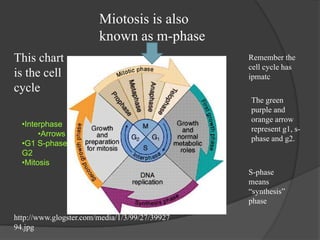
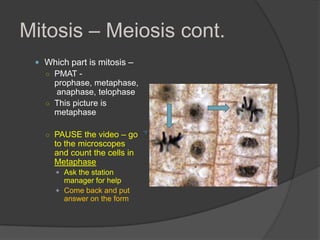
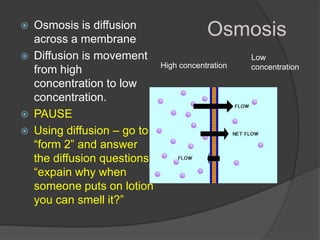
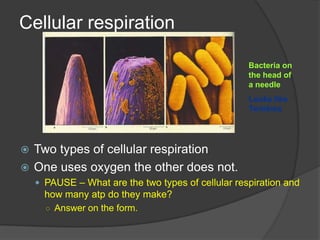
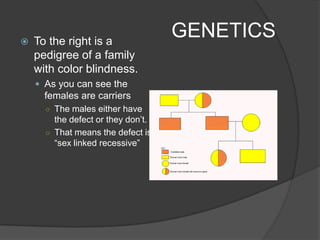
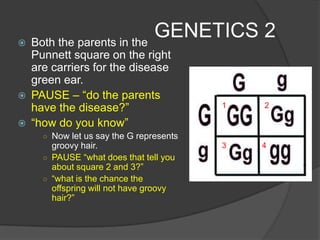
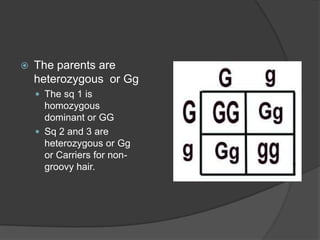
This document provides instructions for an online computer review covering several biology topics. It directs the reader to open multiple windows to view a presentation and answer questions in a Google Form. Various biology concepts are briefly explained, including the cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, diffusion, osmosis, cellular respiration, biodiversity, invasive species, organelles, genetics, chloroplasts, and more. The reader is prompted to pause and answer related questions in the Google Form at several points throughout.