Epilepsy- a guide for teachers
•
3 likes•1,244 views
This document provides teachers with guidance on supporting students with epilepsy. It outlines the important role teachers play in ensuring student safety and well-being. It describes how to recognize seizure signs and appropriately respond to seizures by staying calm, timing the seizure, protecting from injury, and calling for emergency help if needed. The document also addresses common misconceptions about epilepsy and discusses seizure triggers, types, and management strategies to help teachers effectively support students.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Seizures - FY14

Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by recurring seizures caused by a brief disturbance in the brain's electrical activity. It affects 1 in 100 people and is not contagious. There are over 30 types of seizures, which are categorized as either generalized seizures that affect the whole brain or partial seizures that affect only part of the brain. Absence seizures, one of the most common types in children, cause brief staring spells but the child is unaware of their surroundings. Simple partial seizures impair specific functions like memory or movement. Complex partial seizures also cause lack of awareness. Tonic-clonic seizures involve convulsions and loss of consciousness. First aid involves protecting the child and timing seizures. A seizure emergency requires calling 911. Schools should
Seizures

This document provides information about seizures and epilepsy. It defines what a seizure is, the different types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, simple partial and complex partial seizures. It discusses epilepsy as a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures and covers common causes, prevalence, myths and facts. The document outlines appropriate first aid for different seizure types and signs that indicate a medical emergency. It also discusses potential learning impacts and provides tips for supporting students with epilepsy.
Seizure Disorders

Seizure disorders occur when there is a surge of electrical activity in the brain that causes seizures. There are over 40 types of seizures that vary in severity and symptoms. The two most common categories are generalized seizures, which affect the entire brain, and partial seizures, which affect only one part of the brain. As a teacher, it is important to be aware of a student's seizure needs and form an emergency plan with the student and family. The plan should outline medication schedules, contact information, and procedures for responding to seizures. Teachers should also provide academic accommodations like extra time, breaking down assignments, and using organizational strategies to help students with seizure-related memory and focus issues.
Care of the patient with critical illness

This document provides information on end of life care, including definitions of death, the stages of grief, and the physiological and psychological needs of a dying patient. It outlines the nursing responsibilities after a patient has died, such as preparing the body, caring for family members, documenting the death in medical records, and handling the deceased's belongings. The stages of rigor mortis are also discussed. The document provides detailed guidance on proper procedures for post-mortem care.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training-Greenhill School

Presentation created by the health department at Greenhill School for training employees on Bloodborne Pathogens
ORGANIC MENTAL DISORDERS 

This document discusses organic mental disorders, specifically delirium and dementia. It defines delirium as an acute organic brain syndrome characterized by clouding of consciousness and disorientation. Dementia is defined as a chronic mental disorder characterized by impairment of intellectual functions and deterioration of personality. Alzheimer's disease is described as the most common cause of dementia. The document outlines the classification, causes, clinical features, diagnosis and management of delirium and dementia, with specific details provided about Alzheimer's disease.
An interesting case of seizure disorder

This document discusses the case of an 8-year-old male patient who presented with seizure disorder since age 2. Intraoperative monitoring during surgery to remove a right temporal lobe lesion detected epileptiform discharges in the middle and posterior medial temporal lobe. The surgery involved removing the lesion as well as performing a selective amygdalohippocampectomy in the right temporal lobe. Post-operatively, the patient has been seizure-free for 3 weeks while continuing antiepileptic medication.
Delirium

"Delirium is a common clinical syndrome characterized by inattention and acute cognitive dysfunction.”
Recommended
Seizures - FY14

Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by recurring seizures caused by a brief disturbance in the brain's electrical activity. It affects 1 in 100 people and is not contagious. There are over 30 types of seizures, which are categorized as either generalized seizures that affect the whole brain or partial seizures that affect only part of the brain. Absence seizures, one of the most common types in children, cause brief staring spells but the child is unaware of their surroundings. Simple partial seizures impair specific functions like memory or movement. Complex partial seizures also cause lack of awareness. Tonic-clonic seizures involve convulsions and loss of consciousness. First aid involves protecting the child and timing seizures. A seizure emergency requires calling 911. Schools should
Seizures

This document provides information about seizures and epilepsy. It defines what a seizure is, the different types of seizures including absence, tonic-clonic, simple partial and complex partial seizures. It discusses epilepsy as a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures and covers common causes, prevalence, myths and facts. The document outlines appropriate first aid for different seizure types and signs that indicate a medical emergency. It also discusses potential learning impacts and provides tips for supporting students with epilepsy.
Seizure Disorders

Seizure disorders occur when there is a surge of electrical activity in the brain that causes seizures. There are over 40 types of seizures that vary in severity and symptoms. The two most common categories are generalized seizures, which affect the entire brain, and partial seizures, which affect only one part of the brain. As a teacher, it is important to be aware of a student's seizure needs and form an emergency plan with the student and family. The plan should outline medication schedules, contact information, and procedures for responding to seizures. Teachers should also provide academic accommodations like extra time, breaking down assignments, and using organizational strategies to help students with seizure-related memory and focus issues.
Care of the patient with critical illness

This document provides information on end of life care, including definitions of death, the stages of grief, and the physiological and psychological needs of a dying patient. It outlines the nursing responsibilities after a patient has died, such as preparing the body, caring for family members, documenting the death in medical records, and handling the deceased's belongings. The stages of rigor mortis are also discussed. The document provides detailed guidance on proper procedures for post-mortem care.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training-Greenhill School

Presentation created by the health department at Greenhill School for training employees on Bloodborne Pathogens
ORGANIC MENTAL DISORDERS 

This document discusses organic mental disorders, specifically delirium and dementia. It defines delirium as an acute organic brain syndrome characterized by clouding of consciousness and disorientation. Dementia is defined as a chronic mental disorder characterized by impairment of intellectual functions and deterioration of personality. Alzheimer's disease is described as the most common cause of dementia. The document outlines the classification, causes, clinical features, diagnosis and management of delirium and dementia, with specific details provided about Alzheimer's disease.
An interesting case of seizure disorder

