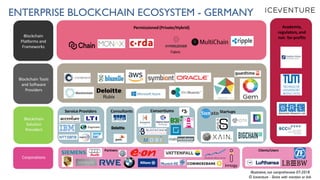
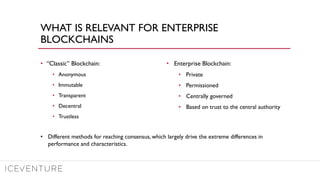
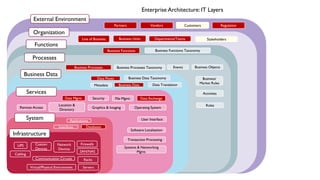
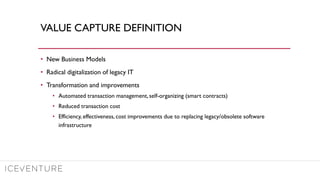
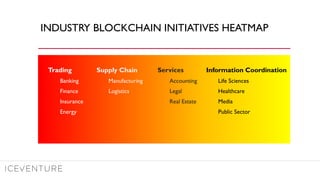
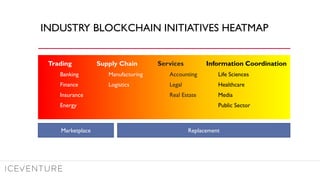
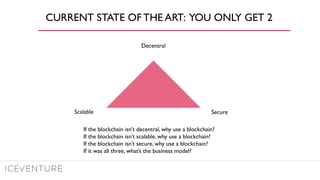
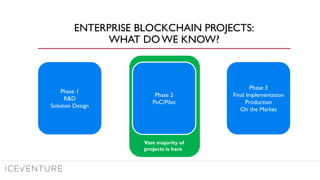
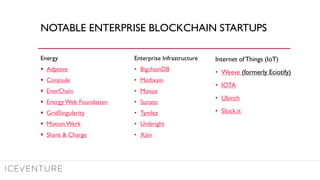
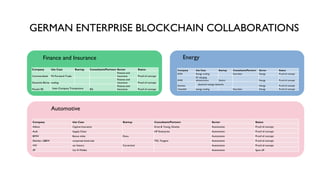
The document provides a comprehensive overview of enterprise blockchain, highlighting its unique characteristics compared to public blockchains, such as being private and permissioned. It discusses critical aspects such as cost, scalability, and integration challenges while outlining the current landscape of enterprise blockchain projects and initiatives within Germany. Additionally, it presents a value capture framework and evaluates the implications of adopting blockchain technology in various industries.