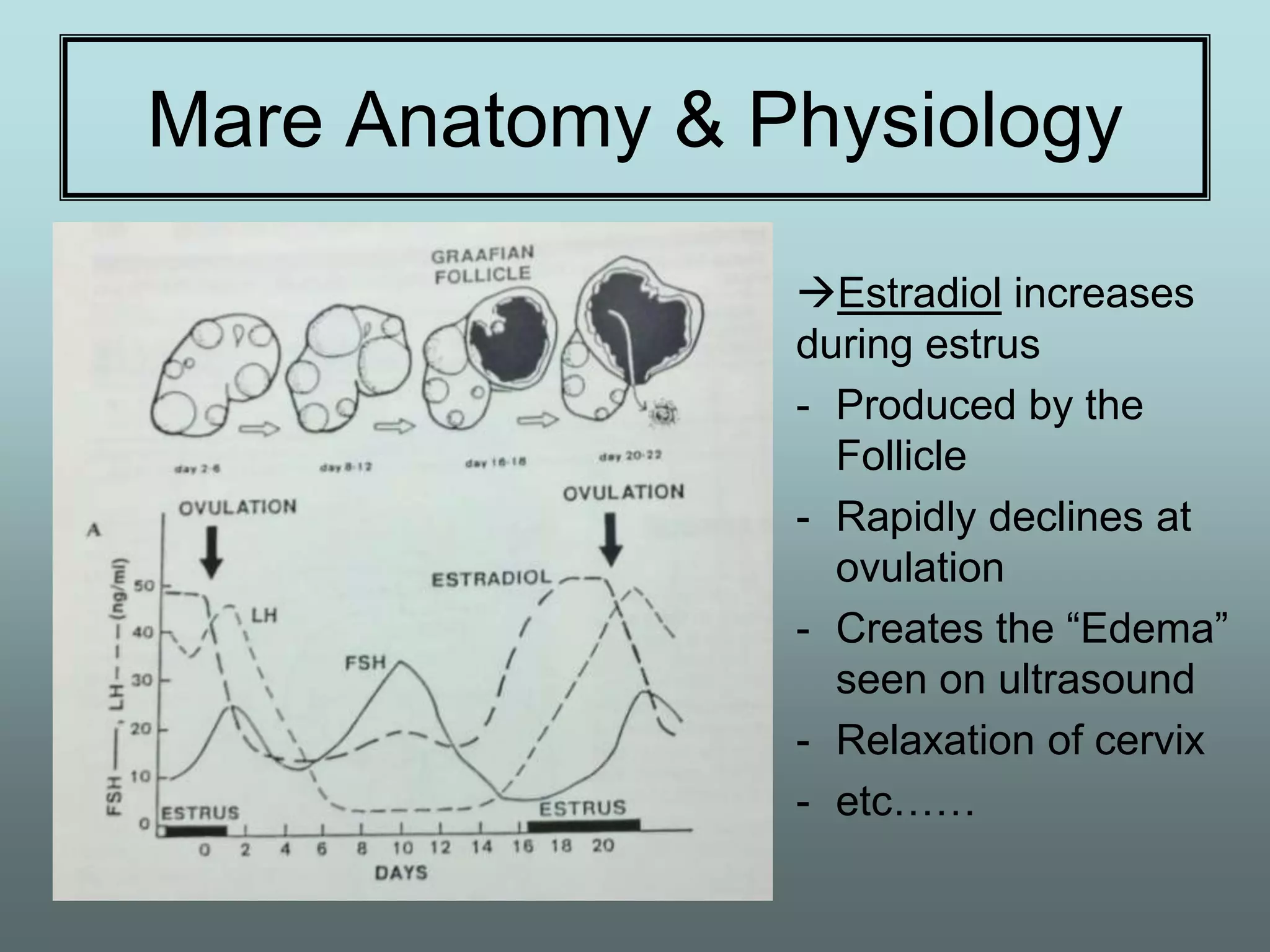
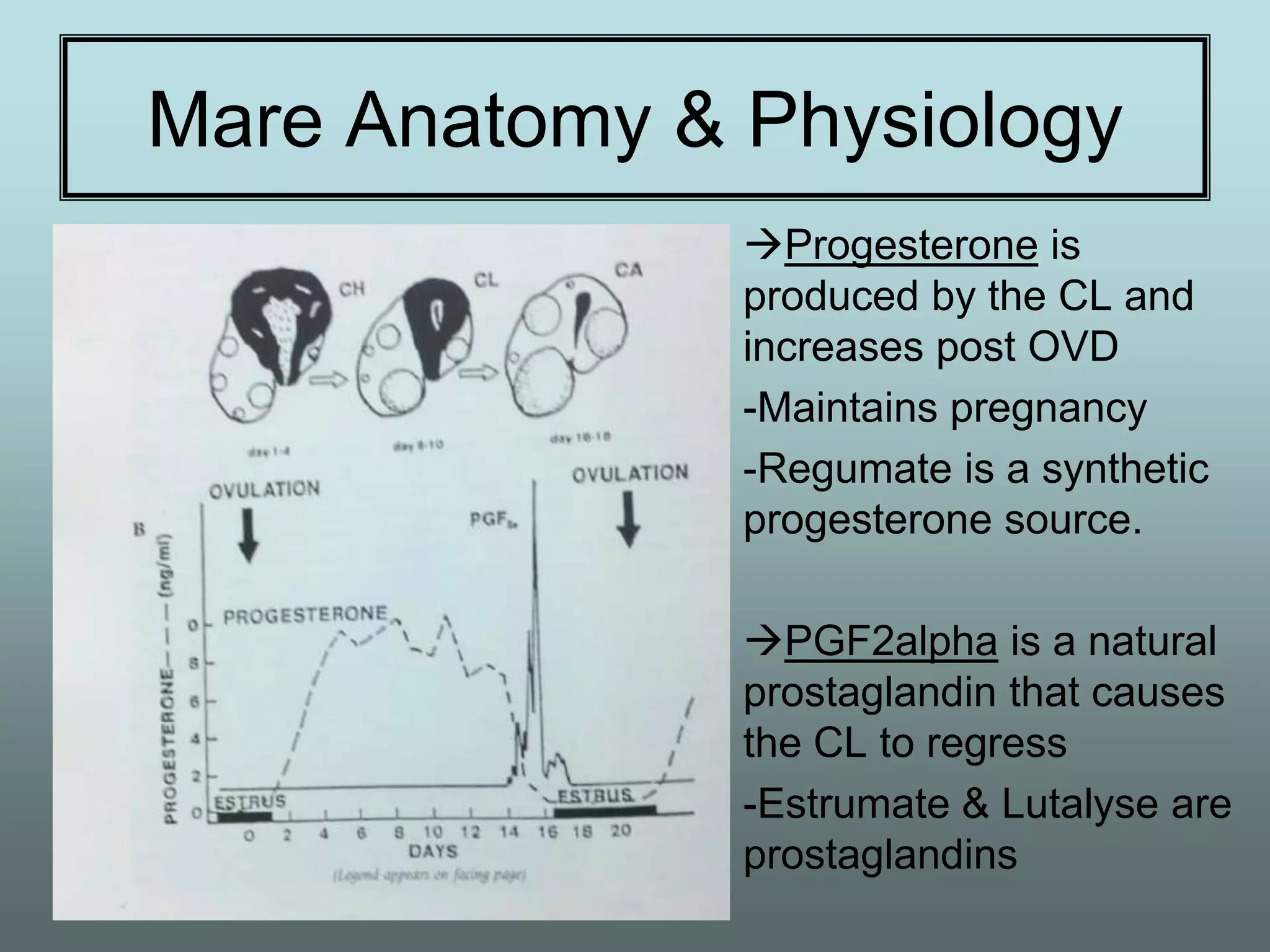
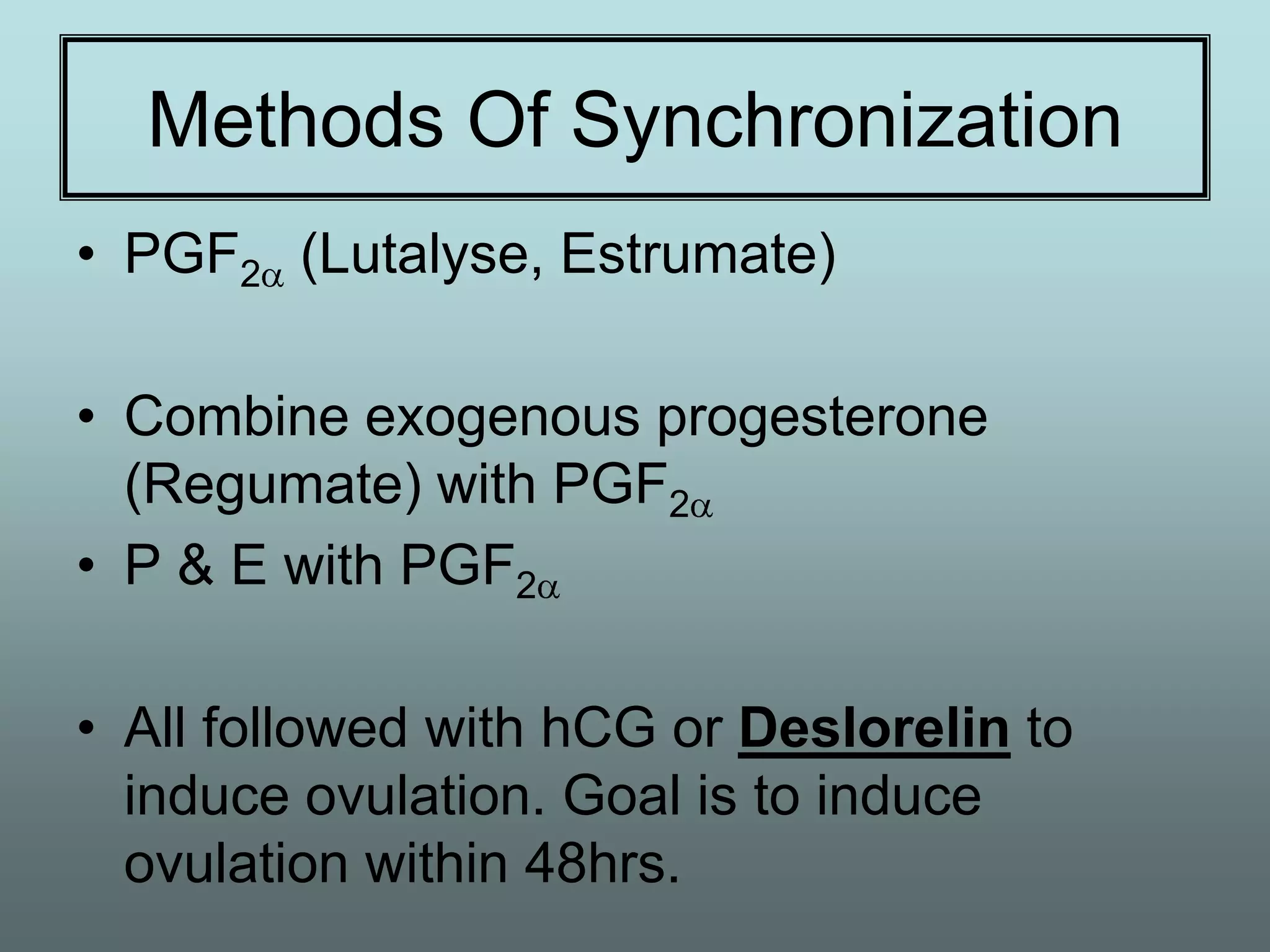