This document discusses the case of an 8-year-old male patient who presented with seizure disorder since age 2. Intraoperative monitoring during surgery to remove a right temporal lobe lesion detected epileptiform discharges in the middle and posterior medial temporal lobe. The surgery involved removing the lesion as well as performing a selective amygdalohippocampectomy in the right temporal lobe. Post-operatively, the patient has been seizure-free for 3 weeks while continuing antiepileptic medication.
Delirium

"Delirium is a common clinical syndrome characterized by inattention and acute cognitive dysfunction.”
Dizziness 

The document discusses the evaluation and potential causes of dizziness in patients. It outlines important aspects of the history to obtain including triggers and associated symptoms. Acute causes mentioned include vestibular neuronitis which presents with sudden vertigo, nausea and vomiting that gradually improves over weeks. Recurrent episodic causes discussed are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), migraine, and Meniere's disease. Red flags are also noted that could indicate a posterior circulation stroke requiring further workup.
Headaches presentation at www.eyenirvaan.com

This document discusses different types of headaches, including their classification, causes, characteristics, and pathophysiology. It covers primary headaches like tension, migraine, and cluster headaches as well as secondary headaches that can result from conditions like head injuries, infections, raised intracranial pressure, and eye diseases. Management involves treating the underlying cause, keeping a headache diary, and referring patients to their GP or an emergency department depending on the severity and suspected etiology of the headache.
EMDR Therapy | Agoraphobia | Digestive Disorders

The document discusses EMDR therapy, agoraphobia, and common digestive disorders. EMDR therapy uses eye movements to help reprocess traumatic memories. It has been effective in treating PTSD and other anxiety disorders. Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder defined by fears of situations where escape may be difficult or help unavailable if panic occurs. Common digestive disorders include irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux, and inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Dementia

Dementia is a broad category of brain diseases that cause a long term and often gradual decrease in the ability to think and remember such that a person's daily functioning is affected.
Dementia is acquired global impairment of intellectual, memory and personality but without impairment of consciousness.
Epilepsy Presentation

The document provides information about seizures and epilepsy. It defines a seizure as overactivity in the brain causing movements and sometimes unconsciousness. It describes different types of seizures and many potential causes. Epilepsy is introduced as a disorder characterized by recurring seizures. The Danny Did Foundation is summarized as working to prevent death from seizures through detection devices and education, founded in memory of founder's son Danny who died from a seizure at age 4.
brain function and stroke facts (simple version)

The document provides an overview of the brain, its injuries, and rehabilitation. It discusses that the brain controls all body functions and is composed of three main parts - the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Each part performs different functions. Injuries to different areas can result in various deficits. Stroke is described as a common type of brain injury that occurs when blood flow is blocked or bleeding occurs in the brain. Symptoms of stroke vary but usually appear suddenly. Rehabilitation is important for recovery and generally begins in the hospital, with the goal of improving independence. A rehabilitation team provides various therapies to help patients regain abilities.
Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that causes hallucinations, delusions, and problems concentrating. It is not contagious and usually lasts a person's lifetime. While the exact cause is unknown, genetics, stress, and differences in brain development may play a role. There is no cure for schizophrenia, but it can be treated with medications like clozapine or electroconvulsive therapy to ease symptoms.
Epilepsy awareness training innovations slideshare

This Epilepsy Awareness training course is aimed at raising awareness of the importance of the safe care and management of epilepsy. The course explores some of the common misconceptions about epilepsy and to care for someone who experiences seizures. On completion of this course staff will be aware of the clinical features of epilepsy and contribute to the care and wellbeing of patients who experience epileptic seizures.
Duration: 2 hours
Experience: None required.
This course is suitable for all staff currently working within health and social care settings in the United Kingdom who may come into contact with patients who experience epileptic seizures.
Number of Trainees: 16 maximum
Course Standard: Certificate of attendance
Equipment Needed: Hand-outs will be provided
Candidates will cover:
•Definitions, diagnosis and symptoms of epilepsy, including the nature and incidence of epilepsy
•Seizures and seizure types
•Care and treatment of epilepsy, including basic first aid and emergency care
•What to do when caring for a patient experiencing an epileptic seizure
•Care and management of patients who experience epileptic seizures
•Living with epilepsy
By the end of the course Candidates will be able to:
•Describe the diagnosis, symptoms and different types of epilepsy
•Understand and demonstrate the care and treatment of patients with epilepsy
•Understand the impact of epileptic seizures
•Contribute to the care-planning and safe management and care of patients who experience epileptic seizures, including basic first aid for epileptic sufferers
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures. Seizures are brief disturbances in the electrical functions of the brain. The assessment of epilepsy involves stabilizing the patient during a seizure by ensuring their airway, breathing, and circulation. Vital signs should be monitored and the duration of convulsions recorded. Underlying causes should be explored, such as eclampsia in pregnant women. Rectal diazepam can be used to stop prolonged seizures when IV access is not available. Status epilepticus requires management in a health facility with IV antiepileptic medications.
Epilepsy in children english

