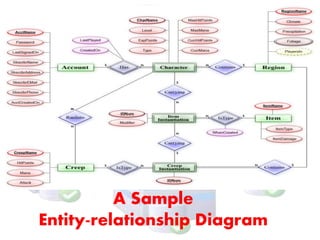
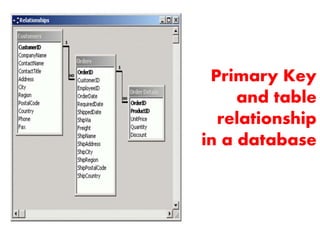
The document discusses database design and related concepts. It begins by defining database design as the logical design of data structures used to store data, such as tables and views in a relational database. It also notes database design involves determining relationships between data elements and structuring data based on these relationships. The document then discusses entity-relationship (ER) diagrams as a tool for efficiently designing databases and includes an example ER diagram. It also outlines the typical steps in the database design process, including determining data types and relationships, structuring data into tables, and applying normalization rules.