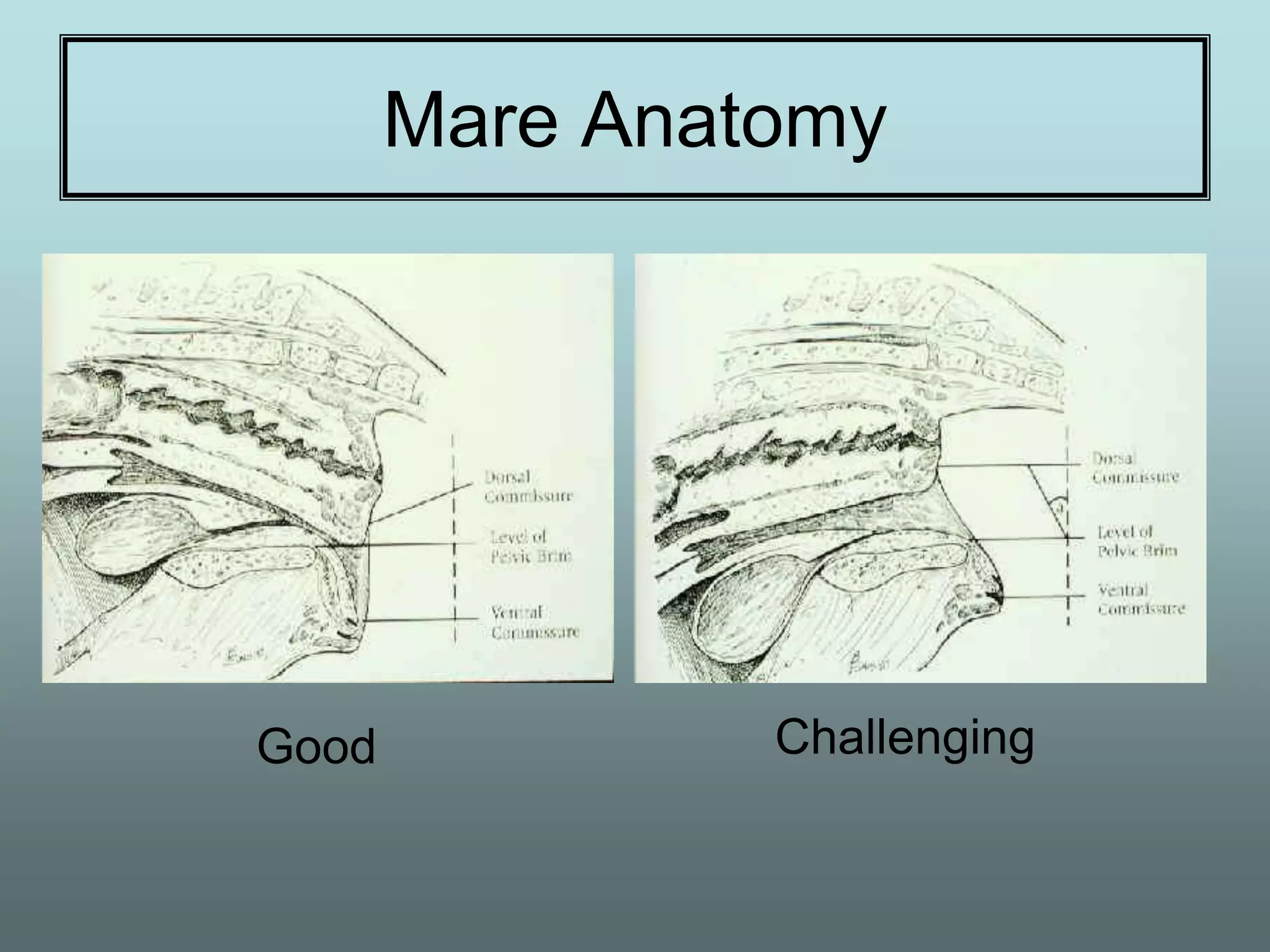
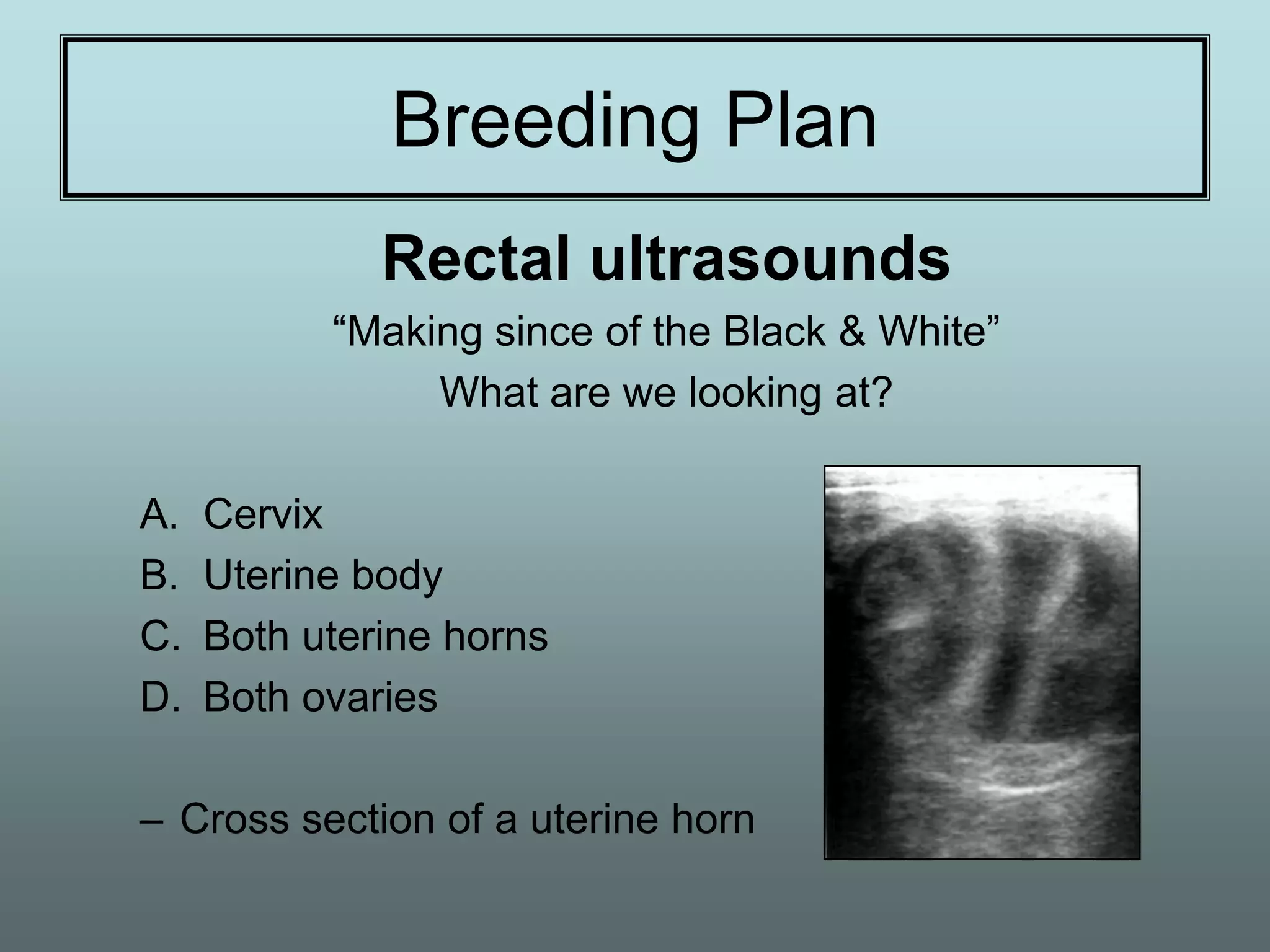
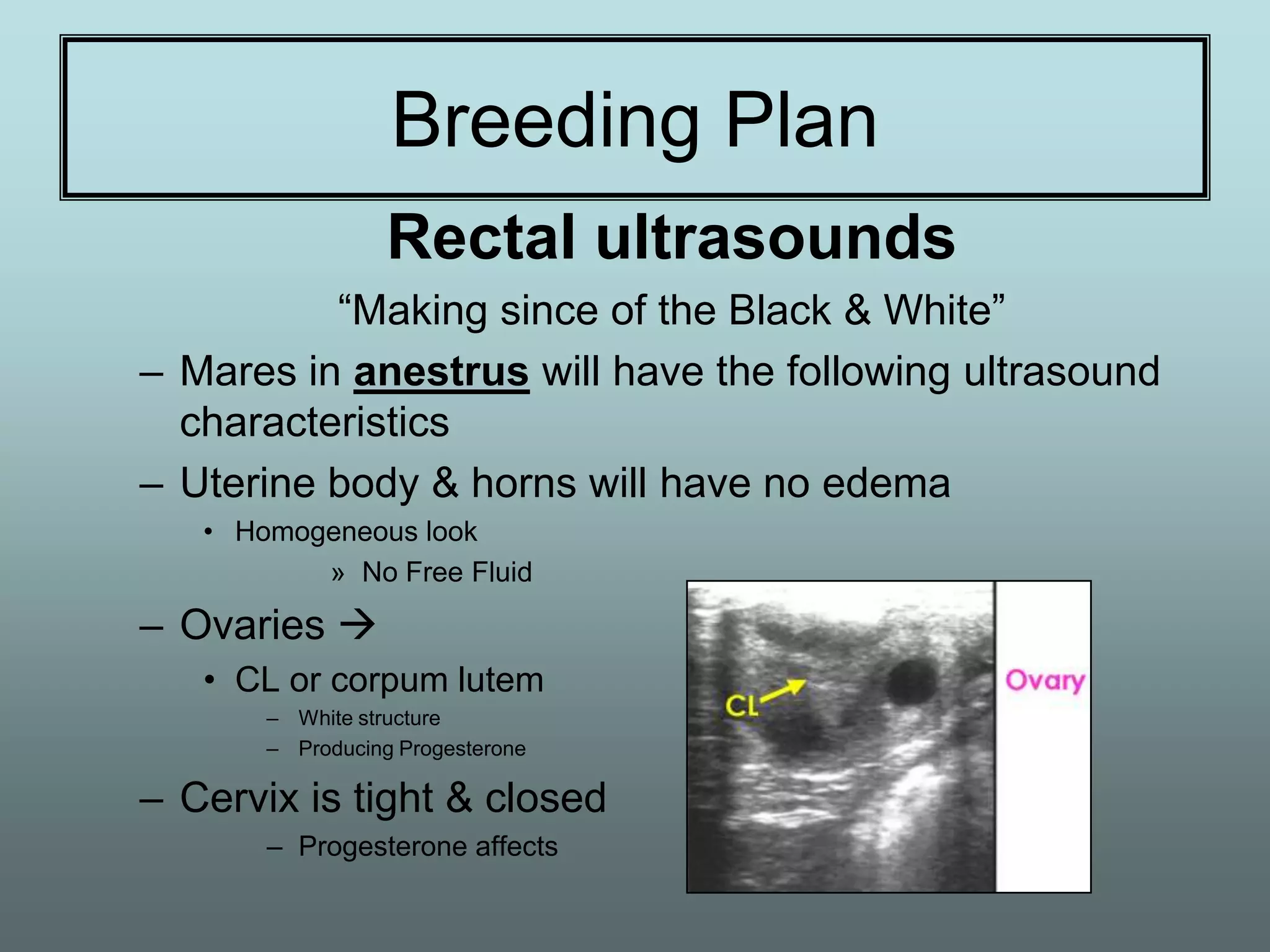
