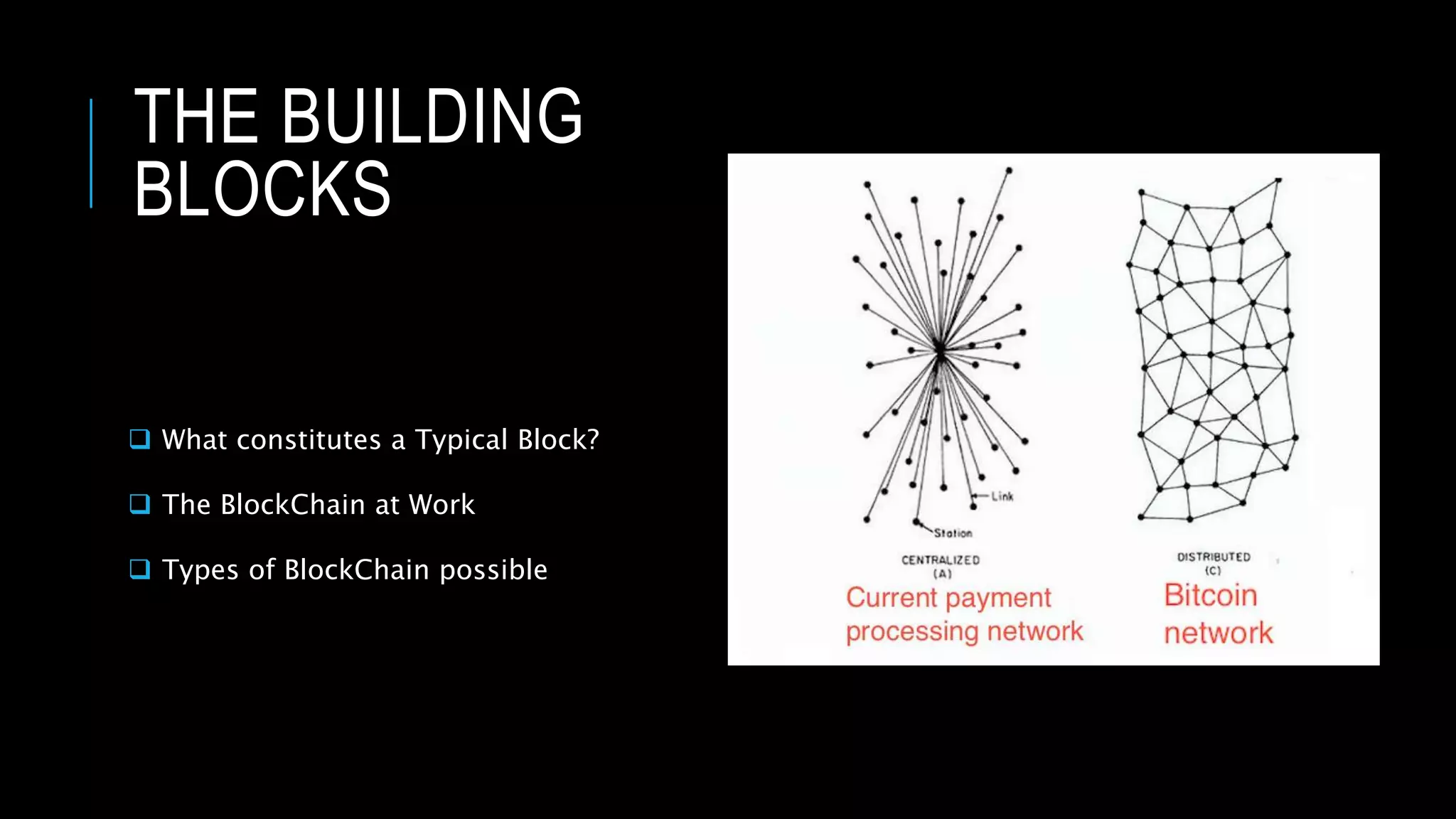
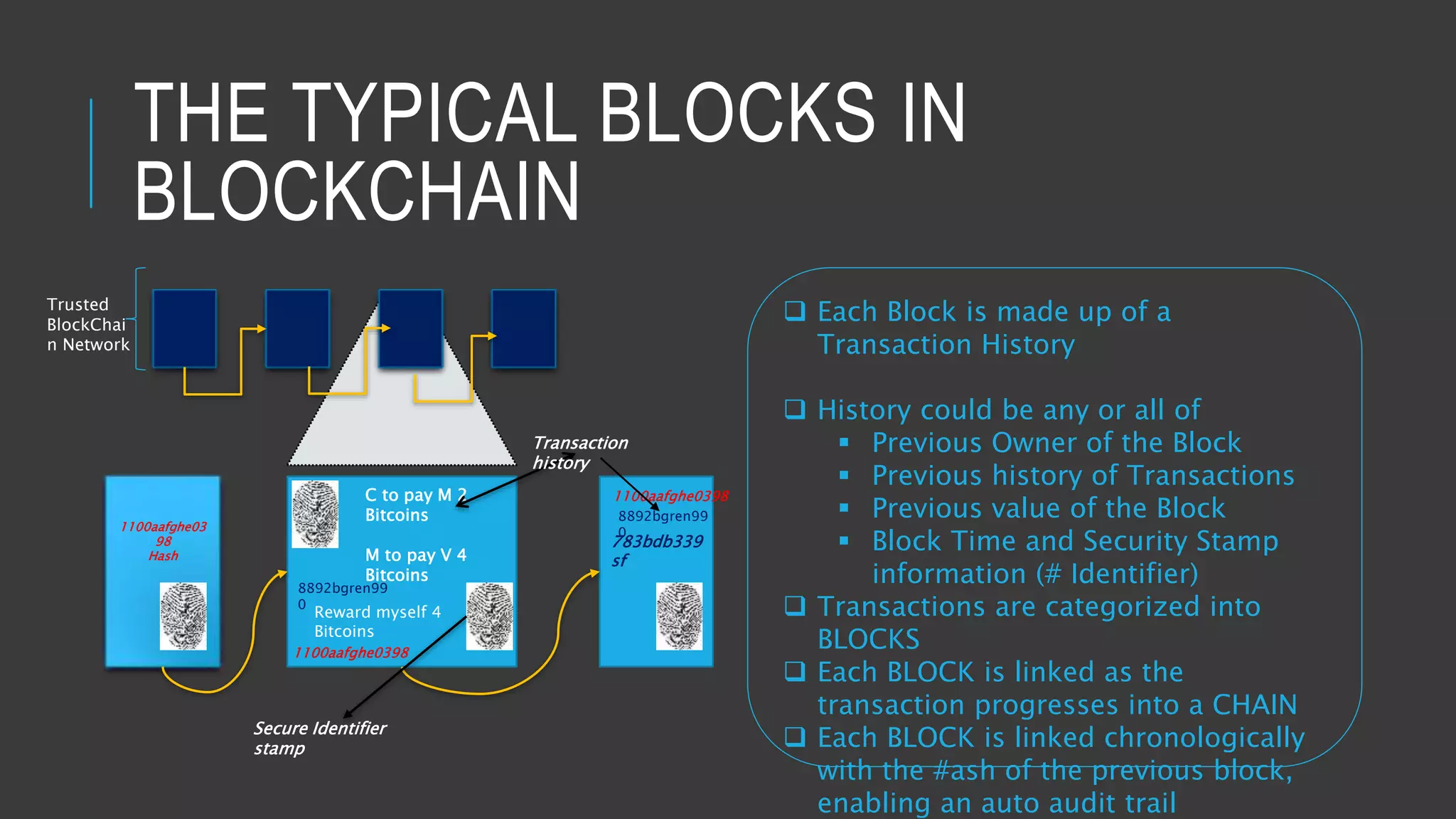
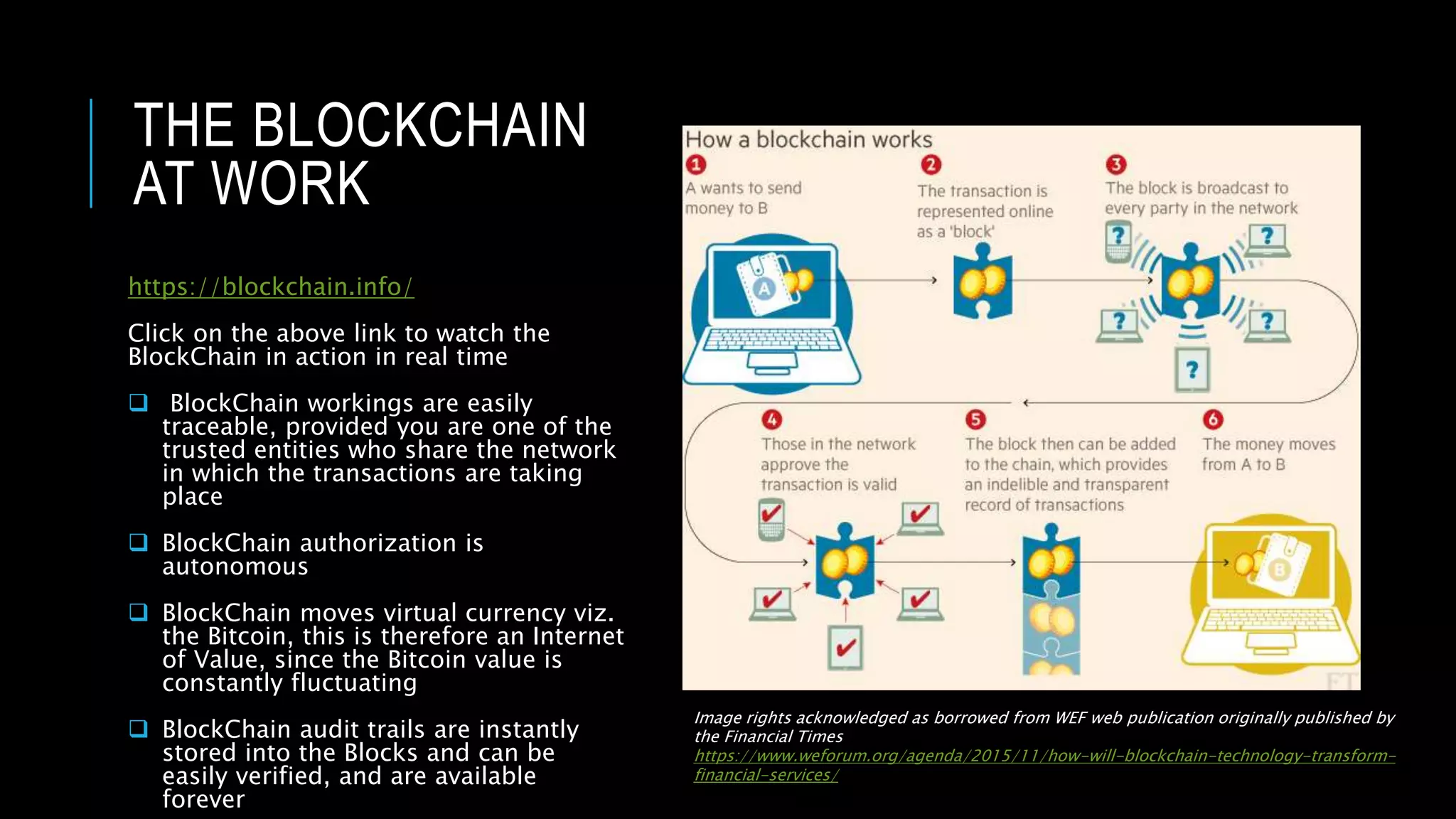