THESE SLIDES ARE PREPAREED TO UNDERSTAND CHILD HEALTH DISORDERS IN EASY WAY Important links- NOTES- https://mynursingstudents.blogspot.com/ youtube channel https://www.youtube.com/c/MYSTUDENTSU... CHANEL PLAYLIST- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPM3VTGVUXIeswKJ3XGaD2p COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPyslPNdIJoVjiXEDTVEDzs CHILD HEALTH NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gANcslmv0DXg6BWmWN359Gvg FIRST AID- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAMvGqeqH2ZTklzFAZhOrvgP HCM- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAM7mZ1vZhQBHWbdLnLb-cH9 FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPFxu78NDLpGPaxEmK1fTao COMMUNICABLE DISEASES- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAOWo4IwNjLU_LCuhRN0ZLeb ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPkI6LvfS8Zu1nm6mZi9FK6 MSN- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAOdyoHnDLAoR_o8M6ccqYBm HINDI ONLY- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAN4L-FJ3s_IEXgZCijGUA1A ENGLISH ONLY- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAMYv2a1hFcq4W1nBjTnRkHP facebook profile- https://www.facebook.com/suresh.kr.lrhs/ FACEBOOK PAGE- https://www.facebook.com/My-Student-S... facebook group NURSING NOTES- https://www.facebook.com/groups/24139... FOR MAKING EASY NOTES YOU CAN ALSO VISIT MY BLOG – BLOGGER- https://mynursingstudents.blogspot.com/ Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/mystudentsu... Twitter- https://twitter.com/student_system?s=08 #PEM, #HEALTH,#NEW,#BORN,#ASSESSMENT, #APPEARENCE,#PULSE,#GRIMACE,#REFLEX,#RESPIRATION,#RESUSCITATION,#NEWBORN,#BABY,#VIRGINIA, #CHILD, #OXYGEN,#CYANOSIS,#OPTICNERVE, #SARACHNA,#MYSTUDENTSUPPORTSYSTEM, #rashes,#nursingclasses, #communityhealthnursing,#ANM, #GNM, #BSCNURING,#NURSINGSTUDENTS, #WHO,#NURSINGINSTITUTION,#COLLEGEOFNURSING,#nursingofficer,#COMMUNITYHEALTHOFFICER
Western Trust Epilepsy Awareness Presentation 2013

This document provides information about epilepsy for healthcare staff. It begins with learning outcomes around recognizing seizure types, appropriate first aid, risks of epilepsy, and the role of staff caring for people with epilepsy. It then defines epilepsy as a neurological disorder characterized by unprovoked seizures. Several types of seizures are described, including focal and generalized seizures like tonic-clonic and absence seizures. Causes, diagnosis, treatment, triggers, classification, and first aid for different seizure types are outlined. The roles and responsibilities of healthcare staff in caring for people with epilepsy are also summarized.
Report ps 3

This document discusses various physical disabilities and health conditions that may affect children in a classroom setting. It provides information on cerebral palsy and its classifications (spasticity, hypotonicity, athetoysis, ataxia), as well as spinal cord injuries, spina bifida, hydrocephalus, muscular dystrophy, hip dysplasia, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, leukemia, sickle cell anemia, heart problems, diabetes, seizure disorders, HIV/AIDS, obesity, undernourishment, and recommendations for teachers on administering medication, handling emergencies, maintaining confidentiality and children's health records.
2.knowledge of developmental disabilities

Developmental disabilities can have various causes including genetic, birth-related, or environmental factors. Four main conditions that qualify for services are autism, cerebral palsy, cognitive disabilities, and epilepsy. Cerebral palsy affects muscle communication with the brain, cognitive disabilities affect learning, autism affects social/communication abilities, and epilepsy causes seizures. Managing developmental disabilities requires understanding each condition and providing appropriate support.
Epilepsy and its management

The document discusses epilepsy and its management. Some key points:
- Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. It affects around 50 million people worldwide.
- Seizures occur due to excessive electrical discharges in the brain and present with symptoms like loss of consciousness and abnormal motor movements.
- Management involves anti-epileptic drug therapy to control seizures as well as addressing psychosocial issues like stigma and quality of life concerns. Surgery may be considered if drug therapy is ineffective. Nursing care includes education, monitoring for side effects, and supporting psychological well-being.
Seizure

This document discusses epilepsy and seizures. It defines seizures and epilepsy, describes different types of seizures including partial and generalized seizures. Common causes of epilepsy including strokes, brain injuries, tumors are mentioned. Management of seizures focuses on preventing injuries, identifying and removing seizure triggers, and treating with anti-seizure medications to control seizures. Nursing care revolves around safety during seizures, airway management, education, and supporting patients' psychosocial needs.
Epilepsy edited

This document provides information about epilepsy including:
- It defines epilepsy as a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures.
- Some key causes of epilepsy include birth injuries, infections, brain tumors, and genetic factors.
- Diagnostic tests include blood tests, EEG, CT/MRI scans. Treatment involves pharmacotherapy with anti-seizure medications and possibly surgery for refractory cases.
- Nursing management focuses on patient safety during seizures, monitoring for complications, educating patients and families, and ensuring proper treatment adherence.
occupational therapy for epilepsy: an overview

This document discusses epilepsy, its causes, prevention, and the role of occupational therapy. It defines epilepsy as abnormal neuronal discharge in the brain that can cause loss of consciousness or odd behavior. Risk factors include premature birth, brain infections, abnormal brain structures, cerebral palsy, hypoxia, brain tumors, stroke, and drug abuse. Occupational therapy focuses on safety, adaptations to the home, relaxation techniques, exercise, routine management, leisure activities, and support groups to help epileptic patients live independently and cope with emotional and cognitive challenges.
Epilepsy first aid

This document provides guidelines for assisting someone experiencing a seizure. It begins by defining what a seizure is and noting that they can be frightening to witness. It explains that seizures are not always convulsions, but can involve staring, movements, smells/sounds, or behaviors. The guidelines recommend remaining calm, protecting the individual from injury, loosening tight clothing, removing eyeglasses, not restraining them or placing things in their mouth. It also advises timing the seizure, calling for emergency help if needed, looking for injuries afterwards, and not letting them drive after a seizure. The goal is to maintain the individual's safety during and after the event.
6 provide first aid medical emergiencies

