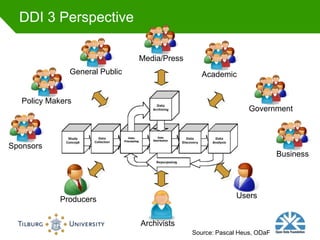
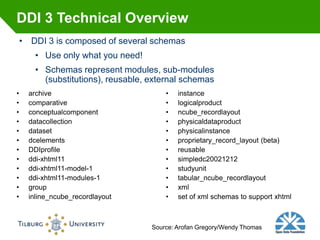
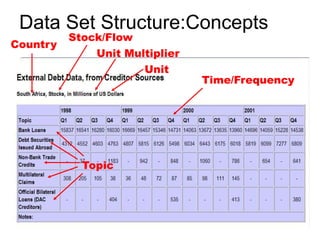
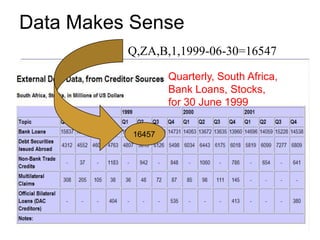
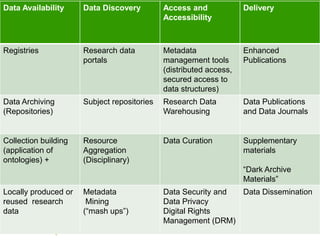
This document summarizes Rob Grim's presentation on e-Science, research data, and the role of libraries. It discusses the Open Data Foundation's work in promoting metadata standards like DDI and SDMX. It also outlines the research data lifecycle and how metadata management can help libraries support research through services like data registration, archiving, discovery and access. Finally, it provides examples of how Tilburg University library supports research data through services aligned with data availability, discovery, access and delivery.