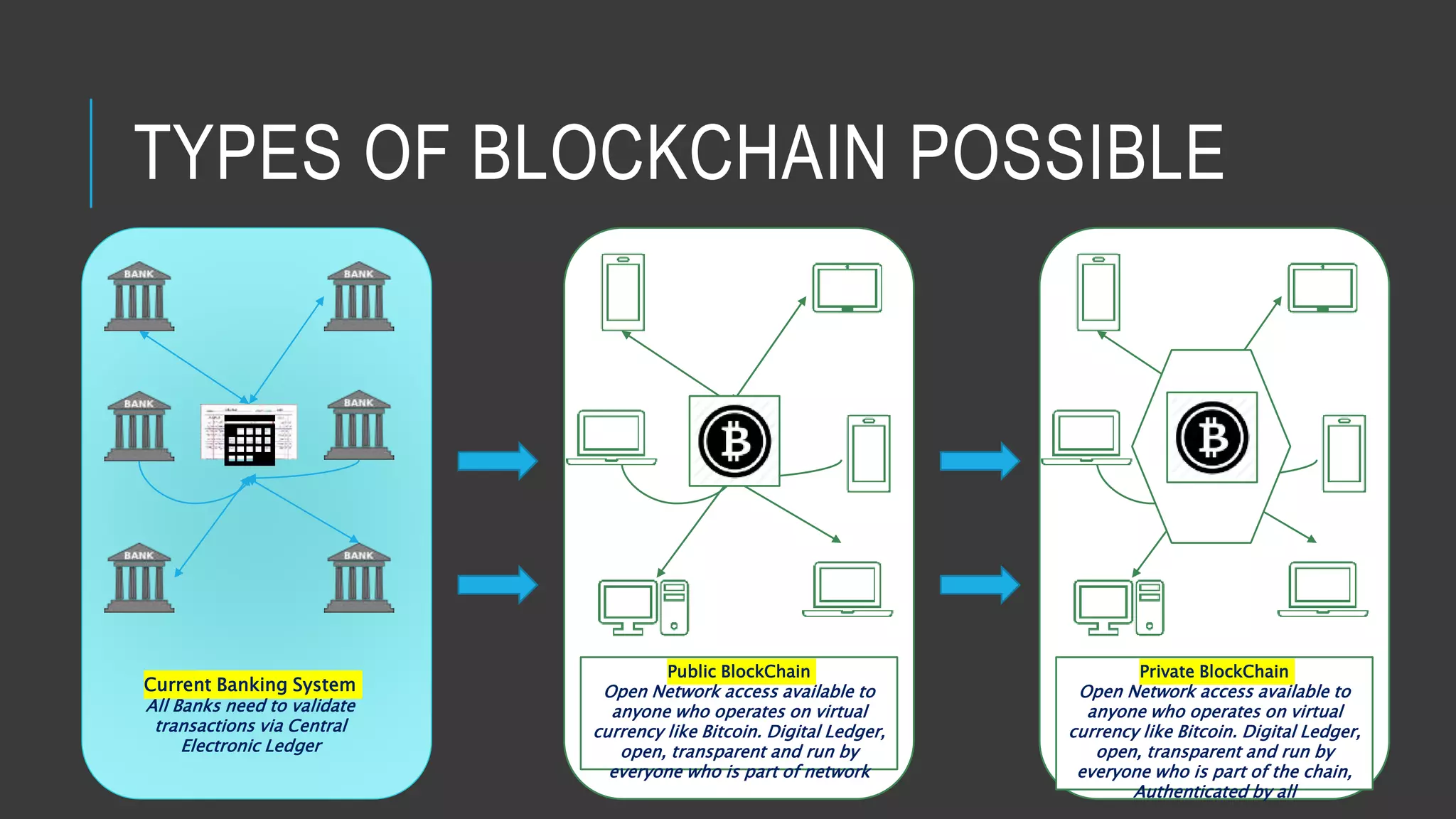
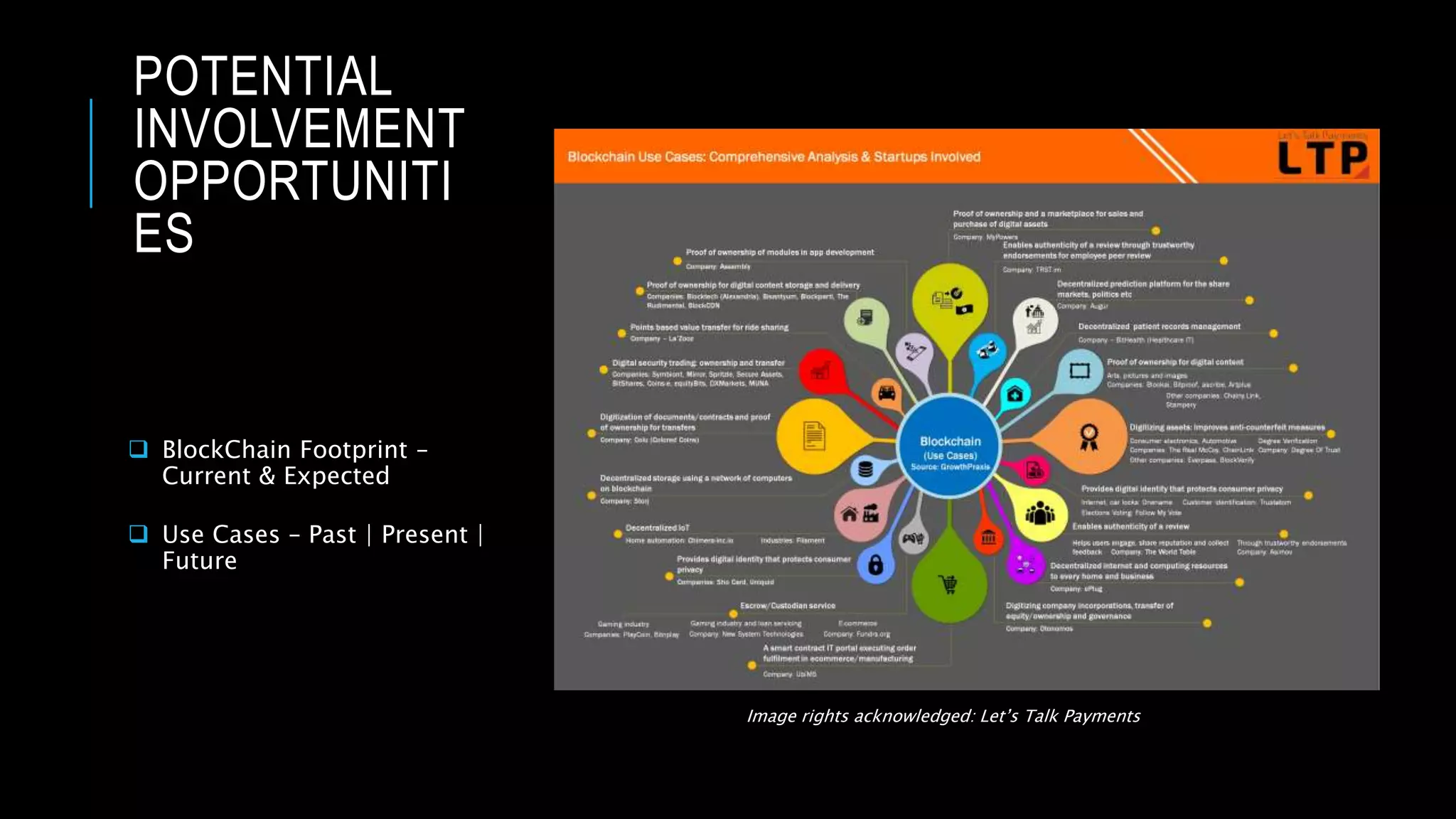
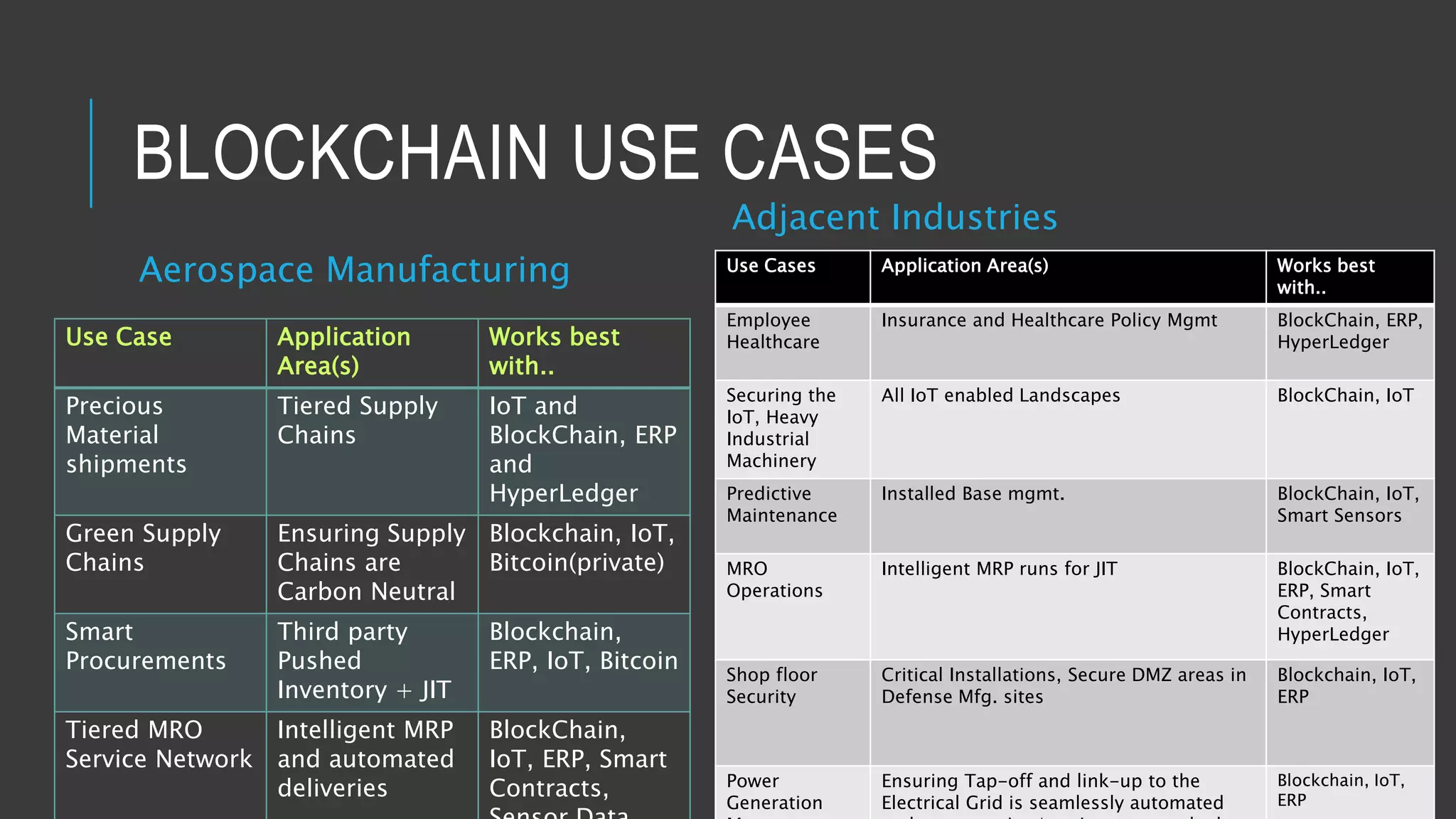