- A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die from lack of oxygen. Signs include weakness/paralysis, difficulty speaking/swallowing, vision problems, and headaches. If suspected, call an ambulance immediately. Do not leave the casualty until help arrives.
- Diabetes is caused by insufficient insulin production. Hypoglycemia causes weakness and confusion from low blood sugar, which is treated by giving sugar. Hyperglycemia has a slower onset from high blood sugar. Never administer insulin yourself.
- Seizures are caused by abnormal brain activity and usually last 1-5 minutes. Protect the casualty from injury and do not restrain them. Call an ambulance
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a group of neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures. It affects about 1% of people worldwide and nearly 80% of cases occur in developing countries. Epileptic seizures are caused by excessive neuronal activity in the brain and can vary from brief episodes to long periods of shaking. While the cause is unknown in most cases, epilepsy can sometimes be caused by brain injury, stroke, tumors or genetic mutations. Treatment involves medication to control seizures in about 70% of patients, while surgery or other options may be considered for uncontrolled cases.
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures. A seizure occurs when there is a sudden surge of electrical activity in the brain. About 2.3 million Americans have epilepsy. While the specific cause is unknown in many cases, common causes include head trauma, brain tumors, strokes, genetic factors, and developmental issues. Treatment involves medications, surgery, dietary therapies and lifestyle modifications, with the goal of eliminating seizures without side effects. The choice of treatment depends on the seizure type, underlying causes, age, and other individual factors.
More Related Content
What's hot
Dizziness 

The document discusses the evaluation and potential causes of dizziness in patients. It outlines important aspects of the history to obtain including triggers and associated symptoms. Acute causes mentioned include vestibular neuronitis which presents with sudden vertigo, nausea and vomiting that gradually improves over weeks. Recurrent episodic causes discussed are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), migraine, and Meniere's disease. Red flags are also noted that could indicate a posterior circulation stroke requiring further workup.
Headaches presentation at www.eyenirvaan.com

This document discusses different types of headaches, including their classification, causes, characteristics, and pathophysiology. It covers primary headaches like tension, migraine, and cluster headaches as well as secondary headaches that can result from conditions like head injuries, infections, raised intracranial pressure, and eye diseases. Management involves treating the underlying cause, keeping a headache diary, and referring patients to their GP or an emergency department depending on the severity and suspected etiology of the headache.
EMDR Therapy | Agoraphobia | Digestive Disorders

The document discusses EMDR therapy, agoraphobia, and common digestive disorders. EMDR therapy uses eye movements to help reprocess traumatic memories. It has been effective in treating PTSD and other anxiety disorders. Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder defined by fears of situations where escape may be difficult or help unavailable if panic occurs. Common digestive disorders include irritable bowel syndrome, celiac disease, gastroesophageal reflux, and inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
Dementia

Dementia is a broad category of brain diseases that cause a long term and often gradual decrease in the ability to think and remember such that a person's daily functioning is affected.
Dementia is acquired global impairment of intellectual, memory and personality but without impairment of consciousness.
Epilepsy Presentation

The document provides information about seizures and epilepsy. It defines a seizure as overactivity in the brain causing movements and sometimes unconsciousness. It describes different types of seizures and many potential causes. Epilepsy is introduced as a disorder characterized by recurring seizures. The Danny Did Foundation is summarized as working to prevent death from seizures through detection devices and education, founded in memory of founder's son Danny who died from a seizure at age 4.
brain function and stroke facts (simple version)

The document provides an overview of the brain, its injuries, and rehabilitation. It discusses that the brain controls all body functions and is composed of three main parts - the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. Each part performs different functions. Injuries to different areas can result in various deficits. Stroke is described as a common type of brain injury that occurs when blood flow is blocked or bleeding occurs in the brain. Symptoms of stroke vary but usually appear suddenly. Rehabilitation is important for recovery and generally begins in the hospital, with the goal of improving independence. A rehabilitation team provides various therapies to help patients regain abilities.
Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that causes hallucinations, delusions, and problems concentrating. It is not contagious and usually lasts a person's lifetime. While the exact cause is unknown, genetics, stress, and differences in brain development may play a role. There is no cure for schizophrenia, but it can be treated with medications like clozapine or electroconvulsive therapy to ease symptoms.
What's hot (7)
Similar to Epilepsy- a guide for teachers
Epilepsy awareness training innovations slideshare

This Epilepsy Awareness training course is aimed at raising awareness of the importance of the safe care and management of epilepsy. The course explores some of the common misconceptions about epilepsy and to care for someone who experiences seizures. On completion of this course staff will be aware of the clinical features of epilepsy and contribute to the care and wellbeing of patients who experience epileptic seizures.
Duration: 2 hours
Experience: None required.
This course is suitable for all staff currently working within health and social care settings in the United Kingdom who may come into contact with patients who experience epileptic seizures.
Number of Trainees: 16 maximum
Course Standard: Certificate of attendance
Equipment Needed: Hand-outs will be provided
Candidates will cover:
•Definitions, diagnosis and symptoms of epilepsy, including the nature and incidence of epilepsy
•Seizures and seizure types
•Care and treatment of epilepsy, including basic first aid and emergency care
•What to do when caring for a patient experiencing an epileptic seizure
•Care and management of patients who experience epileptic seizures
•Living with epilepsy
By the end of the course Candidates will be able to:
•Describe the diagnosis, symptoms and different types of epilepsy
•Understand and demonstrate the care and treatment of patients with epilepsy
•Understand the impact of epileptic seizures
•Contribute to the care-planning and safe management and care of patients who experience epileptic seizures, including basic first aid for epileptic sufferers
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures. Seizures are brief disturbances in the electrical functions of the brain. The assessment of epilepsy involves stabilizing the patient during a seizure by ensuring their airway, breathing, and circulation. Vital signs should be monitored and the duration of convulsions recorded. Underlying causes should be explored, such as eclampsia in pregnant women. Rectal diazepam can be used to stop prolonged seizures when IV access is not available. Status epilepticus requires management in a health facility with IV antiepileptic medications.
Epilepsy in children english