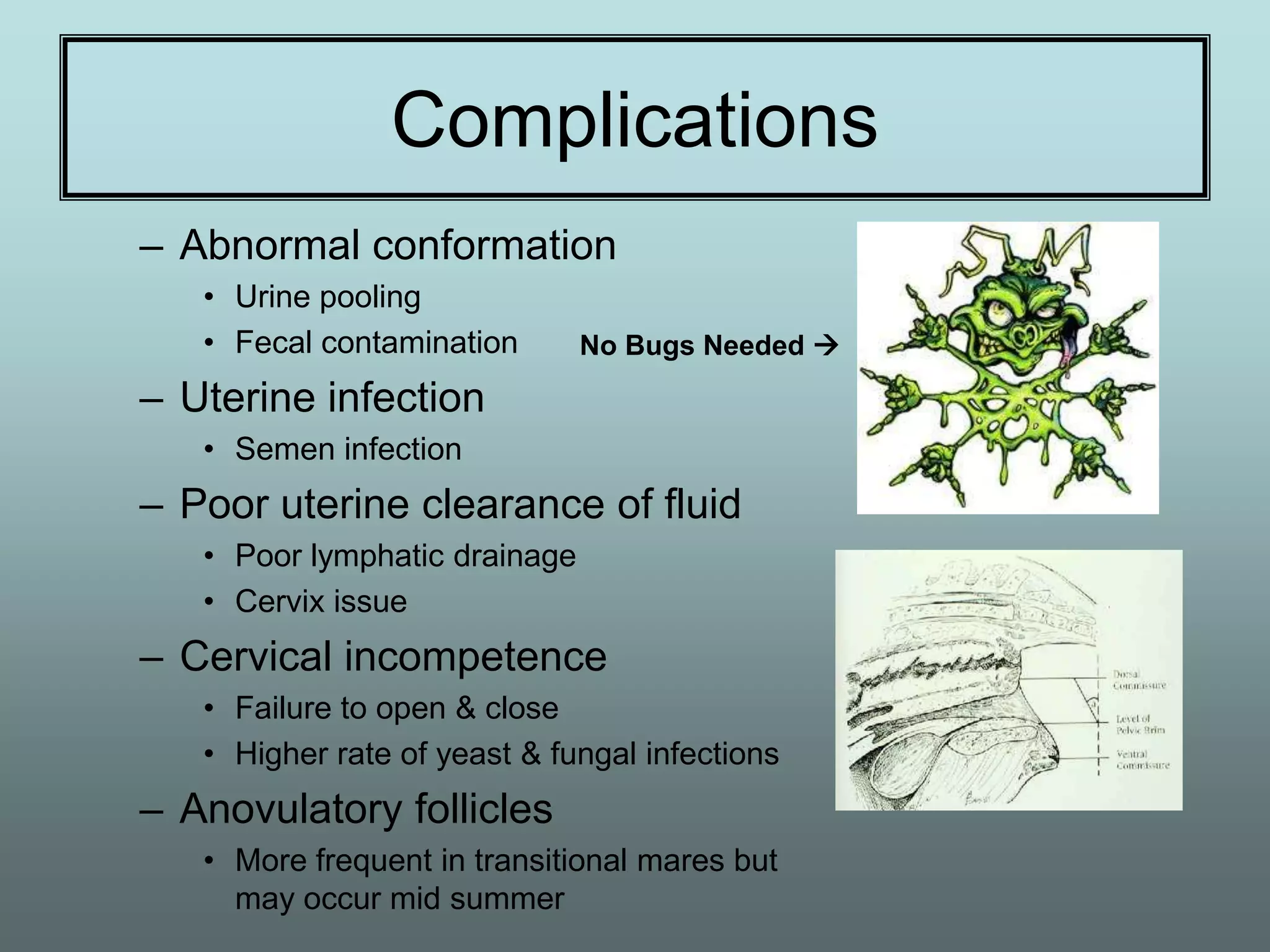
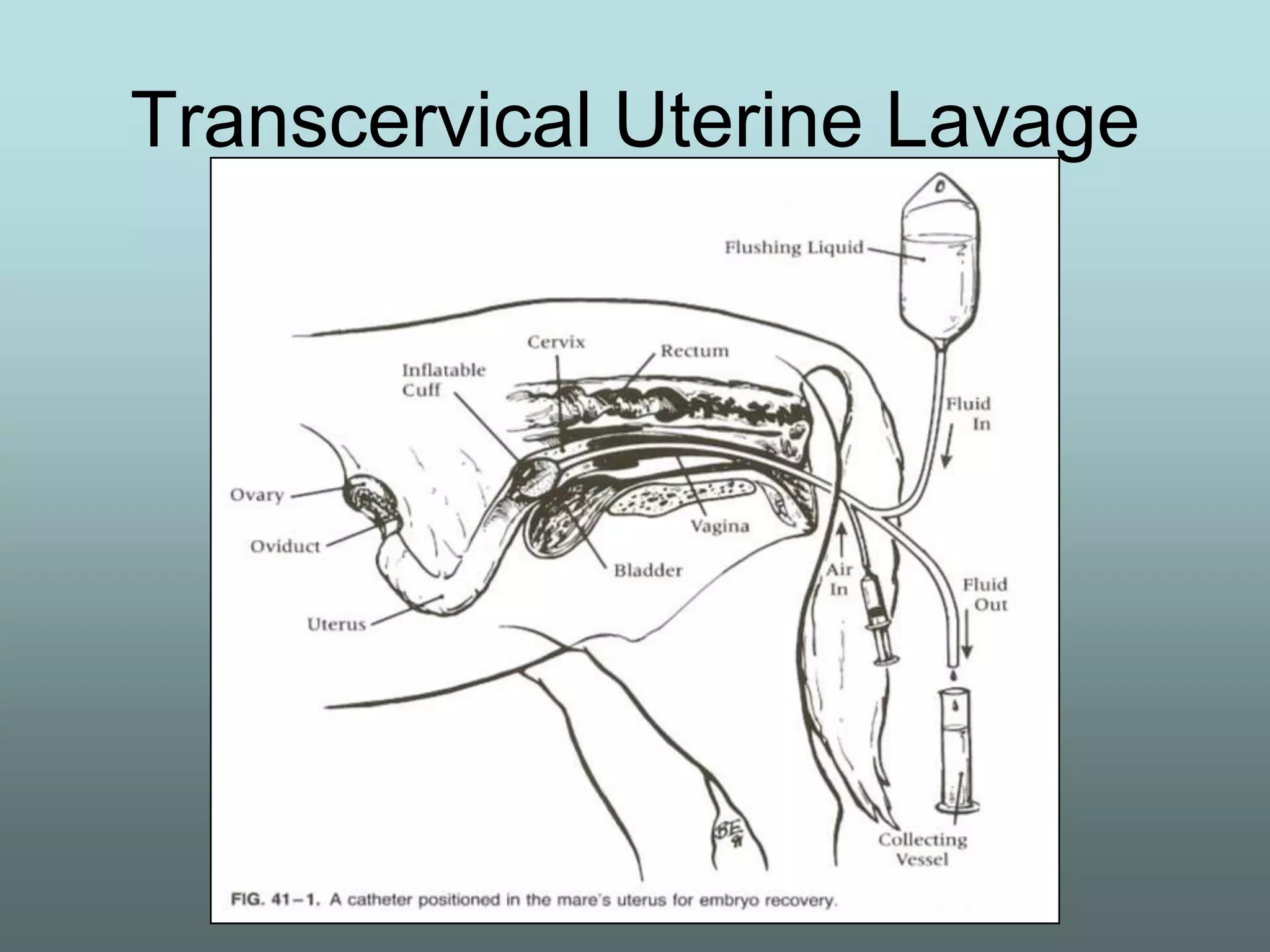
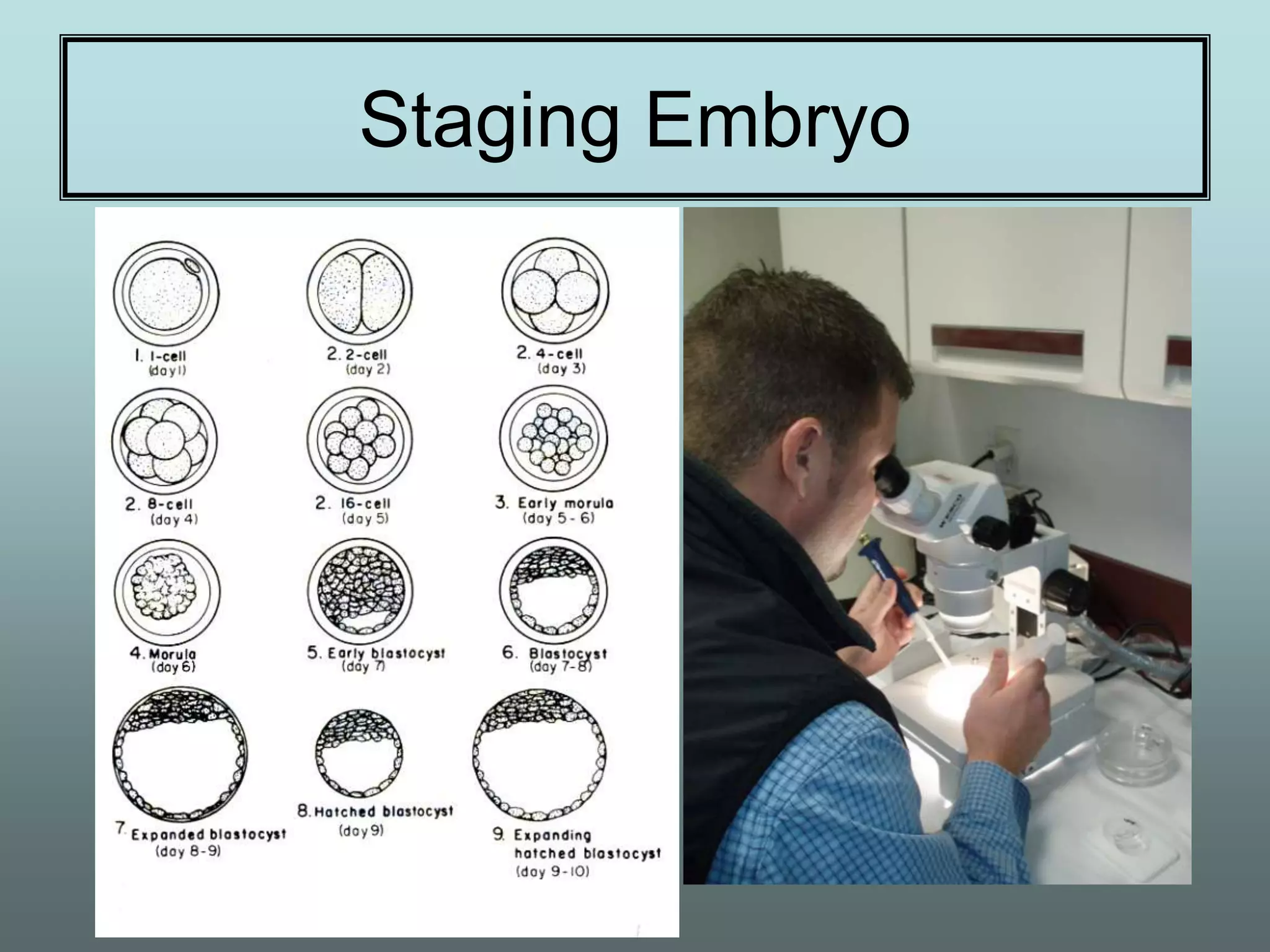
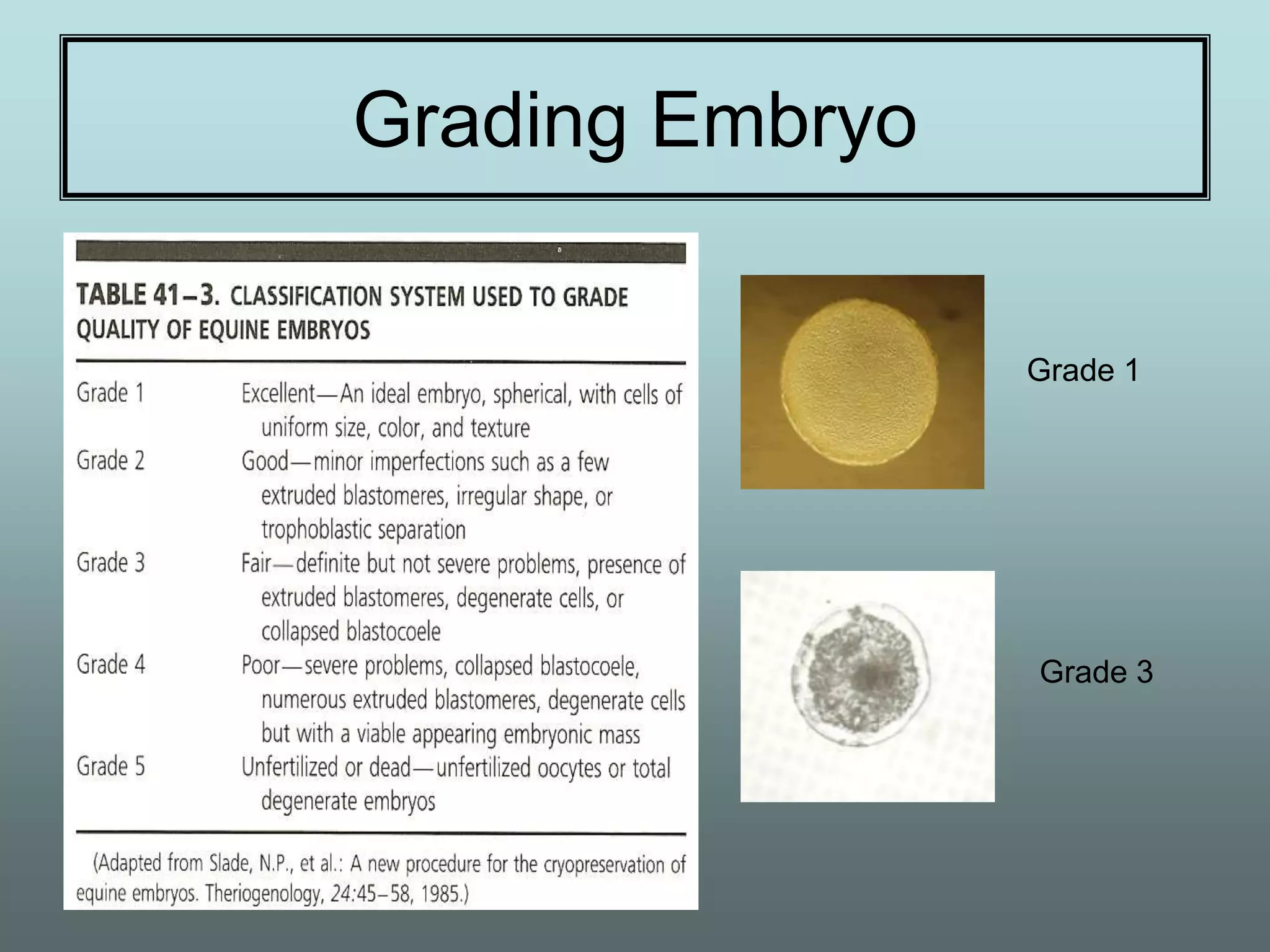