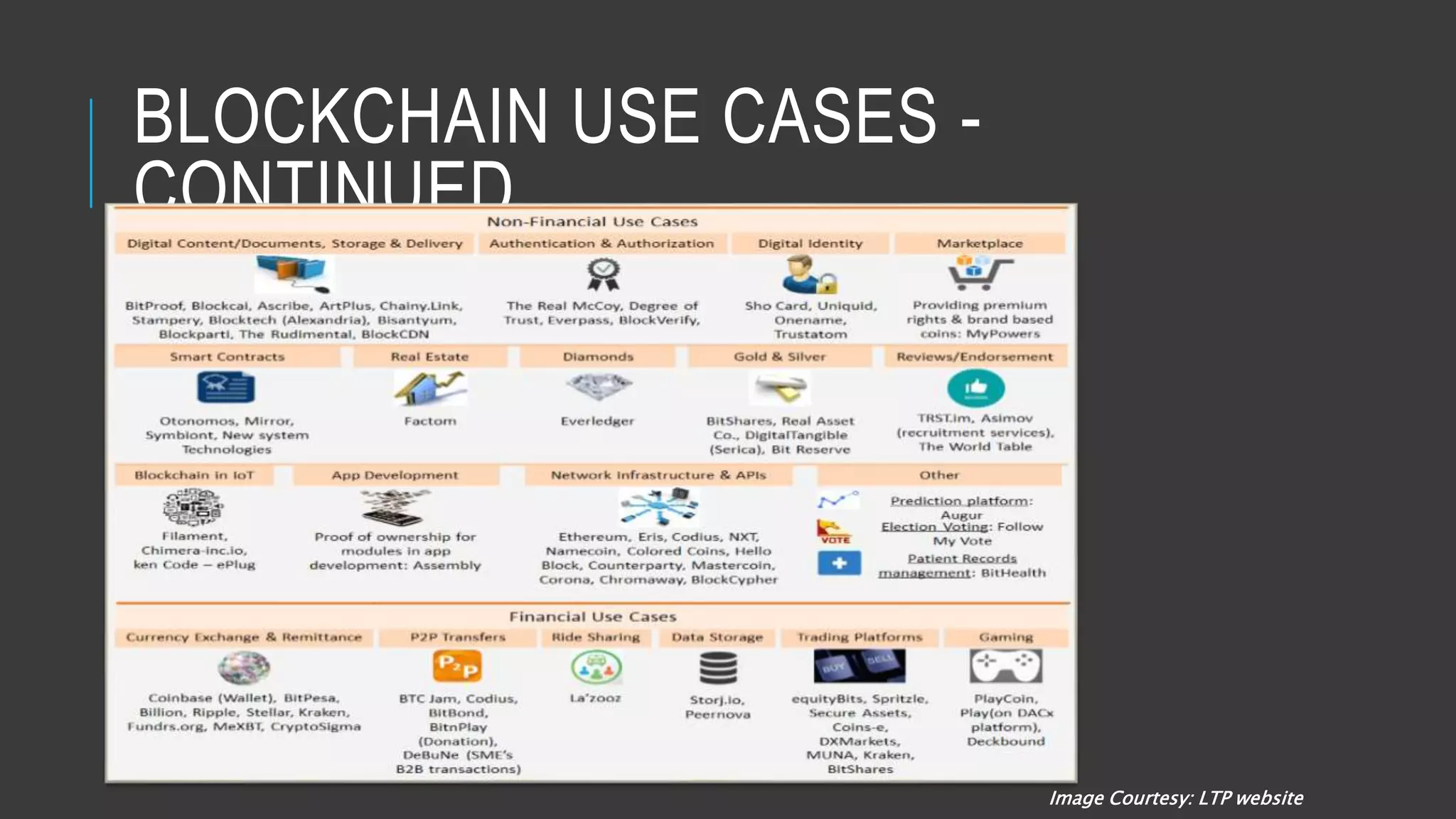
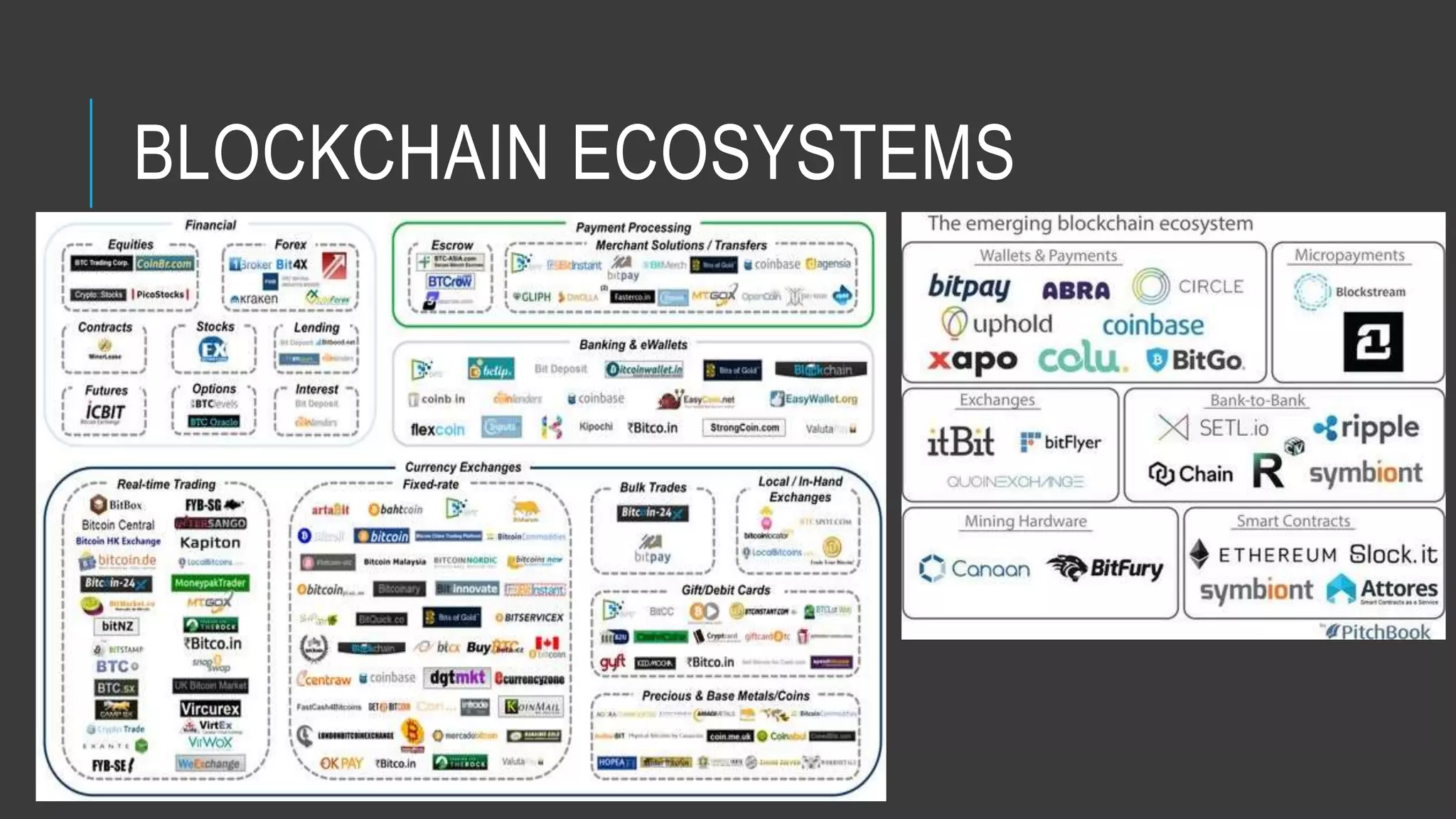
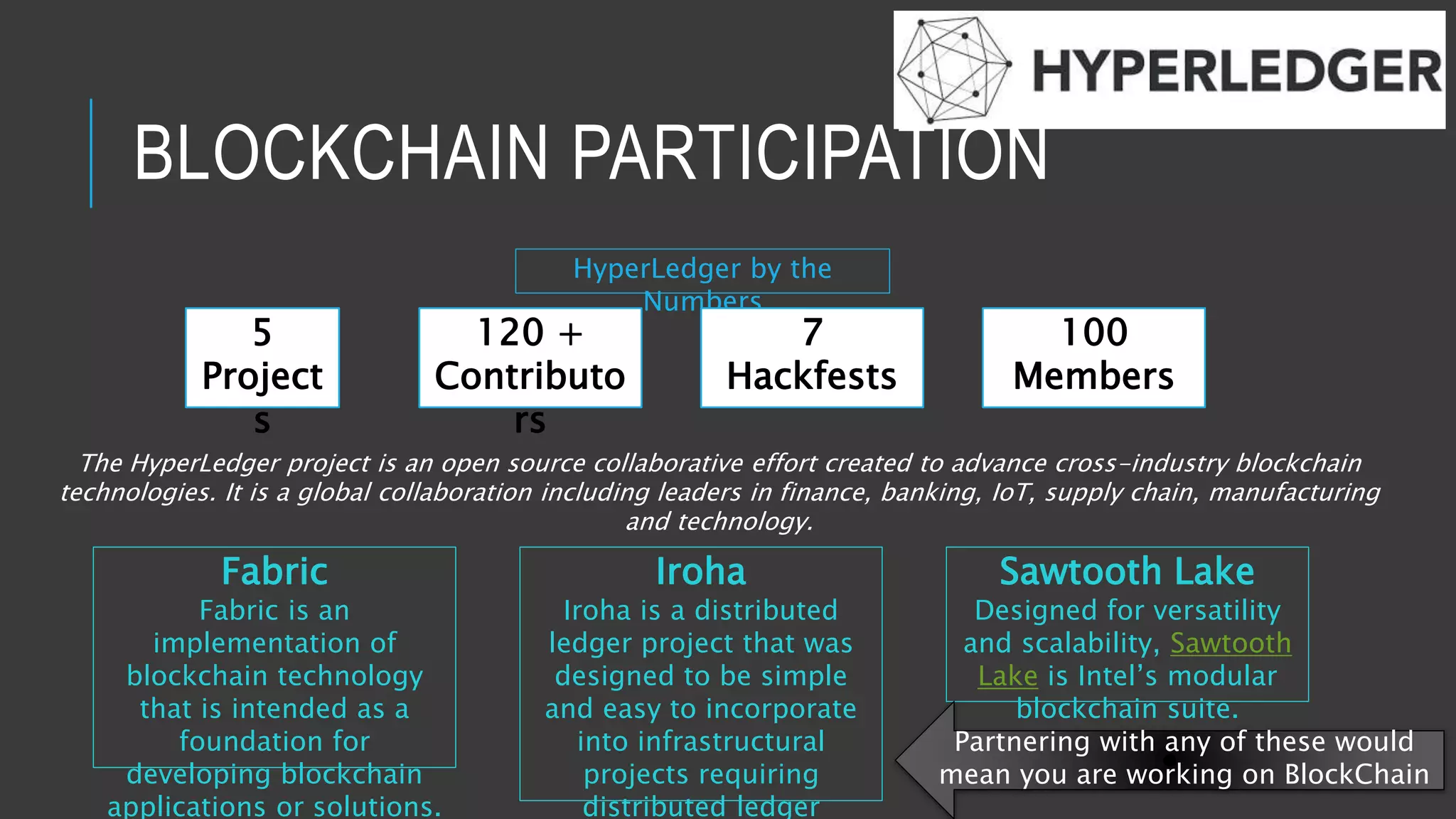
This document provides an overview of blockchain technology and its potential uses. It begins with explaining the origins and basic concepts of blockchain as a decentralized ledger system. It then discusses the building blocks of blockchain, including what constitutes a typical block and how the blockchain works. The document outlines several potential areas of industry involvement for blockchain, such as supply chain management, healthcare, IoT, and more. It also provides examples of specific use cases for blockchain in aerospace manufacturing and adjacent industries. Finally, it discusses strategies for participating in blockchain ecosystems through projects like Hyperledger.