THESE SLIDES ARE PREPAREED TO UNDERSTAND CHILD HEALTH DISORDERS IN EASY WAY Important links- NOTES- https://mynursingstudents.blogspot.com/ youtube channel https://www.youtube.com/c/MYSTUDENTSU... CHANEL PLAYLIST- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY-https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPM3VTGVUXIeswKJ3XGaD2p COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPyslPNdIJoVjiXEDTVEDzs CHILD HEALTH NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gANcslmv0DXg6BWmWN359Gvg FIRST AID- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAMvGqeqH2ZTklzFAZhOrvgP HCM- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAM7mZ1vZhQBHWbdLnLb-cH9 FUNDAMENTALS OF NURSING- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPFxu78NDLpGPaxEmK1fTao COMMUNICABLE DISEASES- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAOWo4IwNjLU_LCuhRN0ZLeb ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAPkI6LvfS8Zu1nm6mZi9FK6 MSN- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAOdyoHnDLAoR_o8M6ccqYBm HINDI ONLY- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAN4L-FJ3s_IEXgZCijGUA1A ENGLISH ONLY- https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL93S13oM2gAMYv2a1hFcq4W1nBjTnRkHP facebook profile- https://www.facebook.com/suresh.kr.lrhs/ FACEBOOK PAGE- https://www.facebook.com/My-Student-S... facebook group NURSING NOTES- https://www.facebook.com/groups/24139... FOR MAKING EASY NOTES YOU CAN ALSO VISIT MY BLOG – BLOGGER- https://mynursingstudents.blogspot.com/ Instagram- https://www.instagram.com/mystudentsu... Twitter- https://twitter.com/student_system?s=08 #PEM, #HEALTH,#NEW,#BORN,#ASSESSMENT, #APPEARENCE,#PULSE,#GRIMACE,#REFLEX,#RESPIRATION,#RESUSCITATION,#NEWBORN,#BABY,#VIRGINIA, #CHILD, #OXYGEN,#CYANOSIS,#OPTICNERVE, #SARACHNA,#MYSTUDENTSUPPORTSYSTEM, #rashes,#nursingclasses, #communityhealthnursing,#ANM, #GNM, #BSCNURING,#NURSINGSTUDENTS, #WHO,#NURSINGINSTITUTION,#COLLEGEOFNURSING,#nursingofficer,#COMMUNITYHEALTHOFFICER
Western Trust Epilepsy Awareness Presentation 2013

This document provides information about epilepsy for healthcare staff. It begins with learning outcomes around recognizing seizure types, appropriate first aid, risks of epilepsy, and the role of staff caring for people with epilepsy. It then defines epilepsy as a neurological disorder characterized by unprovoked seizures. Several types of seizures are described, including focal and generalized seizures like tonic-clonic and absence seizures. Causes, diagnosis, treatment, triggers, classification, and first aid for different seizure types are outlined. The roles and responsibilities of healthcare staff in caring for people with epilepsy are also summarized.
Report ps 3

This document discusses various physical disabilities and health conditions that may affect children in a classroom setting. It provides information on cerebral palsy and its classifications (spasticity, hypotonicity, athetoysis, ataxia), as well as spinal cord injuries, spina bifida, hydrocephalus, muscular dystrophy, hip dysplasia, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, cystic fibrosis, hemophilia, leukemia, sickle cell anemia, heart problems, diabetes, seizure disorders, HIV/AIDS, obesity, undernourishment, and recommendations for teachers on administering medication, handling emergencies, maintaining confidentiality and children's health records.
2.knowledge of developmental disabilities

Developmental disabilities can have various causes including genetic, birth-related, or environmental factors. Four main conditions that qualify for services are autism, cerebral palsy, cognitive disabilities, and epilepsy. Cerebral palsy affects muscle communication with the brain, cognitive disabilities affect learning, autism affects social/communication abilities, and epilepsy causes seizures. Managing developmental disabilities requires understanding each condition and providing appropriate support.
Epilepsy and its management

The document discusses epilepsy and its management. Some key points:
- Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. It affects around 50 million people worldwide.
- Seizures occur due to excessive electrical discharges in the brain and present with symptoms like loss of consciousness and abnormal motor movements.
- Management involves anti-epileptic drug therapy to control seizures as well as addressing psychosocial issues like stigma and quality of life concerns. Surgery may be considered if drug therapy is ineffective. Nursing care includes education, monitoring for side effects, and supporting psychological well-being.
Seizure

This document discusses epilepsy and seizures. It defines seizures and epilepsy, describes different types of seizures including partial and generalized seizures. Common causes of epilepsy including strokes, brain injuries, tumors are mentioned. Management of seizures focuses on preventing injuries, identifying and removing seizure triggers, and treating with anti-seizure medications to control seizures. Nursing care revolves around safety during seizures, airway management, education, and supporting patients' psychosocial needs.
Epilepsy edited

This document provides information about epilepsy including:
- It defines epilepsy as a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures.
- Some key causes of epilepsy include birth injuries, infections, brain tumors, and genetic factors.
- Diagnostic tests include blood tests, EEG, CT/MRI scans. Treatment involves pharmacotherapy with anti-seizure medications and possibly surgery for refractory cases.
- Nursing management focuses on patient safety during seizures, monitoring for complications, educating patients and families, and ensuring proper treatment adherence.
occupational therapy for epilepsy: an overview

This document discusses epilepsy, its causes, prevention, and the role of occupational therapy. It defines epilepsy as abnormal neuronal discharge in the brain that can cause loss of consciousness or odd behavior. Risk factors include premature birth, brain infections, abnormal brain structures, cerebral palsy, hypoxia, brain tumors, stroke, and drug abuse. Occupational therapy focuses on safety, adaptations to the home, relaxation techniques, exercise, routine management, leisure activities, and support groups to help epileptic patients live independently and cope with emotional and cognitive challenges.
Epilepsy first aid

