1. ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is an enterprise-wide information system that coordinates all the resources, information, and activities needed to complete business processes such as order fulfillment and billing.
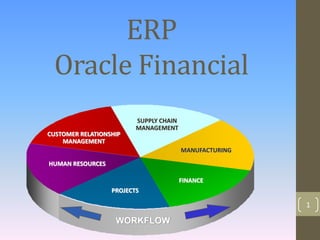
2. The document discusses Oracle's ERP product called Oracle E-Business Suite. It includes various modules related to finance, human resources, projects, supply chain management, manufacturing, and customer relationship management.
3. Key finance modules covered include general ledger, payables, receivables, and fixed assets which help track a company's assets, liabilities, income and expenses to understand their financial health and make business decisions.