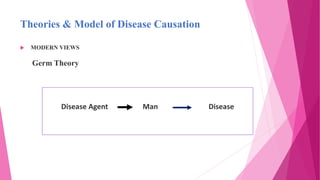
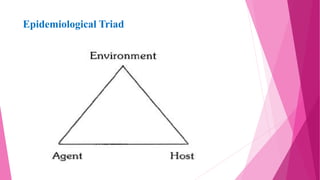
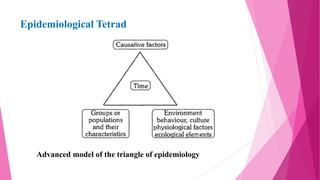
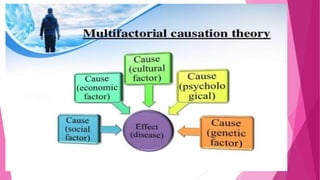
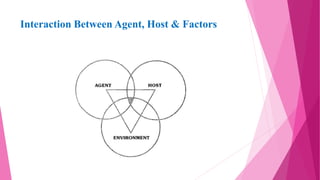
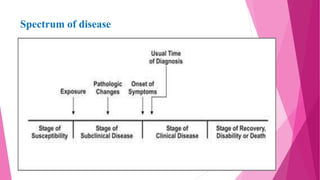
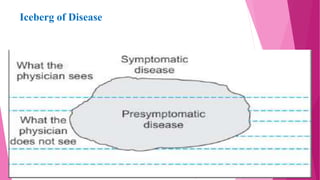
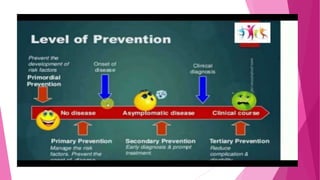
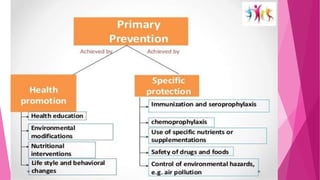
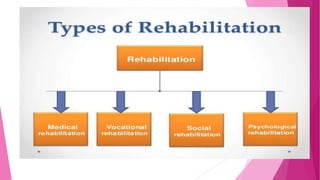
The document discusses concepts related to disease and epidemiology. It defines disease as a disruption of bodily functions and discusses different frameworks for understanding disease causation, including the germ theory and epidemiological triads/tetrads involving agents, hosts, and environmental factors. It also describes levels of disease prevention from primordial to tertiary and modes of intervention like health promotion, specific protection, early diagnosis and treatment, and rehabilitation.