This document provides guidelines for assisting someone experiencing a seizure. It begins by defining what a seizure is and noting that they can be frightening to witness. It explains that seizures are not always convulsions, but can involve staring, movements, smells/sounds, or behaviors. The guidelines recommend remaining calm, protecting the individual from injury, loosening tight clothing, removing eyeglasses, not restraining them or placing things in their mouth. It also advises timing the seizure, calling for emergency help if needed, looking for injuries afterwards, and not letting them drive after a seizure. The goal is to maintain the individual's safety during and after the event.
6 provide first aid medical emergiencies

- A stroke occurs when the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, causing brain cells to die from lack of oxygen. Signs include weakness/paralysis, difficulty speaking/swallowing, vision problems, and headaches. If suspected, call an ambulance immediately. Do not leave the casualty until help arrives.
- Diabetes is caused by insufficient insulin production. Hypoglycemia causes weakness and confusion from low blood sugar, which is treated by giving sugar. Hyperglycemia has a slower onset from high blood sugar. Never administer insulin yourself.
- Seizures are caused by abnormal brain activity and usually last 1-5 minutes. Protect the casualty from injury and do not restrain them. Call an ambulance
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a group of neurological disorders characterized by epileptic seizures. It affects about 1% of people worldwide and nearly 80% of cases occur in developing countries. Epileptic seizures are caused by excessive neuronal activity in the brain and can vary from brief episodes to long periods of shaking. While the cause is unknown in most cases, epilepsy can sometimes be caused by brain injury, stroke, tumors or genetic mutations. Treatment involves medication to control seizures in about 70% of patients, while surgery or other options may be considered for uncontrolled cases.
Epilepsy

Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurring seizures. A seizure occurs when there is a sudden surge of electrical activity in the brain. About 2.3 million Americans have epilepsy. While the specific cause is unknown in many cases, common causes include head trauma, brain tumors, strokes, genetic factors, and developmental issues. Treatment involves medications, surgery, dietary therapies and lifestyle modifications, with the goal of eliminating seizures without side effects. The choice of treatment depends on the seizure type, underlying causes, age, and other individual factors.
EPILEPSY.pptx

Epilepsy is a chronic medical condition characterized by temporary disturbances in electrical activity of the brain that cause seizures. There are two main types of epilepsy - partial seizures which start in one area of the brain and cause physical or emotional effects, and generalized seizures which involve the entire brain and can cause loss of consciousness. Within these categories there are several subtypes including complex partial seizures where consciousness is lost, tonic-clonic seizures which cause stiffening and jerking of the body, and absence seizures where the patient seems disconnected for a few seconds.
Gb syndrome

Guillain-Barre syndrome is an inflammatory disorder of the peripheral nervous system that causes muscle weakness. It is usually triggered by a bacterial or viral infection. The main symptoms include numbness and tingling in the lower body that spreads upwards, causing muscle weakness, paralysis, and difficulty with bodily functions like breathing and swallowing. Diagnosis involves lumbar puncture, electromyography, and nerve conduction tests. Treatment focuses on plasma exchange or immunoglobulin therapy to speed recovery. Nursing care centers around managing symptoms like pain and impaired mobility, as well as risks of complications like respiratory issues.
Neurological Disorder in children13.03.pptx

- A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain that results in changes in behavior, movements, feelings, and levels of consciousness. Seizures can be caused by neurological disorders like epilepsy.
- There are different types of seizures including partial/focal seizures which involve one area of the brain, and generalized seizures which involve both hemispheres of the brain. Common types are absence, tonic-clonic, myoclonic and atonic seizures.
- Diagnosing the cause of seizures involves tests like EEG, CT/MRI scans, and blood tests. Treatment typically involves anti-seizure medications but may include surgery for drug-resistant cases. The goal is to control seizures and minimize risks
Seizure

This study examined the incidence of epilepsy-related injuries and accidents in 292 patients seen at an outpatient epilepsy clinic in Germany over a period of one year. The study found that 14% of patients experienced injuries related to seizures in the past 3 months, with the most common being lacerations, abrasions, bruises, and fractures. Risk factors associated with higher rates of injury included having generalized seizures, a family history of epilepsy, lower quality of life scores, and depression. The results indicate epilepsy poses a risk of injury that clinicians should seek to prevent or minimize through optimized treatment and safety precautions.
care of ill patinet.pptx

The document provides information on caring for unconscious and terminally ill patients. It discusses assessing level of consciousness using the Glasgow Coma Scale. It outlines steps to care for unconscious patients such as maintaining airway and circulation, preventing injury and malnutrition. It also covers managing chronic illnesses through prevention, adjusting lifestyle, and using assistive devices. The stages of terminal illness and palliative/hospice care to improve quality of life are summarized.
Similar to Epilepsy- a guide for teachers (20)
Epilepsy awareness training innovations slideshare

Epilepsy awareness training innovations slideshare
Western Trust Epilepsy Awareness Presentation 2013

Western Trust Epilepsy Awareness Presentation 2013
Teaching Lecture slide of Epilepsy.pptxfor nursing

Teaching Lecture slide of Epilepsy.pptxfor nursing
Recently uploaded
Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central

Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa CentralClinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central
The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration

These lecture slides, by Dr Sidra Arshad, offer a simplified look into the mechanisms involved in the regulation of respiration:
Learning objectives:
1. Describe the organisation of respiratory center
2. Describe the nervous control of inspiration and respiratory rhythm
3. Describe the functions of the dorsal and respiratory groups of neurons
4. Describe the influences of the Pneumotaxic and Apneustic centers
5. Explain the role of Hering-Breur inflation reflex in regulation of inspiration
6. Explain the role of central chemoreceptors in regulation of respiration
7. Explain the role of peripheral chemoreceptors in regulation of respiration
8. Explain the regulation of respiration during exercise
9. Integrate the respiratory regulatory mechanisms
10. Describe the Cheyne-Stokes breathing
Study Resources:
1. Chapter 42, Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology, 14th edition
2. Chapter 36, Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition
3. Chapter 13, Human Physiology by Lauralee Sherwood, 9th edition
Artificial Intelligence Symposium (THAIS)

Artificial Intelligence Symposium (THAIS). Parc Taulí. Sabadell
TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd...

TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd Edition by DeMarco, Walsh, Verified Chapters 1 - 25, Complete Newest Version TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd Edition by DeMarco, Walsh, Verified Chapters 1 - 25, Complete Newest Version TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd Edition by DeMarco, Walsh, Verified Chapters 1 - 25, Complete Newest Version Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Pdf Chapters Download Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Pdf Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Study Guide Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Ebook Download Stuvia Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Questions and Answers Quizlet Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Studocu Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Quizlet Test Bank For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Stuvia Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Pdf Chapters Download Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Pdf Download Course Hero Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Answers Quizlet Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Ebook Download Course hero Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Questions and Answers Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Studocu Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Quizlet Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Stuvia Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Pdf Chapters Download Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Pdf Download Stuvia Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Study Guide Questions and Answers Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Ebook Download Stuvia Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Questions Quizlet Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Studocu Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Quizlet Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice 3rd Edition Test Bank Stuvia
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

A proprietary approach developed by bringing together the best of learning theories from Psychology, design principles from the world of visualization, and pedagogical methods from over a decade of training experience, that enables you to: Learn better, faster!
Identifying Major Symptoms of Slip Disc.

Our backs are like superheroes, holding us up and helping us move around. But sometimes, even superheroes can get hurt. That’s where slip discs come in.
Histololgy of Female Reproductive System.pptx

Dive into an in-depth exploration of the histological structure of female reproductive system with this comprehensive lecture. Presented by Dr. Ayesha Irfan, Assistant Professor of Anatomy, this presentation covers the Gross anatomy and functional histology of the female reproductive organs. Ideal for students, educators, and anyone interested in medical science, this lecture provides clear explanations, detailed diagrams, and valuable insights into female reproductive system. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of this essential aspect of human biology.
LOOPS in orthodontics t loop bull loop vertical loop mushroom loop stop loop

vertical loop
horizontal loop
Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat

Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat
Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx

Do you have abnormal smell after periods? It may be vaginitis. Do not worry, herbal medicine Fuyan Pill can help you get a cure.
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

It includes regulation of combination products and medical devices. FDA and industry liaisons.
All info about Diabetes and how to control it.

One health condition that is becoming more common day by day is diabetes.
According to research conducted by the National Family Health Survey of India, diabetic cases show a projection which might increase to 10.4% by 2030.
Recently uploaded (20)
Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central

Clinic ^%[+27633867063*Abortion Pills For Sale In Tembisa Central
Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Muscles of Mastication by Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration

The Nervous and Chemical Regulation of Respiration
TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd...

TEST BANK For Community and Public Health Nursing: Evidence for Practice, 3rd...
Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx

Ear and its clinical correlations By Dr. Rabia Inam Gandapore.pptx
CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf

CHEMOTHERAPY_RDP_CHAPTER 6_Anti Malarial Drugs.pdf
Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes

Promoting Wellbeing - Applied Social Psychology - Psychology SuperNotes
LOOPS in orthodontics t loop bull loop vertical loop mushroom loop stop loop

LOOPS in orthodontics t loop bull loop vertical loop mushroom loop stop loop
Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat

Histopathology of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Visual treat
Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx

Post-Menstrual Smell- When to Suspect Vaginitis.pptx
REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx

