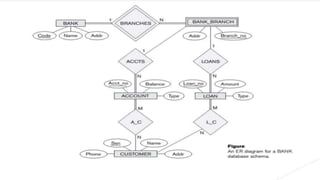
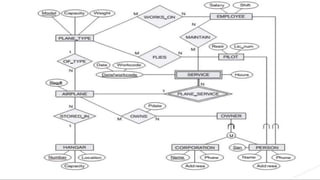
This document contains descriptions of several entity relationship diagrams (ERDs). The first section describes an ERD for tracking ships and locations. The second section shows an ERD for an airport database tracking airplanes, owners, employees and pilots. The third section provides requirements for a library database to track libraries, books, borrowers, copies of books and loans.