This document discusses different types of environmental pollution including water pollution, air pollution, land pollution, and noise pollution. It provides details on the causes and sources of each type of pollution as well as their effects. The key points are:
1) Water pollution can be caused by municipal, industrial, and agricultural waste, as well as thermal power plants, and affects freshwater sources. Industrial waste is a major source of water pollution.
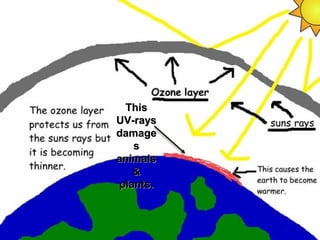
2) Air pollution stems from carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel burning and deforestation as well as sulfur dioxide from fossil fuel combustion. It can cause health issues in humans and damage plants and animals.
3) Land pollution results from construction, agriculture, and domestic and industrial waste