REGULATION FOR COMBINATION PRODUCTS AND MEDICAL DEVICES.pptx
Epilepsy- a guide for teachers
- 1. - 1 - CARE
- 2. - 2 - CARE Epilepsy- A guide for Teachers
- 3. - 3 - CARE Importance of teachers • Teachers play a vital role in the physical, emotional, and academic well-being of students with epilepsy. • Teachers who know how to respond to seizures both improve safety standards in the school and influence the reactions of fellow students and school staff.
- 4. - 4 - CARE Importance of teachers... contd • A teacher who reacts to seizures calmly and supportively will help others learn to do the same. • In some cases, teachers are the first to notice and recognize the symptoms of seizures in a student. • Teachers who understand, encourage, and inspire students with epilepsy facilitate learning, independence, and self-esteem.
- 5. - 5 - CARE How to recognize seizures • Seizures take many different forms. A seizure may last for a few seconds and involve a blank stare or a sudden fall. It may last for a few minutes and involve a convulsion or random, purposeless movements such as chewing motions or pulling at clothing. Sometimes it is difficult to distinguish between a seizure and unusual behavior. What is important to watch for is a pattern of behavior that happens too often to be by chance.
- 6. - 6 - CARE Signs that may indicate that a student is having a seizure include (1/2): • A sudden loss of awareness, may appear like daydreaming • A brief lack of response • Memory gaps • Rhythmic head nodding • Rapid eye blinking • Repeated movements that appear unnatural
- 7. - 7 - CARE Signs that may indicate that a student is having a seizure include (2/2): • Repeated jerking movements of the body, arms, or legs • Sudden falls without an apparent reason • Sudden stomach pain followed by sleepiness and confusion • Frequent complaints that things taste, sound, smell, look, or feel strange • Sudden fear, panic, or anger without an apparent reason.
- 8. - 8 - CARE • If you notice these symptoms, record your observations • Discuss the observations with the school nurse/ school doctor and/or principal, and • Comply with the school policy regarding reporting to parents.
- 9. - 9 - CARE Let’s Get Rid of Misconceptions! Epilepsy is NOT… •Contagious. •A mental illness. •Demonic possession. •A type of mental retardation. •A sign of low intelligence.
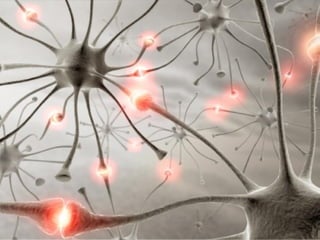
- 10. - 10 - CARE Why seizures happen? • The brain is made up of billions of nerve cells or neurons that communicate through electrical and chemical signals. • When there is a sudden, excessive electrical discharge that disrupts the normal activity of the nerve cells, may result in a change in the person’s behavior or function. • This abnormal activity in the brain that results in a change in the person’s behavior or function is a seizure.
- 11. - 11 - CARE How does one get epilepsy? Known Causes: Head trauma, brain infection, stroke, drug/alcohol, Alzheimer’s disease, tumors, toxins, birth trauma. Idiopathic: No clear cause but believed to arise from combination of genetics & environment. Missed medication 70% 30%
- 12. - 12 - CARE Seizure Triggers… Stress, anger, anxiety Overstimulation, excitement Fatigue, lack of sleep Hormonal Alcohol, drug abuse
- 13. - 13 - CARE Heat, dehydration IllnessHyperventilation Extreme heat or cold Flashing or flickering light Seizure Triggers…
- 14. - 14 - CARE What Is Epilepsy? • Epilepsy is characterized by a person having two or more unprovoked seizures. • Epilepsy is also known as a “seizure disorder.” • Epilepsy is the most common neurological disorder in the world.
- 15. - 15 - CARE An estimated 4 crore Indians suffer from epilepsy-related seizures. Epilepsy Is More Common Than You Might Think
- 16. - 16 - CARE Who epilepsy affects? • People of all ages have epilepsy. • The condition can begin at any age although its onset is most often in childhood or in the later years of life.
- 17. - 17 - CARE Seizure Types Generalized Seizures Involve the whole brain Common types include tonic-clonic, absence, atonic, myoclonic, etc. Symptoms may include convulsions, staring, muscle spasms and falls Partial Seizures Involve only part of the brain Common types include simple partial and complex partial Symptoms relate to the part of the brain affected
- 18. - 18 - CARE Status Epilepticus • A continuous seizure state, or status epilepticus, is a life threatening condition. • Seizures are prolonged or occur one after another without full recovery between seizures. • The seizures may be convulsive or non-convulsive. • Immediate medical care is necessary.
- 19. - 19 - CARE SUDEP • Sudden Unexplained Death in Epilepsy (SUDEP) • The cause of SUDEP, where death occurs suddenly for no discernible reason, is unknown. • This is rare.
- 20. - 20 - CARE How Seizures Are Controlled • Emergency management • Anti-Epileptic drugs • Surgery • Vagus nerve stimulation • Ketogenic diet
- 21. - 21 - CARE How to Respond to Seizures (1/2) • You cannot stop a seizure from occurring. • Stay calm and track time. • Most seizures last for seconds or several minutes and will end naturally. • Once a seizure is over, the student will typically return to normal.
- 22. - 22 - CARE How to Respond to Seizures (2/2) • As a teacher, • it is important to assure that the student is not in jeopardy during and following the seizure and • be aware of how to differentiate between a typical seizure and what is considered a medical emergency.
- 23. - 23 - CARE First Aid • Stay with the person. Let the seizure take its course. • Speak calmly and explain to others what is happening. • Move dangerous objects out of the way. • DO NOT restrain the person. • Gently guide the person away from danger or hazards. • After the seizure, talk reassuringly to the person. • Stay with the person until complete awareness returns. What To Do If Someone Has A Non-Convulsive Seizure (staring blankly, confused, not responding, movements are purposeless)
- 24. - 24 - CARE First Aid (1/2) • Stay calm. Let the seizure take its course. • Time the seizure. • Protect from injury. If necessary, ease the person to the floor. Move hard or sharp objects out of the way. Place something soft under the head. • Loosen anything tight around the neck. • Check for medical identification. • DO NOT restrain the person. What To Do If Someone Has A Non-Convulsive Seizure (characterized by stiffening, falling, jerking)
- 25. - 25 - CARE First Aid (2/2) • DO NOT put anything in the mouth. • The person will not swallow his or her tongue. • Gently roll the person onto his or her side as the convulsive seizure subsides to allow saliva or other fluids to drain away and keep the airway clear. • After the seizure, talk to the person reassuringly. • Do not leave until the person is re-oriented. • The person may need to rest or sleep. What To Do If Someone Has A Non-Convulsive Seizure (characterized by stiffening, falling, jerking)
- 26. - 26 - CARE CALL AN AMBULANCE (1/2): • If a convulsive seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes. • If consciousness or regular breathing does not return after the seizure has ended. • If seizure repeats without full recovery between seizures. • If confusion after a seizure persists for more than one hour.
- 27. - 27 - CARE CALL AN AMBULANCE (2/2): • If a seizure occurs in water and there is any chance that the person has inhaled water. Inhaling water can cause heart or lung damage. • If it is a first-time seizure, or the person is injured, pregnant, or has diabetes. • A person with diabetes may experience a seizure as a result of extremely high or low blood sugar levels.
- 28. - 28 - CARE After first aid procedures have been followed, teachers or school staff should (1/2): • Reassure and comfort the student if confusion follows the seizure. • Allow the student to remain in the classroom until full awareness returns. • Help to re-orient the student. • Allow rest if required. • Allow for the student to go to the restroom if the student lost bowel or bladder control during the seizure.
- 29. - 29 - CARE After first aid procedures have been followed, teachers or school staff should (2/2): • Provide a change of clothing if required A change of clothing should be kept at school • Inform the student of what instruction was missed. • Help others to understand what happened. • Allow time for discussion. • Encourage a positive reaction amongst classmates. • Proceed with regular class work.
- 30. - 31 - CARE How teachers can help? • Communicate • Offer support • Educate others • Create An Enriching Learning Experience • Create A Safe School Environment • Allow Participation • Record Seizures and Other Changes • Be Informed
- 31. - 32 - CARE We can all help in the fight for epilepsy awareness
Editor's Notes
- NOTES Do mention that people with seizures do work, have families, play sports and are productive members of society
- NOTES - Example for common triggers for a seizure: pregnancy, college kids doing all-nighters, binge drinking, drug binges, alcohol withdrawal, etc