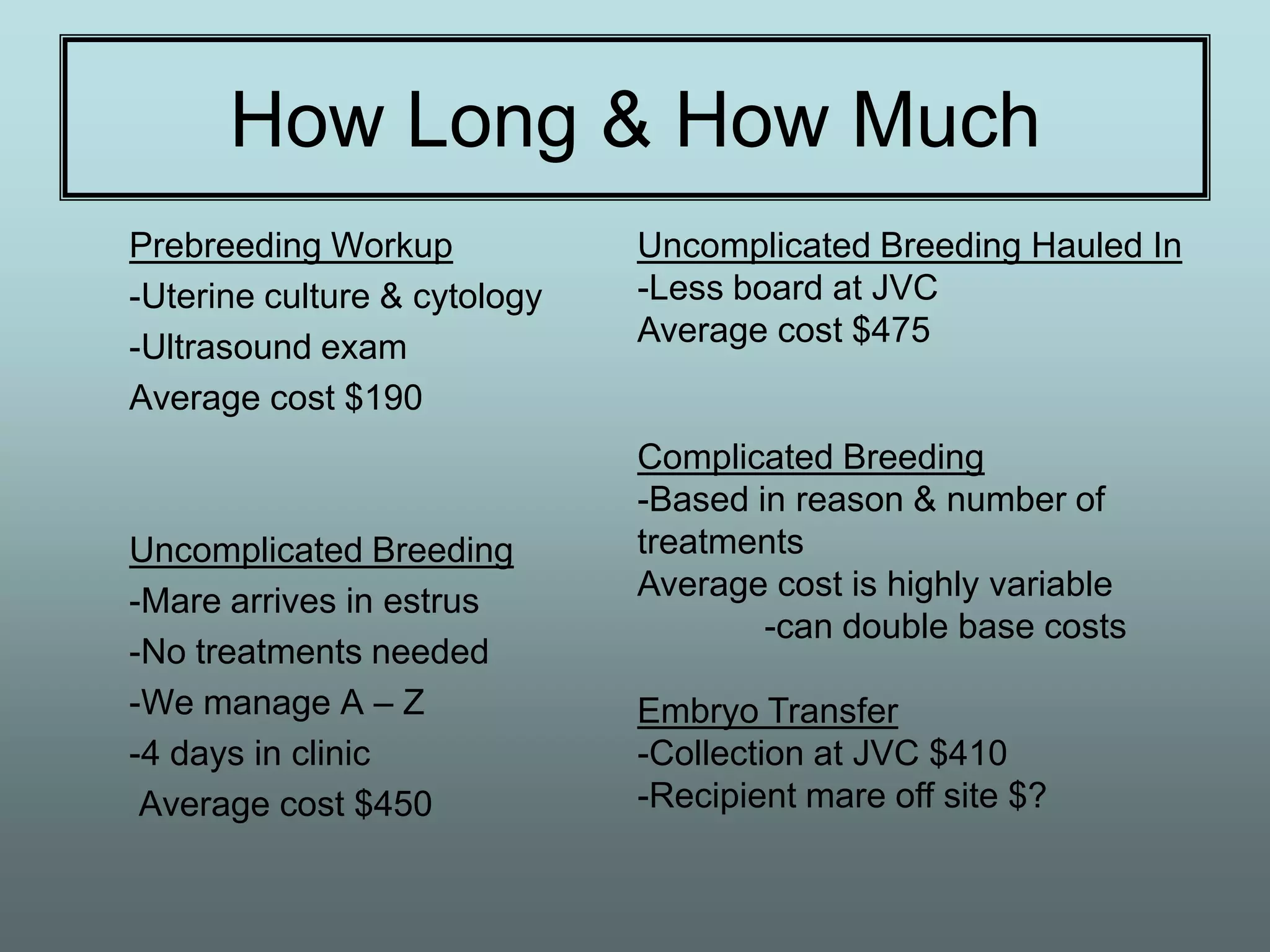
This document discusses equine reproduction, covering topics like mare anatomy and physiology, pre-breeding plans, breeding plans, complications that can arise, embryo transfer, and gestation. Specifically, it describes the reproductive organs of mares, their estrus cycles, ultrasound exams during breeding, artificial insemination procedures, common breeding complications and their treatments, the history and process of embryo transfer, and what to expect during a mare's 11-month gestation period. It also addresses the variables that can affect the duration and costs of a breeding plan.