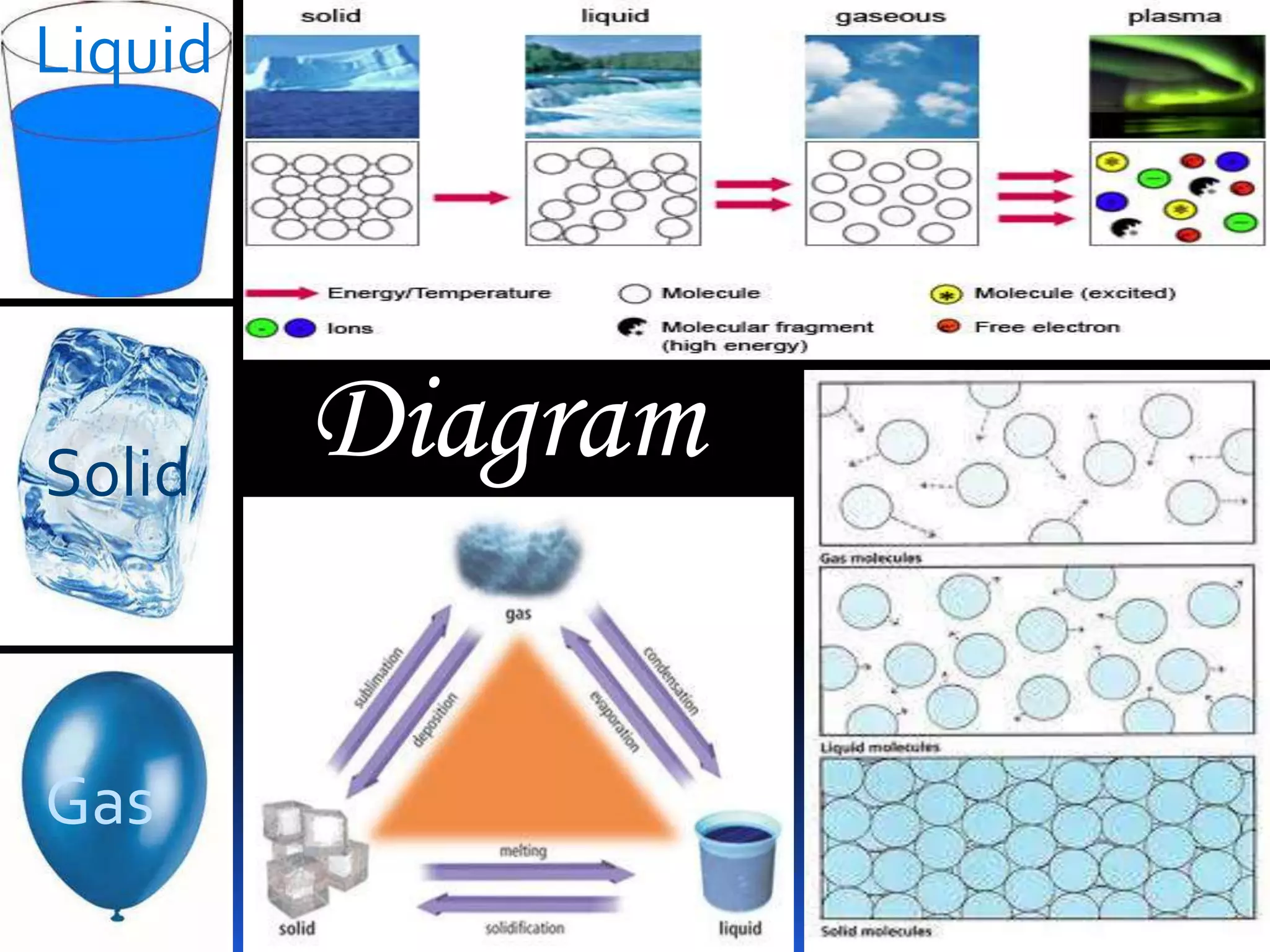
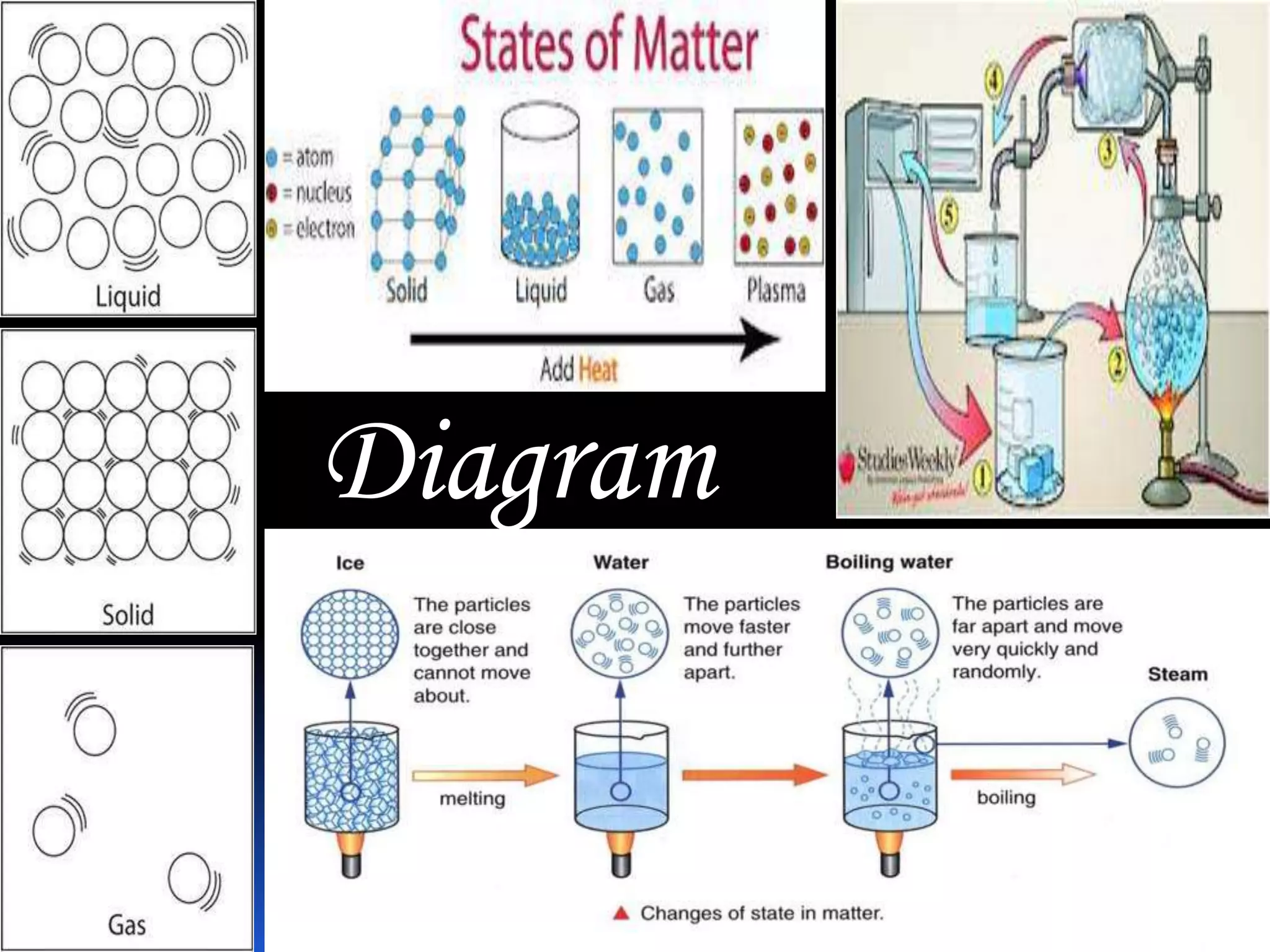
This document discusses the three common states of matter - solid, liquid, and gas. It provides properties and examples for each state. Solids have a definite volume and shape, liquids have a definite volume but no shape, and gases have no definite volume or shape. The strength of intermolecular forces determines if a substance is a solid, liquid or gas, with solids having the strongest forces and gases the weakest. A phase change, such as melting or boiling, occurs when heating or cooling provides enough energy for molecules to overcome these intermolecular forces.